 |
SUBSIDIARY BOOKS |
| << RECORDING OF PROVISION FOR BAD DEBTS |
| A PERSON IS BOTH DEBTOR AND CREDITOR >> |
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Lesson-26
SUBSIDIARY
BOOKS
A number of books
are opened in connection with
control accounts to reduce the
volume of general
ledger.
These
books are called `Subsidiary
Books'.
It is
important to note that only
credit sales/purchases become part of
control accounts.
Cash
sales/purchases
are not included in the control
accounts.
SUBSIDIARY
BOOKS FOR
SALES/DEBTORS
Three
subsidiary books are maintained in case
of sales / debtors.
� Sales
Journal / Sales Day Book
individual invoice wise
sales are recorded in this
Journal. This
book
serves as source for all the
recording of Credit sales.
� Sales
Return / Return Inward Journal if volume
of returns is also high then,
these are also
recorded
in a
separate register.
� Debtors
Ledger this ledger maintains
record of individual
debtor.
The
information flows to the debtors
control account in the general
ledger as follows:
Opening
balance of
List
of debtors balances drawn up to the end
of previous period.
debtors
This
also confirms with the aggregate
balance of the debtors
ledger.
Credit
Sales
Individual
credit sale is recorded in the sales
journal. Periodical total
of this
journal is posted into the
debtors control
account.
Sales
Return
In
case, the transaction volume of
sales return is high, then
these are
recorded
in the sales return journal.
The total is posted in
the
debtors
control account periodically.
Cheques
/ Cash
List
of receipts is extracted from
cash and bank book. Or a
separate
Received
column is
maintained in cash and bank books for
this purpose.
Closing
Balance
This
is the balancing figure. It can also be
checked with the total
of
balances
in debtors' ledger.
173
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
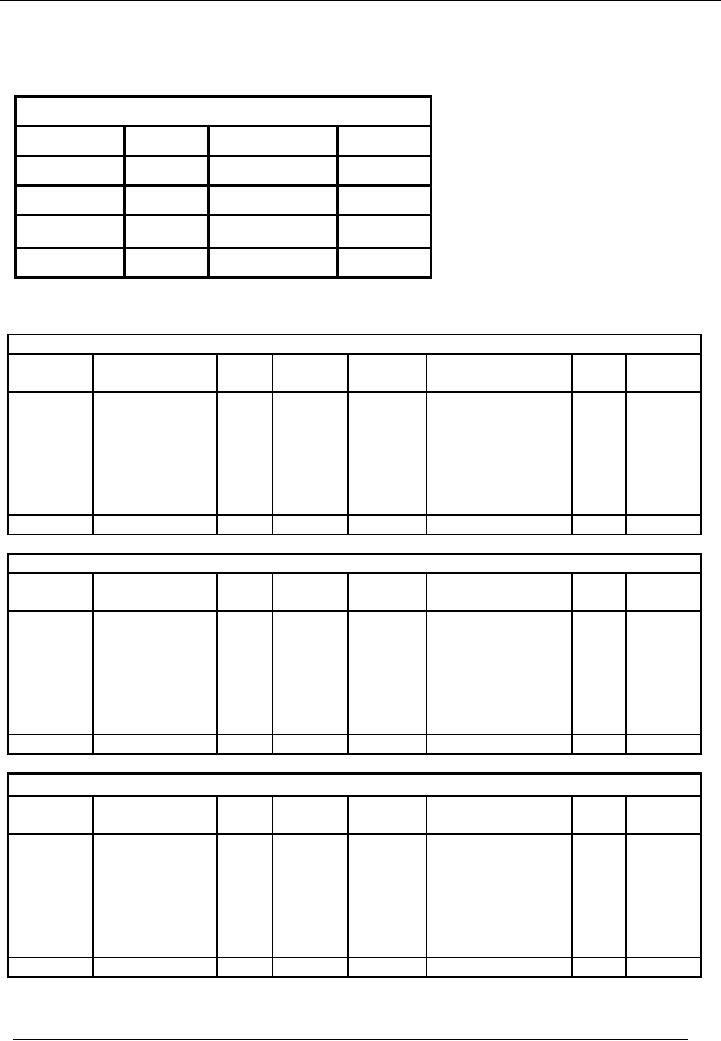
EXAMPLE
# 1
Let's
suppose that the sales
journal provides the following record
for the month of March,
2002:
Sales
Journal
Date
Invoice
#
Name /
Debtor
Amount
Mar
01, 2002
01
A
10,000
Mar
15, 2002
02
B
15,000
Mar
31, 2002
03
C
20,000
Total
45,000
The
above mentioned record will be
posted in the personal ledger
accounts of A, B & C (Debtors
ledger
account)
in the following manner:
A's
Account
Account
code----
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
01/03
10,000
Balance
b/d
10,000
Total
10,000
Total
10,000
B's
Account
Account
code----
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
15/03
15,000
Balance
b/d
15,000
Total
15,000
Total
15,000
C's
Account
Account
code----
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
31/03
20,000
Balance
b/d
20,000
Total
20,000
Total
20,000
174
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
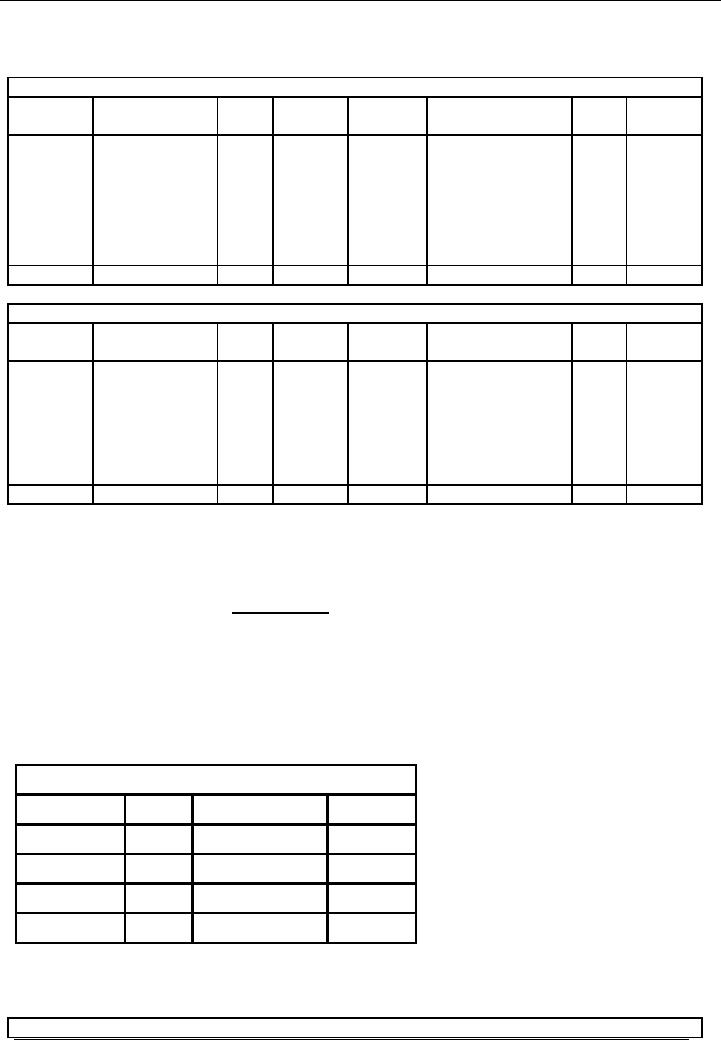
In the
general ledger, the amount of total
sales will be booked in the
following manner:
Sales
Account
Account
code----
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
31/03
Total
sales for the
45,000
month
of march,
2002
Balance
b/d
45,000
Total
45,000
Total
45,000
Debtors
Control Account
Account
code----
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
31/03
Total
sales for
45,000
the
month of
march,
2002
Balance
b/d
45,000
Total
45,000
Total
45,000
Now if
we total the balance of three
accounts of the debtors' ledger on Mar
31, 2002:
A
10,000
B
15,000
C
20,000
Total
45,000
It
will be the same as the balance in the
debtors control account of the
general ledger.
RECORDING
OF SALES RETURN
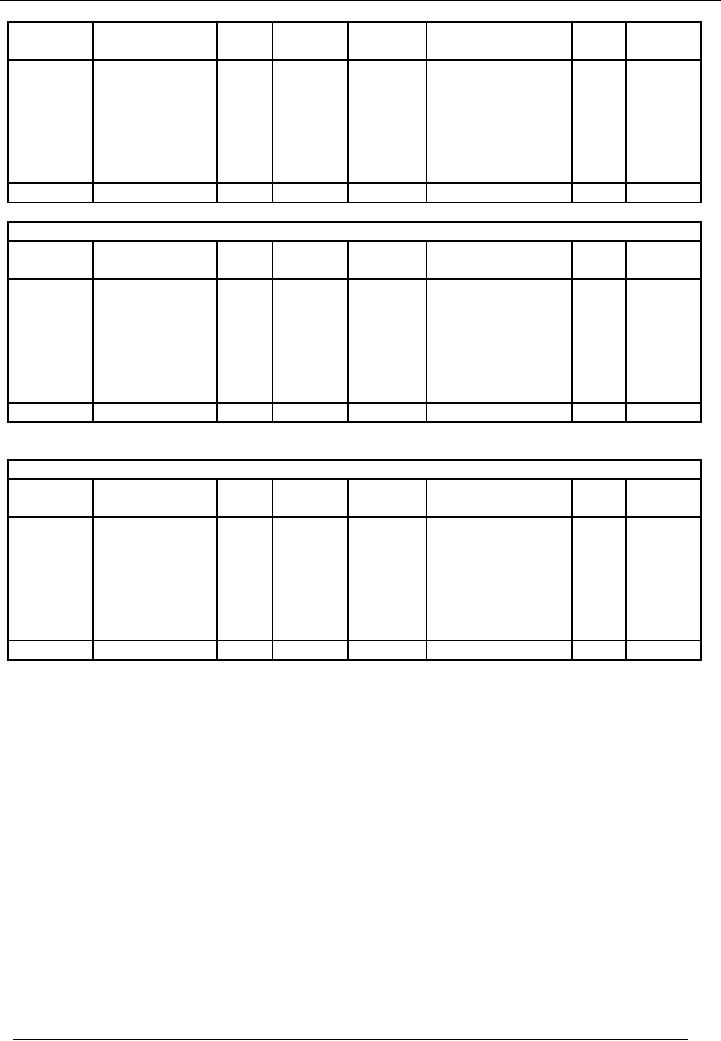
Let's
say that sales return
journal for the month of
March, 2002 give the following
record:
Sales
Journal
Date
Name /
Debtor
Amount
Jan
15, 20--
A
1,000
Jan
20, 20--
B
2,000
Jan
25, 20--
C
3,000
Total
6,000
The
above mentioned record will be
posted in the personal ledger
accounts of A, B & C (Debtors
ledger
account)
in the following manner:
A's
Account
Account
code----
175
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
01/03
10,000
15/03
1,000
Balance
b/d
9,000
Total
10,000
Total
10,000
B's
Account
Account
code----
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
15/03
15,000
20/03
2,000
Balance
b/d
13,000
Total
15,000
Total
15,000
C's
Account
Account
code----
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
31/03
20,000
25/03
3,000
Balance
b/d
17,000
Total
20,000
Total
20,000
176
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
In the
general ledger, the amount of total
sales return will be booked
in the following manner:
Sales
Account
Account
code----
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
Total
sales
6,000
31/03
Total
sales for the
45,000
return
for the
month
of march,
month
of
2002
march,
2002
Balance
b/d
39,000
Total
45,000
Total
45,000
Debtors
Control Account
Account
code----
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
31/03
Total
sales for
45,000
Total
sales return
6,000
the
month of
for
the month of
march,
2002
march,
2002
Balance
b/d
39,000
Total
45,000
Total
45,000
Again
if we total the balance of three
accounts of the debtors ledger on
Mar 31,2002:
A
9,000
B
13,000
C
17,000
Total
39,000
It
will be the same as the balance in the
debtors control account of the
general ledger.
RECEIPTS
FROM DEBTORS
Here, we
need a total figure of
receipts from debtors. Therefore, when
control accounts are used,
we
maintain
cash and bank books with
separate pages for receipts
and payments i.e. two column
cash/bank
books
are not used. On the
receipts side of the cash
and bank book, a column is added in
which receipts
from
debtors are separately noted. This type
of cash / bank book is also
called multi column cash /
bank
book.
177
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
A
sample of the receipt side of
cash / bank book is given
hereunder:
Cash /
Bank Book
Receipt
Side
Date
No
Narration /
Ledger
Receipt
Receipt
from
Particulars
Code
Amount
Debtors
10,000
500
Received
from A
5,000
5,000
300
Received
from B
2,500
2,500
Received
from A
1,000
1,000
Received
from C
1,500
1,500
950
1,000
Total
22,750
9,000
SUBSIDIARY
BOOKS FOR
PURCHASES/CREDITORS
Recording
of creditors is similar to debtors.
The subsidiary books maintained in case
of purchases /
creditors
are:
� Purchase
Journal / Purchase Day Book
individual purchases are
recorded in this Journal.
� Purchase
Return / Return outward Journal If the volume of
returns is also high, then
these
are
also recorded in a separate
register.
� Creditors
Ledger this ledger maintains
record of individual
creditors.
The
information flows to the creditor
control account in the general
ledger as follows:
Opening
balance of
List
of creditor balances drawn up to the end
of previous period.
creditors
This
also confirms with the aggregate
balance of the creditors
ledger.
Credit
Purchases
Individual
credit purchase is recorded in the
purchase journal.
Total
of this
journal is posted into the
creditors control
account
periodically.
Purchase
Return
In
case the transaction volume of
purchase return is high,
then,
these
are recorded in the purchase
return journal. Periodically, the
total
is posted in the creditors control
a/c.
Cheques
/ Cash Paid List of payments
is extracted from cash and
bank book. Or a
separate
column is maintained in cash and bank books
for this
purpose.
Closing
Balance
This
is the balancing figure. It can also be
checked with the total
of
balances
in creditors' ledger.
178
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
EXAMPLE
# 2
Let's
consider the following data
for the month of March,
2002:
Purchase
Journal
Date
Name /
Debtor
Amount
Mar
01, 2002
X
5,000
Mar
10, 2002
Y
10,000
Mar
25, 2002
Z
15,000
Total
30,000
The
above mentioned record will be
posted in the personal ledger
accounts of X, Y & Z (Creditors
ledger
account)
in the following manner:
X's
Account Account code----
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
5,000
01/03
5,000
Balance
b/d
Total
5,000
Total
5,000
Y's
Account Account code----
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
10,000
10/03
Balance
b/d
10,000
Total
10,000
Total
10,000
179
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Z's
Account Account code----
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
25/03
15,000
Balance
b/d
15,000
Total
15,000
Total
15,000
In the
general ledger, the amount of total
purchases will be booked in the
following manner:
Purchases
Account
Account
code----
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
31/03
Total
purchases
30,000
for
the month
of
march, 2002
Balance
b/d
30,000
Total
30,000
Total
30,000
Creditors
Control Account
Account
code----
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
31/03
Total
purchases for
30,000
the
month of
march,
2002
Balance
b/d
30,000
Total
30,000
Total
30,000
Now,
if we total the balance of three
accounts of the creditor's ledger on Mar
31, 2002:
X
5,000
Y
10,000
Z
15,000
Total
30,000
It
will be the same as the balance in the
creditors control account of the
general ledger.
180
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
RECORDING
OF PURCHASE RETURN
Let's
say that the purchase return
journal show the following picture
for the month of March,
2002:
Purchase
Return Journal
Date
Name /
Debtor
Amount
Mar
01, 2002
X
500
Mar
10, 2002
Y
1,000
Mar
25, 2002
Z
1,500
Total
3,000
The
above mentioned record will be
posted in the personal ledger
accounts of X, Y & Z (Creditors
ledger
account)
in the following manner:
X's
Account Account code----
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
01/03
500
01/03
5,000
Balance
b/d
4,500
Total
5,000
Total
5,000
Y's
Account Account code----
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
10/03
1,000
10/03
10,000
Balance
b/d
9,000
Total
10,000
Total
10,000
181
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Z's
Account Account code----
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
25/03
1,500
25/03
15,000
Balance
b/d
13,500
Total
15,000
Total
15,000
In the
general ledger, the amount of total
purchases will be booked in the
following manner:
Purchases
Account
Account
code----
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
31/03
Total
purchases
30,000
31/03
Total
purchases
3,000
for
the month
return
for the
of
march, 2002
month
of march,
2002
Balance
b/d
27,000
Total
30,000
Total
30,000
Creditors
Control Account
Account
code----
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
31/03
Total
purchases
3,000
31/03
Total
purchases for
30,000
return
for the
the
month of
month
of
march,
2002
march,
2002
Balance
b/d
27,000
Total
30,000
Total
30,000
Now,
if we total the balance of three
accounts of the creditor's ledger on Mar
31, 2002:
X
4,500
Y
9,000
Z
13,500
Total
27,000
It
will be the same as the balance in the
creditors control account of the
general ledger.
PAYMENT
TO CREDITORS
182
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Here, we
need a total figure of
payment to creditors. Therefore, when
control accounts are used,
we
maintain
cash and bank books with
separate pages for receipts
and payments i.e. two column
cash/bank
books
are not used. On the payment
side of the cash and bank
book, a column is added in which
payments
to
creditors are separately noted. This type
of cash / bank book is also
called multi column cash /
bank
book.
A
sample of the payment side of
cash / bank book is given
hereunder:
Cash /
Bank Book
Payment
Side
Date
No
Narration /
Ledger
Payment
Payment
to
Particulars
Code
Amount
Creditors
500
5,000
Received
from A
2,500
2,500
3,000
Received
from B
1,500
1,500
1,000
Received
from C
1,500
1,500
1,950
1,500
Total
18,450
5,500
183
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Financial Accounting
- Basic Concepts of Business: capital, profit, budget
- Cash Accounting and Accrual Accounting
- Business entity, Single and double entry book-keeping, Debit and Credit
- Rules of Debit and Credit for Assets, Liabilities, Income and Expenses
- flow of transactions, books of accounts, General Ledger balance
- Cash book and bank book, Accounting Period, Trial Balance and its limitations
- Profit & Loss account from trial balance, Receipt & Payment, Income & Expenditure and Profit & Loss account
- Assets and Liabilities, Balance Sheet from trial balance
- Sample Transactions of a Company
- Sample Accounts of a Company
- THE ACCOUNTING EQUATION
- types of vouchers, Carrying forward the balance of an account
- ILLUSTRATIONS: Ccarrying Forward of Balances
- Opening Stock, Closing Stock
- COST OF GOODS SOLD STATEMENT
- DEPRECIATION
- GROUPINGS OF FIXED ASSETS
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 1
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 2
- REVALUATION OF FIXED ASSETS
- Banking transactions, Bank reconciliation statements
- RECAP
- Accounting Examples with Solutions
- RECORDING OF PROVISION FOR BAD DEBTS
- SUBSIDIARY BOOKS
- A PERSON IS BOTH DEBTOR AND CREDITOR
- RECTIFICATION OF ERROR
- STANDARD FORMAT OF PROFIT & LOSS ACCOUNT
- STANDARD FORMAT OF BALANCE SHEET
- DIFFERENT BUSINESS ENTITIES: Commercial, Non-commercial organizations
- SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
- Financial Statements Of Manufacturing Concern
- Financial Statements of Partnership firms
- INTEREST ON CAPITAL AND DRAWINGS
- DISADVANTAGES OF A PARTNERSHIP FIRM
- SHARE CAPITAL
- STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 1
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 2
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED, QUOTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES