 |
DIFFERENT BUSINESS ENTITIES: Commercial, Non-commercial organizations |
| << STANDARD FORMAT OF BALANCE SHEET |
| SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP >> |

Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Lesson-31
DIFFERENT
BUSINESS ENTITIES
There
are two types of
entities:
� Commercial
organizations
� Non-commercial
organizations
COMMERCIAL
ORGANIZATION
Commercial
organization is the entity that is
working to earn profit. At the
end of the financial year, the
profit
is distributed among the owners of the
business. Normally, commercial
organizations include:
� Sole
proprietorship
� Partnership,
and
� Limited
Company
NON
COMMERCIAL ORGANIZATION
Non
Commercial organization is the entity
that is not working to earn
profit. At the end of the financial
year,
the
profit is not distributed
among the owners, but is
used for the objective of the organization.
Normally,
commercial
organizations include:
� Co-operative
institutions
� NGO's
� Trusts
COMMERCIAL
ORGANIZATION
Sole
proprietorship business
It is a
business that is owned by an individual.
He may have employed any number of
persons to work for
him,
but he is the sole owner of the
business.
Partnership
Partnership
is the type of business where more
than one person (called
partners) enters into a
legal
agreement
to run a business on a profit
and loss sharing
basis.
Limited
Company
Limited
company is a legal entity,
separate from its owners
(called shareholders). The
basic difference
between
a partnership and a limited company is
the concept of limited
liability.
� If a
partnership business runs into
losses and is unable to pay
its liabilities, its partners
will have to
pay
the liabilities from their
own wealth.
� Whereas,
in case of limited company, the
shareholders don't lose
anything more than the amount
of
capital
they have contributed in the company.
i.e., their personal wealth is
not at stake and
their
liability
is limited to the amount of share capital
they have contributed.
The
concept of limited company is to
mobilize the resources of a large number
of people for a project,
which
they would not be able to
afford independently and then, get it
managed by experts.
201
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
ACCOUNTING
REQUIREMENTS
Sole
Proprietorship
In
case of sole proprietor, he is the
sole owner of the business. So,
there is no restriction on him for
drawing
money
for his personal
use.
For
accounting purposes, an account
titled Proprietor's Drawings is opened in
the General Ledger and
all
payments
and receipts, if any, from
the proprietor are recorded in this
account.
Accounting
Entries
Cash
Drawn by Proprietor
Debit
Proprietor's
drawing
Credit
Cash
Amount
paid in by proprietor through
cheque
Debit
Bank
Credit
Proprietor's
drawing
The
balance in drawings account is
transferred to Capital Account at the
year end.
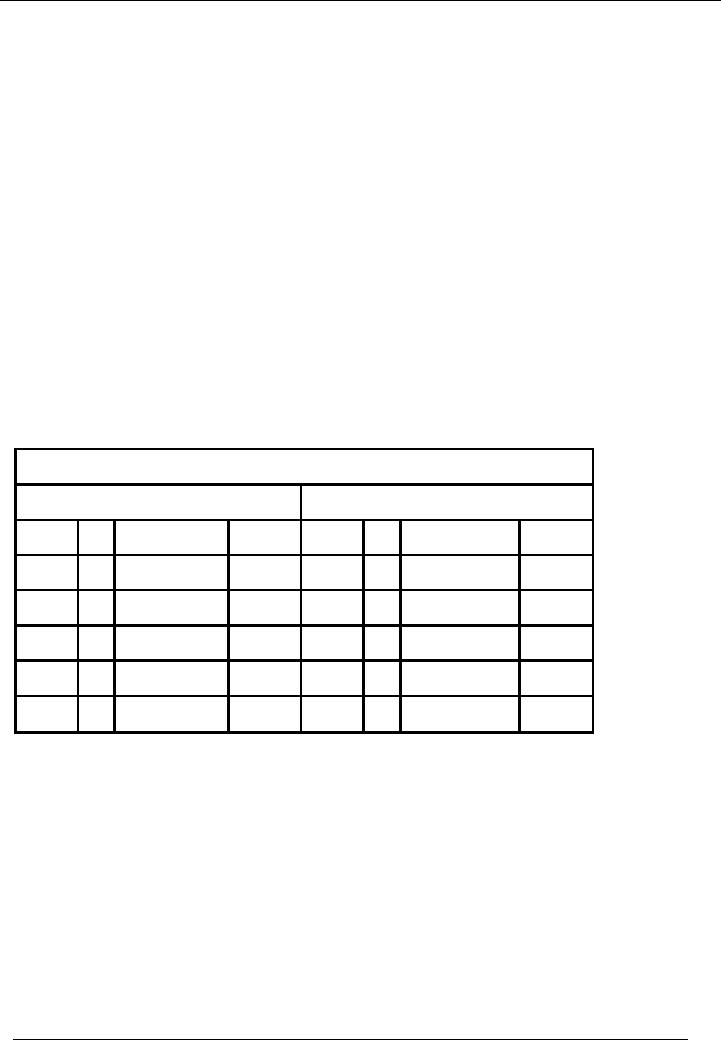
The
sample of general ledger of Capital
account, in case of profit
earned by the business, is as
follows:
Capital
Account
Debit
Side
Credit
Side
Date
No
Narration
Dr.
Rs.
Date
No
Narration
Cr.
Rs.
Jun
30
Drawings
45,000
Jul 01
Balance
B/F
100,000
Jun
30
P & L
Account
50,000
Jun
30
Balance
C/F
105,000
Total
150,000
Total
150,000
202
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
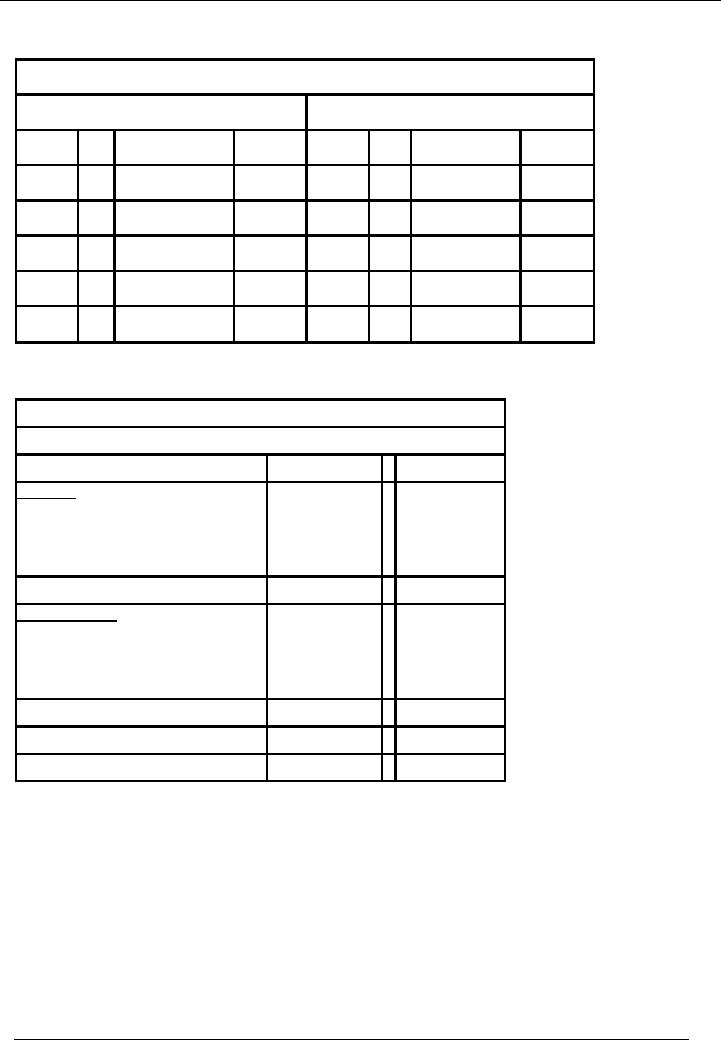
The
sample of general ledger of Capital
account, in case of loss
sustained by the business, is as
follows:
Capital
Account
Debit
Side
Credit
Side
Date
No
Narration
Dr.
Rs.
Date
No
Narration
Cr.
Rs.
Jun
30
P & L
Account
10,000
Jul 01
Balance
B/F
100,000
Jun
30
Drawings
45,000
Jun
30
Balance
C/F
45,000
Total
100,000
Total
100,000
The
balance sheet of sole
proprietor is as follows:
Name
of Business
Balance
Sheet As At ----
Particulars
Amount
Rs.
Amount
Rs.
ASSETS
Fixed
Assets
X
Long
Term Assets
X
Current
Assets
X
TOTAL
X
LIABILITIES
Capital
X
Add:
Profit / Loss For The
Year
X
Less:
Drawings
(X)
X
Long
Term Liabilities
X
Current
Liabilities
X
TOTAL
X
PARTNERSHIP
There
are two types of capital
accounts in partnership:
� Fixed
capital
� Fluctuating
capital
203

Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Fixed
Capital
In this
case, capital account shows
movement in capital only i.e.
actual increase or decrease in
capital, by
partners
and all other transactions,
such as Drawings and Profit
etc. are not recorded in
capital account.
Fluctuating
capital
In
fluctuating capital account,
all transactions relating to partners,
such as drawings, salaries
etc. are recorded
in
capital account, in addition to
entries relating to capital
account.
Current
Account
In
case of fixed capital
accounts, other transactions
such as Drawings and Profit
etc. are recorded in
a
separate
account called Current
Account.
JOURNAL
ENTRIES
�
Capital
Introduced by Partner
Debit
Cash /
Bank
Credit
Partner's
Capital Account
Separate
capital account is opened in
general ledger for each
partner.
�
Drawing
by Partner
Debit
Individual
Partner's Current
Account
Credit
Cash /
Bank
�
Excess
Drawn Amount Returned by
Partner
Debit
Bank /
cash
Credit
Individual
Partner's Current
Account
�
Profit
Distribution
Debit
Profit
and Loss Appropriation
Account
Credit
Partner
A's Current Account
Credit
Partner
B's Current Account
Credit
Partner
C's Current Account
204
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
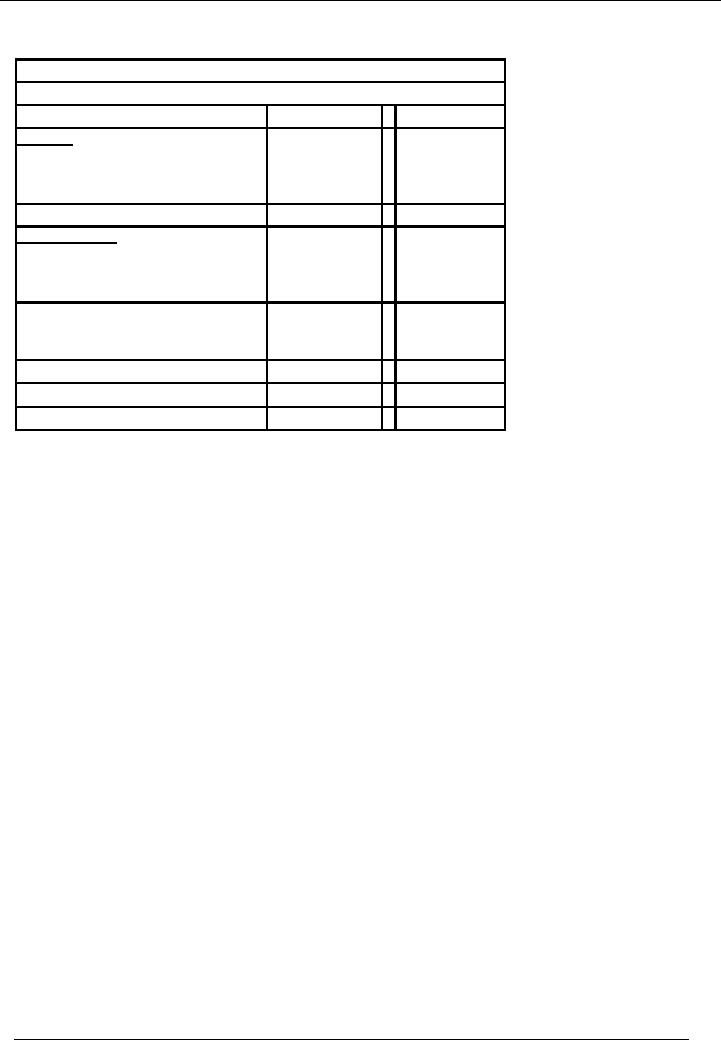
BALANCE
SHEET OF PARTNERSHIP
ACCOUNTS
Name
of Business
Balance
Sheet As At ----
Particulars
Amount
Rs.
Amount
Rs.
ASSETS
Fixed
Assets
X
Long
Term Assets
X
Current
Assets
X
TOTAL
X
LIABILITIES
Capital
A
X
B
X
C
X
X
Current
Account
A
X
B
X
C
X
X
Long
Term Liabilities
X
Current
Liabilities
X
TOTAL
X
LIMITED
COMPANIES
There
are two types of
companies:
� Public
Limited Companies
� Private
Limited Companies
Public
Limited Companies
In
public limited companies,
there is no restriction on number of persons to be
its members. There is
one
restriction.
i.e., there should be a minimum
of
three members
to form a public limited
company.
Private
Limited Companies
Two to
fifty persons can form a
private limited company.
Minimum two members are
elected to form a
board of
directors. This board is given the responsibility to
run day to day business of
the company.
SHARE
CAPITAL
Capital of the
company is divided into
small units / denominations. These units /
denominations are called
shares
and the capital is called
share capital. Owners
purchase these shares and
are, therefore, called
shareholders.
As, there are so many
shareholders in a company, profit is
distributed among the
members/shareholders
of the company on the basis of number of
shares held by each shareholder.
The
profit
distributed among shareholders is
called DIVIDEND.
205
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Financial Accounting
- Basic Concepts of Business: capital, profit, budget
- Cash Accounting and Accrual Accounting
- Business entity, Single and double entry book-keeping, Debit and Credit
- Rules of Debit and Credit for Assets, Liabilities, Income and Expenses
- flow of transactions, books of accounts, General Ledger balance
- Cash book and bank book, Accounting Period, Trial Balance and its limitations
- Profit & Loss account from trial balance, Receipt & Payment, Income & Expenditure and Profit & Loss account
- Assets and Liabilities, Balance Sheet from trial balance
- Sample Transactions of a Company
- Sample Accounts of a Company
- THE ACCOUNTING EQUATION
- types of vouchers, Carrying forward the balance of an account
- ILLUSTRATIONS: Ccarrying Forward of Balances
- Opening Stock, Closing Stock
- COST OF GOODS SOLD STATEMENT
- DEPRECIATION
- GROUPINGS OF FIXED ASSETS
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 1
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 2
- REVALUATION OF FIXED ASSETS
- Banking transactions, Bank reconciliation statements
- RECAP
- Accounting Examples with Solutions
- RECORDING OF PROVISION FOR BAD DEBTS
- SUBSIDIARY BOOKS
- A PERSON IS BOTH DEBTOR AND CREDITOR
- RECTIFICATION OF ERROR
- STANDARD FORMAT OF PROFIT & LOSS ACCOUNT
- STANDARD FORMAT OF BALANCE SHEET
- DIFFERENT BUSINESS ENTITIES: Commercial, Non-commercial organizations
- SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
- Financial Statements Of Manufacturing Concern
- Financial Statements of Partnership firms
- INTEREST ON CAPITAL AND DRAWINGS
- DISADVANTAGES OF A PARTNERSHIP FIRM
- SHARE CAPITAL
- STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 1
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 2
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED, QUOTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES