 |
RECAP |
| << Banking transactions, Bank reconciliation statements |
| Accounting Examples with Solutions >> |

Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Lesson-23
RECAP
In the
last lecture we studied, what is Bank
Statement and how does it
differ from our Bank Book.
We told
you
that money lying in our bank
account is our asset. Therefore, it
usually has a DEBIT BALANCE.
Also,
when
we deposit cash in our Bank, we DEBIT the
Bank Book / Bank Account. Whereas,
for Bank, the
money
lying in our Bank Account is a
liability that bank has to
return to us. Therefore, in Bank
Statement
which
is a ledger account for bank
normally has a CREDIT
BALANCE. When we deposit cash in
our bank
account
the liability of the bank to pay us
increases. Therefore, our account in
Books of Bank is
CREDITED.
Bank Statement is, therefore, a MIRROR
IMAGE of our bank book.
Then,
we studied about the reasons that
create differences between
our bank book and bank
statement. Such
as:
� Bank
Charges debited to our bank account by
the bank without our knowledge.
� Profit
credited to our bank
account.
� Payments
made on our behalf by the bank,
through our standing instructions,
that we did not
record
in our
books.
� Money
paid in our account by our
customers, dealers, agents,
etc. without our
knowledge.
� Un-presented
cheques.
� Un-cleared
cheques.
The
last two arise because we
record payment or receipt in
our books when we receive / issue a
cheque. But
the bank
records the transaction in our
account at the time of actual receipt or
payment. These
differences
are
included in the bank reconciliation statement.
The first four items
are either adjusted in the bank book
or
shown
in the reconciliation statement, depending
upon whether we have closed
our books for the period
or
not.
If we have closed our books of
accounts, these differences
will be presented in the bank
reconciliation
statement.
If our books of accounts are
not closed as yet, we will
adjust our bank book and
give effect of all
these
adjustments in the bank
book.
The
main idea behind bank
reconciliation is that we adjust
our bank book for the
transactions, that
remain
untraced,
either through a Voucher (charges,
profit, standing instruction) or
through a Reconciliation
Statement
(un-presented, un-credited
cheques).
EXAMPLE
# 1
From
the following particulars, prepare Bank
reconciliation statement of Mr. Naveed as
on June 30, 2002.
�
Balance
as per bank book
Dr.
32,000
�
Cheques
deposited but not yet
collected by bank
20,200
�
Cheques
issued but not yet paid by
bank
13,000
�
Dividend
credited by bank on June 30,
but the intimation
was
received later.
2,000
� Interest
credited by bank
250
� Bank
charges debited by bank
50
It is
assumed that books of accounts
are not closed as
yet.
SOLUTION
As books of
accounts are not closed, we
will find out the adjusted
balance first:
Rs.
Balance
as per bank book
Dr.
32,000
Add/Debit
Dividend credited by bank
Dr.
2,000
160
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Add/Debit
Interest credited by bank
Dr.
250
Less/Credit
Bank charges
Cr.
(50)
Adjusted
balance as per bank
book
Dr.
34,200
These
adjustments in the ledger account of bank
will look like as
follows:
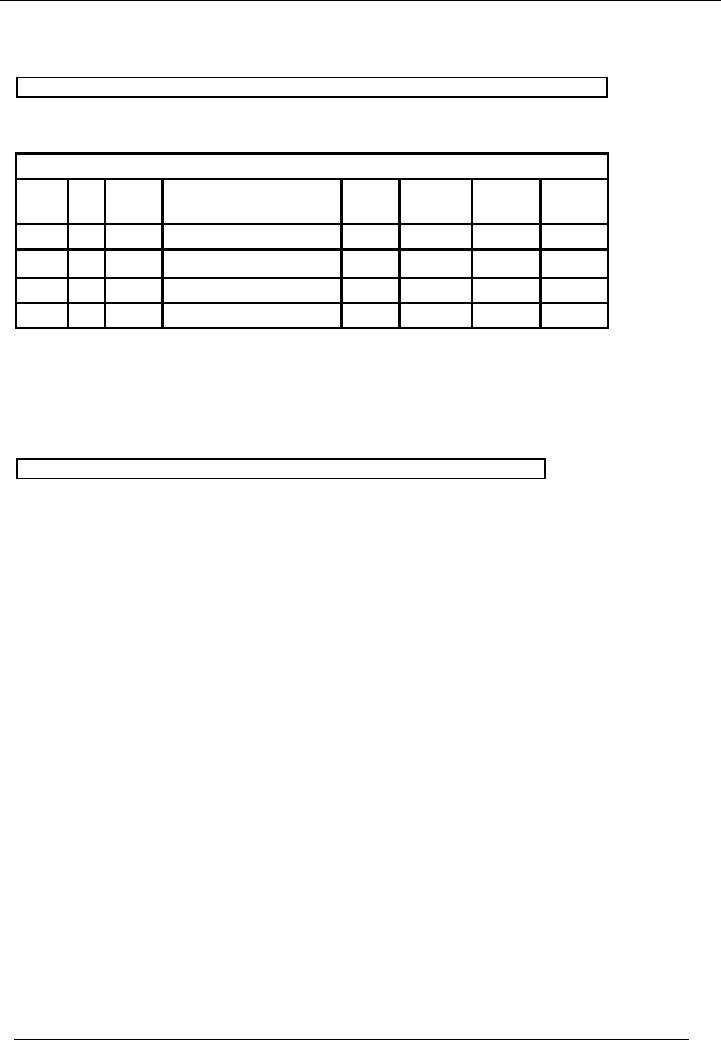
Mr.
Naveed
Bank
Book (Bank Account
Number)
Account
Code --
Date
Vr.
Chq.
Narration
/
Ledger
Receipt
Payment
Balance
20--
#
No.
Particulars
Code
Amount
Amount
Dr/(Cr)
Jun30
Balance
B/f
32,000
32,000
Jun30
Dividend
received
2,000
34,000
Jun30
Interest
received
250
34,250
Jun30
Bank
charges
50
34,200
BANK
RECONCILIATION STATEMENT
Rs.
Balance
as per bank book
Dr.
34,200
Add:
Un-presented cheques
Dr.
13,000
Less:
Un-credited cheques
(Cr.)
(20,200)
Balance
as per bank statement
Cr.
27,000
In this
example, books of accounts are
not closed, all other
transactions except un-presented
cheques and
un-credited
cheques, will be recorded in the bank
book by passing journal
entries and adjusted balance
of
bank
book will be presented in the bank
reconciliation statement.
To this
point, we have considered a favourable
balance i.e. Debit in bank
book and Credit in bank
statement.
But
there is a possibility that we may
have an unfavourable balance. This can
happen if we have taken a
loan
from
our bank.We can also
call it an overdraft i.e. we
have drawn more money from
our bank than we had
deposited
in it. The reconciliation
procedure would be the same as
before.
161
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
The
solution of above example
will show the following
picture:
SOLUTION
As books of
accounts are not closed, we
will find out the adjusted
balance first:
Rs.
Balance
as per bank book
Cr.
(32,000)
Add/Debit
Dividend credited by bank
Dr.
2,000
Add/Debit
Interest credited by bank
Dr.
250
Less/Credit
Bank charges
Cr.
(50)
Adjusted
balance as per bank
book
Dr.
(34,200)
These
adjustments in the ledger account of bank
will look like as
follows:
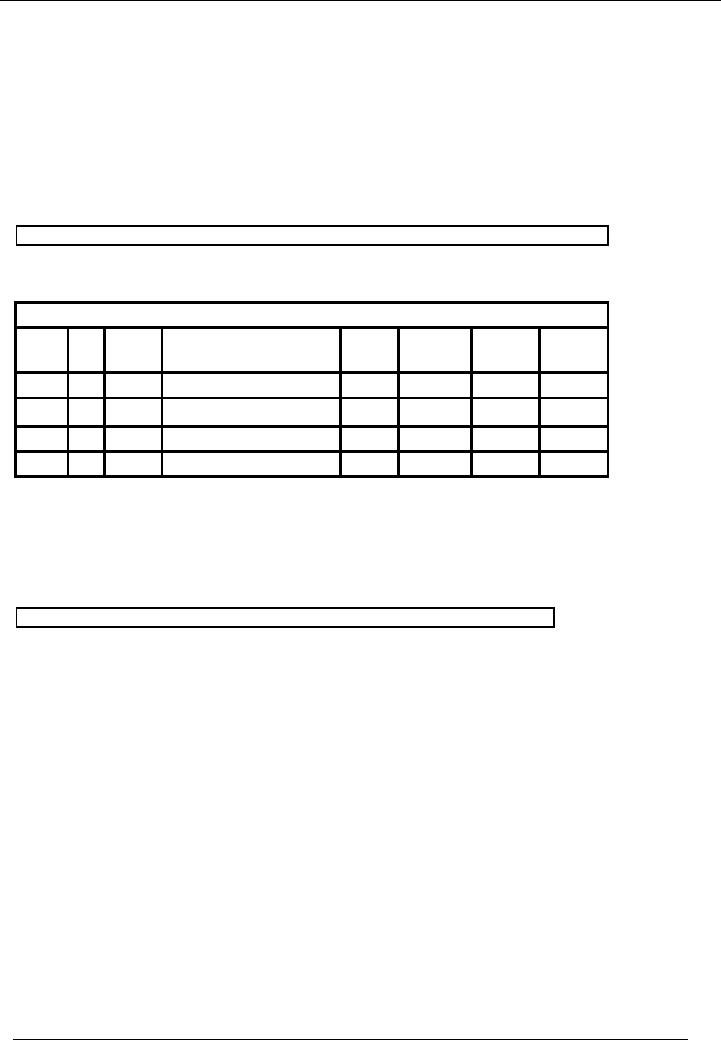
Mr.
Naveed
Bank
Book (Bank Account
Number)
Account
Code --
Date
Vr.
Chq.
Narration
/
Ledger
Receipt
Payment
Balance
20--
#
No.
Particulars
Code
Amount
Amount
Dr/(Cr)
Jun30
Balance
B/f
32,000
(32,000)
Jun30
Dividend
received
2,000
(34,000)
Jun30
Interest
received
250
(34,250)
Jun30
Bank
charges
50
(34,200)
BANK
RECONCILIATION STATEMENT
Rs.
Balance
as per bank book
Cr.
(34,200)
Add:
Un-presented cheques
Dr.
13,000
Less:
Un-credited cheques
(Cr.)
(20,200)
Balance
as per bank statement
Dr.
(41,400)
In this
case the balance of bank statement is
debit because this amount is receivable
by bank; it is an asset of
the bank. On the
other hand, this balance is a credit
balance in bank book, it is
payable to bank by the
business.
So, it is a liability of the business.
Balance of bank statement in the first
case does not match
with
the
balance calculated above.
The reason being, the
balance in the first solution
was debit, i-e. balance
was
our
asset and drawing more money
from bank reduced our asset.
On the other hand, balance in this
case is
credit,
i-e. we have already drawn
more than what we have
deposited in the bank. So, it is our
liability. This
balance
is shown with negative sign.
So, when we add/debit any
amount, it will reduce our
liability and when
we less/credit
any amount from bank, it will
enhance our liability. This
difference in treatment will result in
a
different
balance of bank statement.
162
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Financial Accounting
- Basic Concepts of Business: capital, profit, budget
- Cash Accounting and Accrual Accounting
- Business entity, Single and double entry book-keeping, Debit and Credit
- Rules of Debit and Credit for Assets, Liabilities, Income and Expenses
- flow of transactions, books of accounts, General Ledger balance
- Cash book and bank book, Accounting Period, Trial Balance and its limitations
- Profit & Loss account from trial balance, Receipt & Payment, Income & Expenditure and Profit & Loss account
- Assets and Liabilities, Balance Sheet from trial balance
- Sample Transactions of a Company
- Sample Accounts of a Company
- THE ACCOUNTING EQUATION
- types of vouchers, Carrying forward the balance of an account
- ILLUSTRATIONS: Ccarrying Forward of Balances
- Opening Stock, Closing Stock
- COST OF GOODS SOLD STATEMENT
- DEPRECIATION
- GROUPINGS OF FIXED ASSETS
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 1
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 2
- REVALUATION OF FIXED ASSETS
- Banking transactions, Bank reconciliation statements
- RECAP
- Accounting Examples with Solutions
- RECORDING OF PROVISION FOR BAD DEBTS
- SUBSIDIARY BOOKS
- A PERSON IS BOTH DEBTOR AND CREDITOR
- RECTIFICATION OF ERROR
- STANDARD FORMAT OF PROFIT & LOSS ACCOUNT
- STANDARD FORMAT OF BALANCE SHEET
- DIFFERENT BUSINESS ENTITIES: Commercial, Non-commercial organizations
- SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
- Financial Statements Of Manufacturing Concern
- Financial Statements of Partnership firms
- INTEREST ON CAPITAL AND DRAWINGS
- DISADVANTAGES OF A PARTNERSHIP FIRM
- SHARE CAPITAL
- STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 1
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 2
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED, QUOTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES