 |
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Lesson-7
Areas
Covered in this lecture
�
Cash
book and bank book.
�
Accounting
Period.
�
Trial
Balance and its
limitations.
Flow
of Transaction
In Financial
Accounting, any business
transaction flows as
follows:
�
The
business transaction is recorded in a
voucher. The voucher is the first document
prepared in the
financial
accounting.
�
All
credit transactions are then
posted in the journal.
�
In
these days, voucher is directly
fed in the books of accounts by means of
computers.
�
From
the books of accounts, trial balance is
prepared, which shows the arithmetic
accuracy of the
accounting
system.
�
Finally,
financial statements. i.e., Profit &
Loss Account and Balance
Sheet is prepared from
trial
balance.
Cash
Book & Bank Book
�
Cash
book and bank book are
part of general
ledger.
�
All
entries including payables
and receivables are recorded
in the general ledger. Expenses,
income,
assets
and liabilities are recorded
in different head of accounts to
analyze the expenses incurred in
different
head of accounts.
�
Due to
large volume of transactions, entries
related to cash and bank are
recorded in the separate
books.
Cash
Book
�
All
cash transactions (receipts
and payments) are recorded
in the cash book.
�
Cash
book balance shows the amount of
cash in hand at a particular time.
�
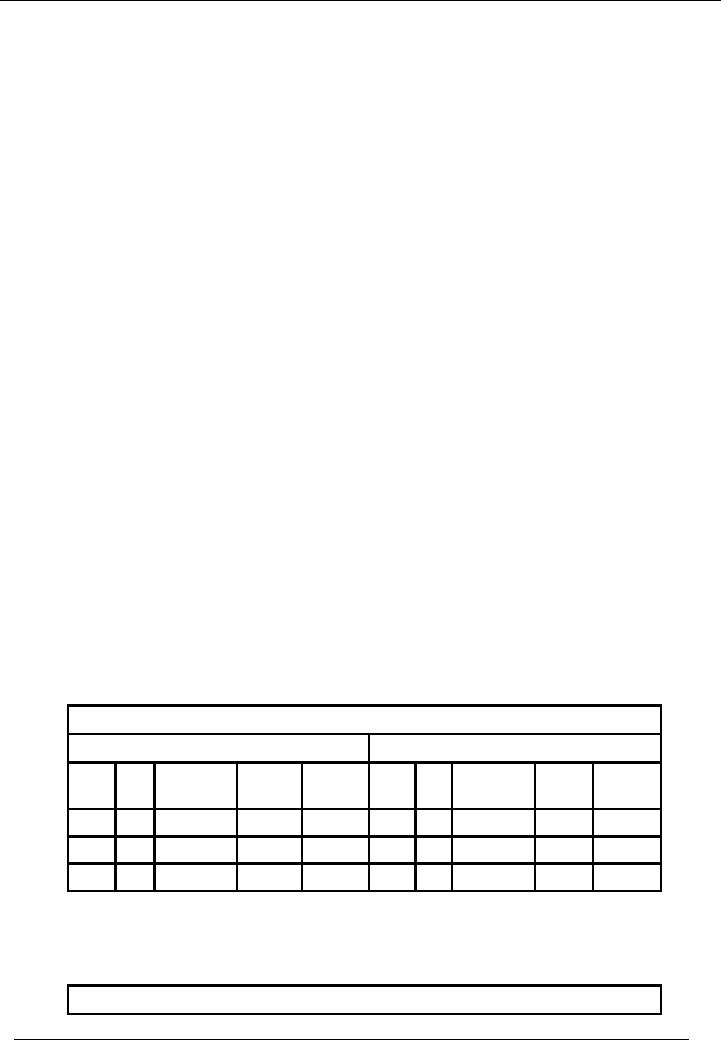
Format of
cash book is here
under:
Cash
Book
Account
Code 01
Receipt
Side
Payment
Side
Date
No. Narration /
Ledger
Receipt
Date No. Narration / Ledger
Payment
Particulars
Code
Amount
Particulars
Code Amount
OR
Cash
Book
Account
Code 01
23
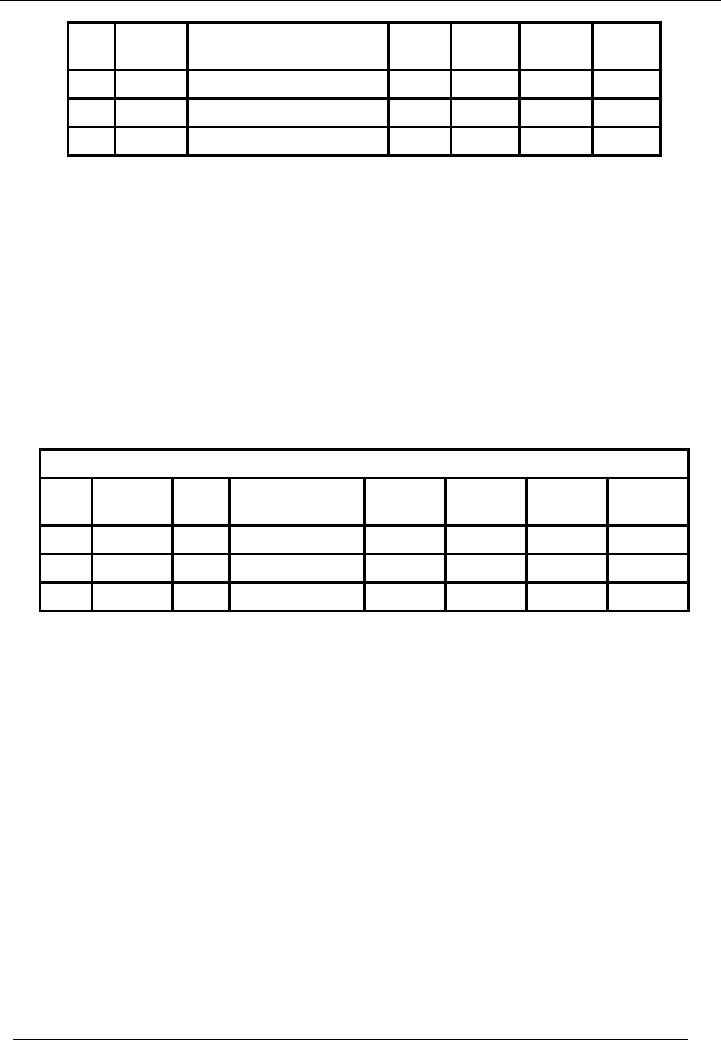
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Date
Voucher
Narration
/
Ledger
Receipt
Payment
Balance
Number
Particulars
Code
Amount
Amount
Dr/(Cr)
�
Two
formats of cash book are
shown above. In the first
format, receipt side and
payment side are
shown
separately. In the second format,
two columns are shown
for receipt and payment
with an
extra
column of balance. The balance column
shows the net balance of cash
available for use.
�
The
ledger code shows the code
of that head of account
which contains the second effect of
the
cash
transactions because debits
and credits are always
equal in financial accounting.
�
Both of
these formats are correct. A
business can use any
format considering its
policies and
requirements.
Bank
Book
�
All
bank transactions are recorded in the
bank book.
�
The
balance of bank book reflects the
cash available at bank at a particular
time.
�
Format of bank
book is hereunder:
Bank
Book (Bank Account
Number)
Account
Code 02
Date
Voucher
Chq.
Narration
/
Ledger
Receipt
Payment
Balance
Number
No.
Particulars
Code
Amount
Amount
Dr/(Cr)
�
The
format of bank book is same as
that of cash book except the
column of cheque no.
�
This
column is added in the format because
all payments made by cheque
and the number of
cheque
is written in that column to keep the
accounting record
updated.
Accounting
Period
�
Accounting
period is any period for
which a profit and loss
account is prepared.
�
The
length of the accounting period
can be anything between one
day to one year
�
The
legal or statutory definition is a
maximum of one year.
�
The
only exception in this case is the
formation of a new company
which is formed before the
start
of accounting period.
24
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Financial
year ("a period of 12 month
duration")
�
In
Pakistan, financial year starts
from 1st
of July
and ends on 30th of
June.
�
Exceptions
are:
o Specialized
business. e.g., Textile,
banks, Sugar mills
etc.
�
Financial reports
can be made for a week or a
month, depending upon the requirements of
the
company.
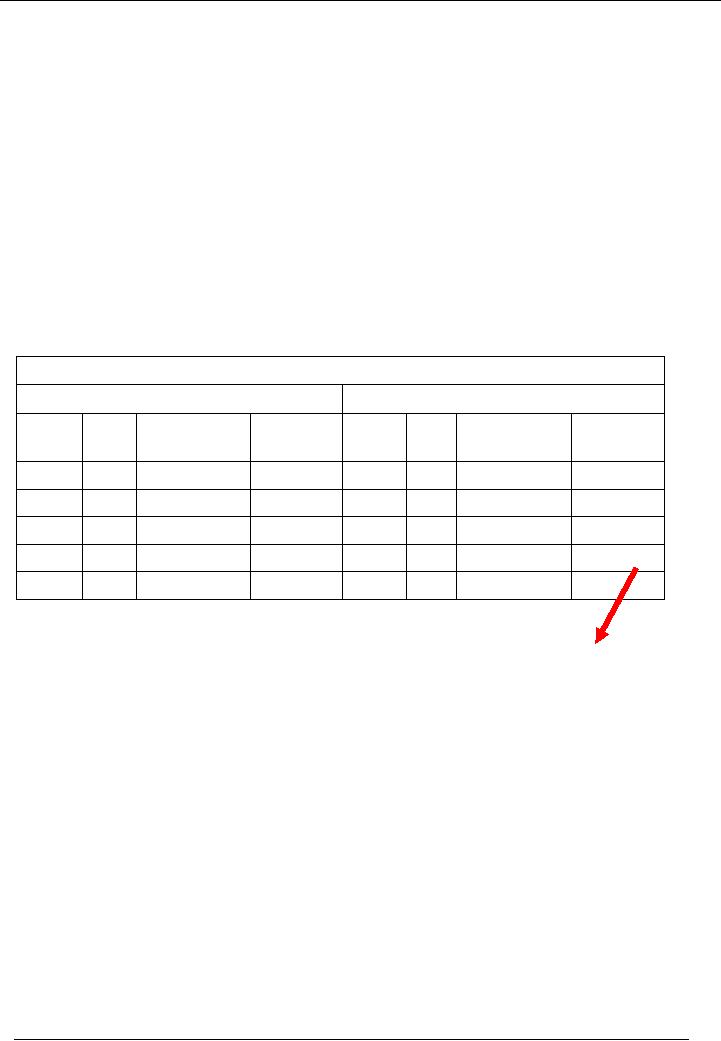
Debit
& Credit Balances
�
It has
already been mentioned that
both sides i.e. Debit
and credit side of a ledger
must be equal.
�
If
debit side of a ledger is
greater that credit side.
The balance will be written
on the credit side and
it
will be called Debit
Balance. The reason being,
the balance is written on the credit side
because of
excessive
debit balance. Therefore, it is called
Debit Balance. For
example:
Title of
Account
Account
Code 01
Debit
Side
Credit
Side
Narration
/
Receipt
Narration
/
Payment
Date
No.
Date
No.
Particulars
Amount
Particulars
Amount
1
100,000
3
80,000
2
20,000
4
30,000
120,000
110,000
Balance
10,000
A Debit
Balance
�
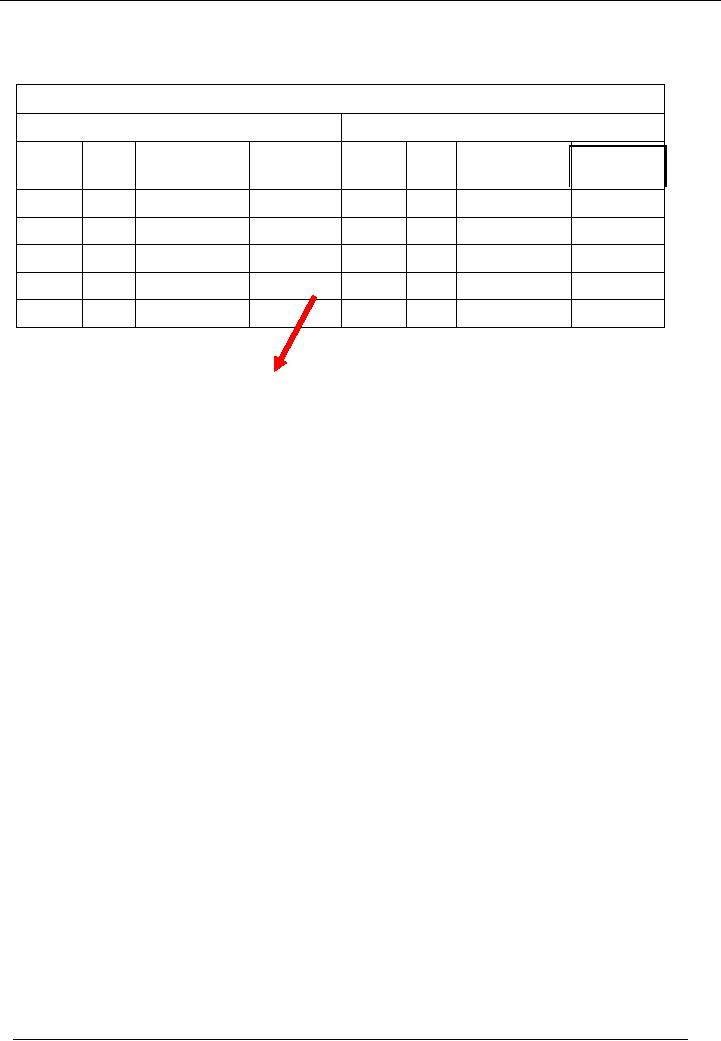
Similarly, if
credit side is greater than
debit side, the balance will
be written on the debit side.
This
balance
is called. Credit Balance.
For Example:
25
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Title of
Account
Account
Code 01
Debit
Side
Credit
Side
Narration
/
Receipt
Narration
/
No.
Date
Date
No.
Payment
Particulars
Amount
Particulars
Amount
1
80,000
3
100,000
2
30,000
4
20,000
110,000
120,000
Balance
10,000
A
Credit Balance
Trial
Balance
�
At the
end of accounting period, a
list of all ledger balances
is prepared. This list is
called trial
Balance.
�
Both
sides of trial balance i.e.
Debit side and credit side
must be equal. If both sides
are not equal,
there
are errors in the books of
accounts.
�
Trial
balance shows the mathematical
accuracy of the books of accounts.
Limitations
of Trial Balance
�
Trial
balance only shows the
mathematical accuracy of the
accounts.
�
If
both sides of trial balance
are equal, books of accounts
are considered to be correct.
But this
might
not be true in all the
cases.
�
If any
transaction is not recorded at all,
trial balance can not
detect the omitted
transaction.
�
If any
transaction is recorded in the wrong
head e.g. if an expense is debited to an
assets account.
Trial
balance will not be able to
detect that mistake
too.
26
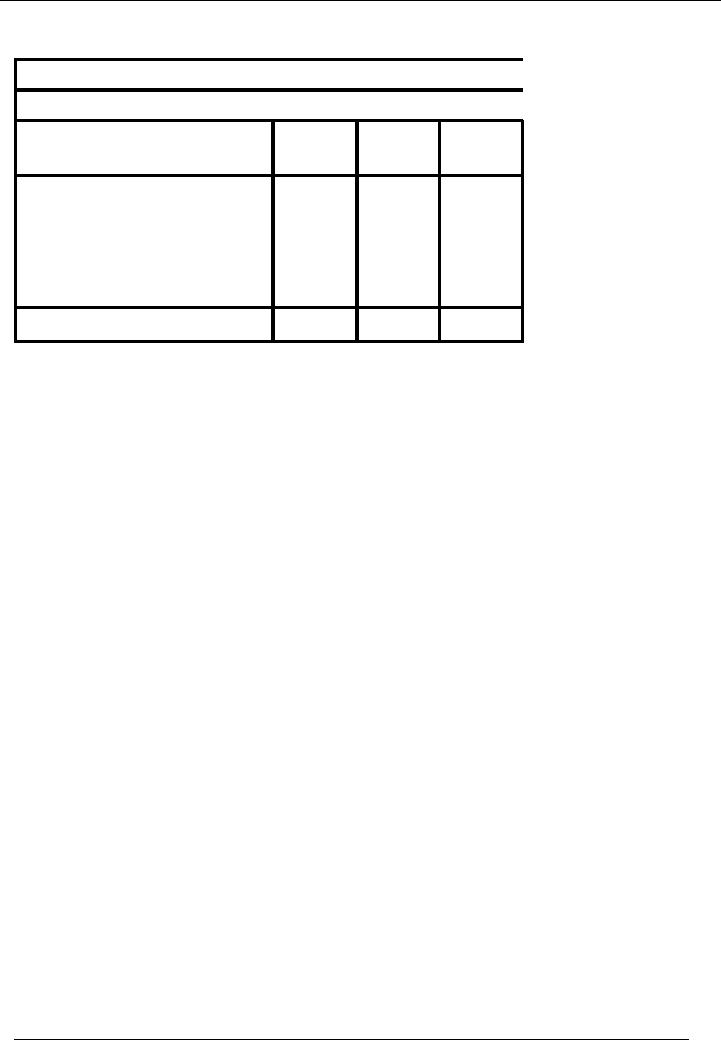
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
A
Sample Trial
Balance
Name Of
The Organization
Trial
Balance As On (Date on Which Trial
Balance is Drawn)
Title
of Account
Account
Debit
Credit
Code
Amount
Amount
Cash
in Hand
01
xy
Cash
at bank
02
xy
Capital
03
xy
Assets
04
xy
xy
Liabilities
05
Income
06
xy
Expenses
07
xy
Total
xyz
xyz
27
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Financial Accounting
- Basic Concepts of Business: capital, profit, budget
- Cash Accounting and Accrual Accounting
- Business entity, Single and double entry book-keeping, Debit and Credit
- Rules of Debit and Credit for Assets, Liabilities, Income and Expenses
- flow of transactions, books of accounts, General Ledger balance
- Cash book and bank book, Accounting Period, Trial Balance and its limitations
- Profit & Loss account from trial balance, Receipt & Payment, Income & Expenditure and Profit & Loss account
- Assets and Liabilities, Balance Sheet from trial balance
- Sample Transactions of a Company
- Sample Accounts of a Company
- THE ACCOUNTING EQUATION
- types of vouchers, Carrying forward the balance of an account
- ILLUSTRATIONS: Ccarrying Forward of Balances
- Opening Stock, Closing Stock
- COST OF GOODS SOLD STATEMENT
- DEPRECIATION
- GROUPINGS OF FIXED ASSETS
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 1
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 2
- REVALUATION OF FIXED ASSETS
- Banking transactions, Bank reconciliation statements
- RECAP
- Accounting Examples with Solutions
- RECORDING OF PROVISION FOR BAD DEBTS
- SUBSIDIARY BOOKS
- A PERSON IS BOTH DEBTOR AND CREDITOR
- RECTIFICATION OF ERROR
- STANDARD FORMAT OF PROFIT & LOSS ACCOUNT
- STANDARD FORMAT OF BALANCE SHEET
- DIFFERENT BUSINESS ENTITIES: Commercial, Non-commercial organizations
- SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
- Financial Statements Of Manufacturing Concern
- Financial Statements of Partnership firms
- INTEREST ON CAPITAL AND DRAWINGS
- DISADVANTAGES OF A PARTNERSHIP FIRM
- SHARE CAPITAL
- STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 1
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 2
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED, QUOTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES