 |
CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 1 |
| << GROUPINGS OF FIXED ASSETS |
| CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 2 >> |
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Lesson-19
CAPITAL
WORK IN PROGRESS
If an
asset is not completed at
that time when balance sheet
is prepared, all costs incurred on
that asset up to
the
balance sheet date are
transferred to an account called
Capital
Work in Progress Account.
This
account
is shown separately in the balance
sheet below the fixed asset.
Capital work in progress
account
contains
all expenses incurred on the asset
until it is converted into working
condition. All these
expenses
will
become part of the cost of
that asset. When an asset is
completed and it is ready to
work, all costs in
the
capital
work in progress account
will transfer to the relevant asset
account through the following
entry:
Debit:
Relevant
asset account
Credit:
Capital
work in progress
account
ILLUSTRATION
# 1
A
machine is purchased for Rs.
400,000. Its useful life is
estimated to be five years.
Its residual value is
Rs.
25,000.
After four years, it was
sold for Rs. 40,000.
For the purpose of WDV, its
depreciation rate is 40%.
You
are required to show calculation of depreciation
for four years. Also
calculate profit or loss on
disposal.
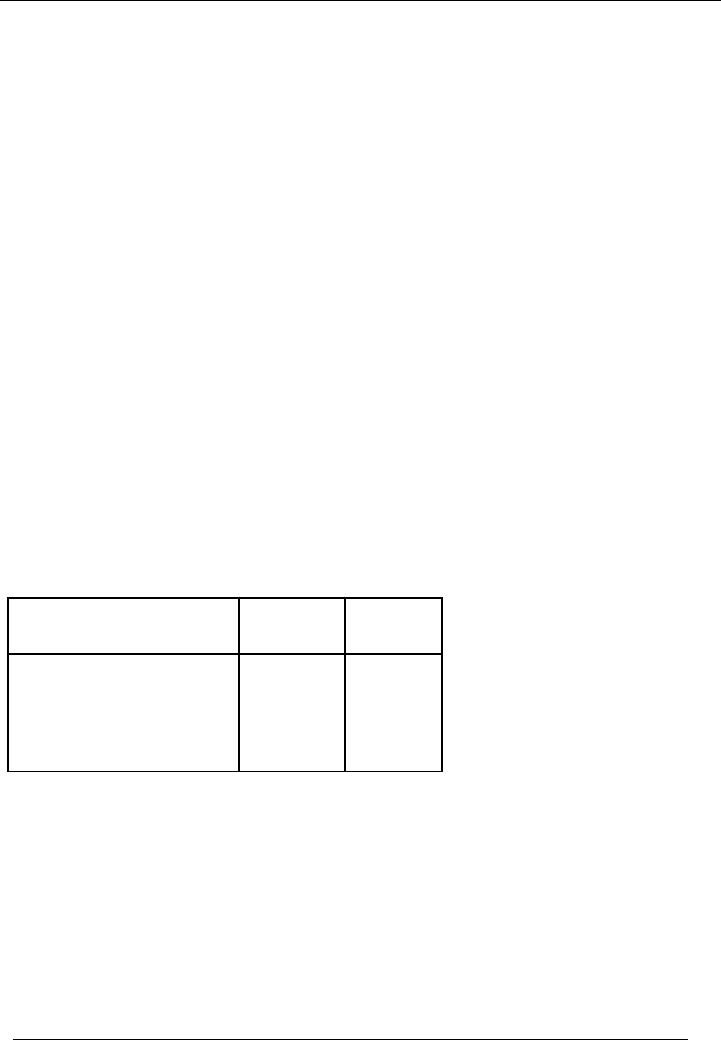
SOLUTION
Calculation of
depreciation and profit & loss on the
basis of straight line method:
Depreciation/year
= (400,000 25,000)/5 = 75,000
(Straight line method)
As,
machine was sold after four
years but its useful
life was estimated for
five years, when we
calculate
depreciation of the
asset under straight line method, we will
divide its WDV over
five years, not on
four
years.
Particulars
Depreciation
Written
(Rs)
Down
Value
(Rs.)
375,000
Depreciable
cost
Dep.
Of the 1st year
(75,000)
300,000
Dep.
Of the 2nd year
(75,000)
225,000
(75,000)
150,000
Dep.
Of the 3rd year
Dep.
Of the 4th year
(75,000)
75,000
Book
value after four
years
Rs.
75,000
Sale
price
Rs.
40,000
Profit/(loss)
on sale
Rs.
(35,000) i-e.(40,000
75,000)
140
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
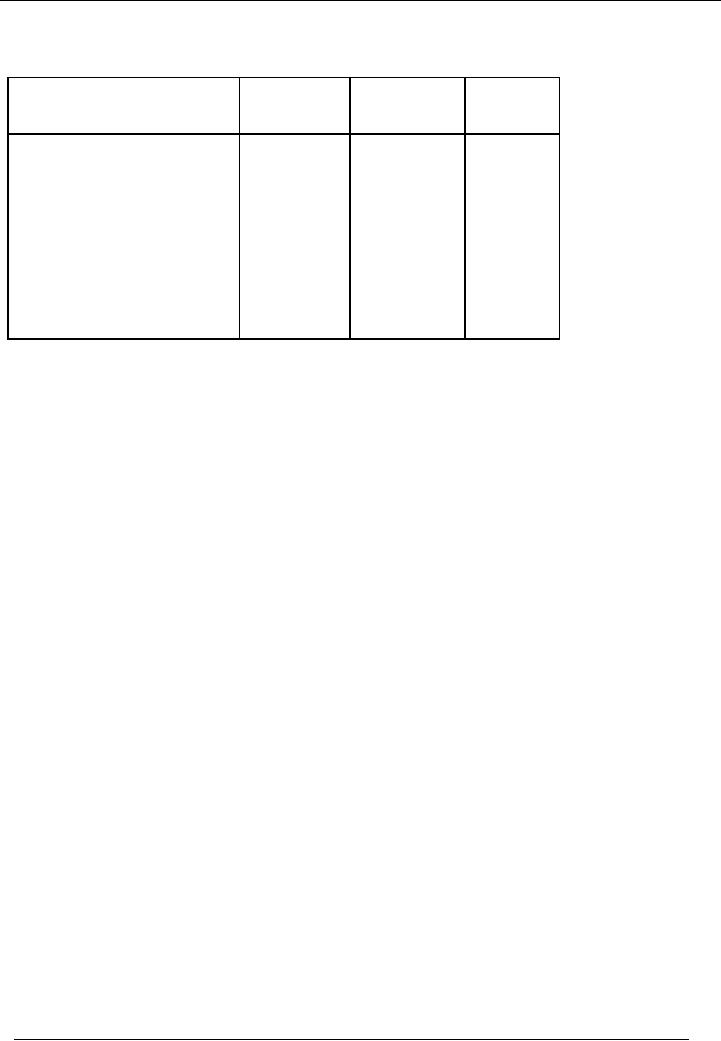
Calculation of
depreciation and profit & loss on the
basis of reducing balance
method:
Depreciation
rate = 40%
Particulars
Depreciation
Accumulated
Written
(Rs)
Depreciation
Down
(Rs.)
Value
(Rs.)
Depreciable
cost
400,000
Dep.
Of the 1st year
400,000
x 40%
160,000
160,000
240,000
Dep.
Of the 2nd year
96,000
256,000
144,000
240,000
x 40%
Dep.
Of the 3rd year
144,000
x 40%
57,600
313,600
86,400
Dep.
Of the 4th year
86,400
x 40%
34,560
348,160
51,840
Book
value after four
years
Rs.
51,840
Sale
price
Rs.
40,000
Profit/(loss)
on sale
Rs.
(11,840) i-e.(40,000
51,840)
ILLUSTRATION
# 2
Following
information of machinery account is
available in Year 2004:
� Machine
# 1 is purchased on September 1, 2000
for Rs. 100,000
� Machine
# 2 is purchased on January 31,
2002 for Rs.
200,000
� Machine
# 3 is purchased on July 1, 2003
for Rs. 50,000
� Machine
# 1 is disposed on March 31,
2004
Depreciation
is charged @ 25% reducing balance method.
Financial year is closed on June 30
every year.
Show
the calculation of depreciation on machinery for
four years using the
following policies:
� Depreciation
is charged on the basis of
use
� Full
depreciation is charged in the year of
purchase and no depreciation is charged
in the year of
disposal.
141
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
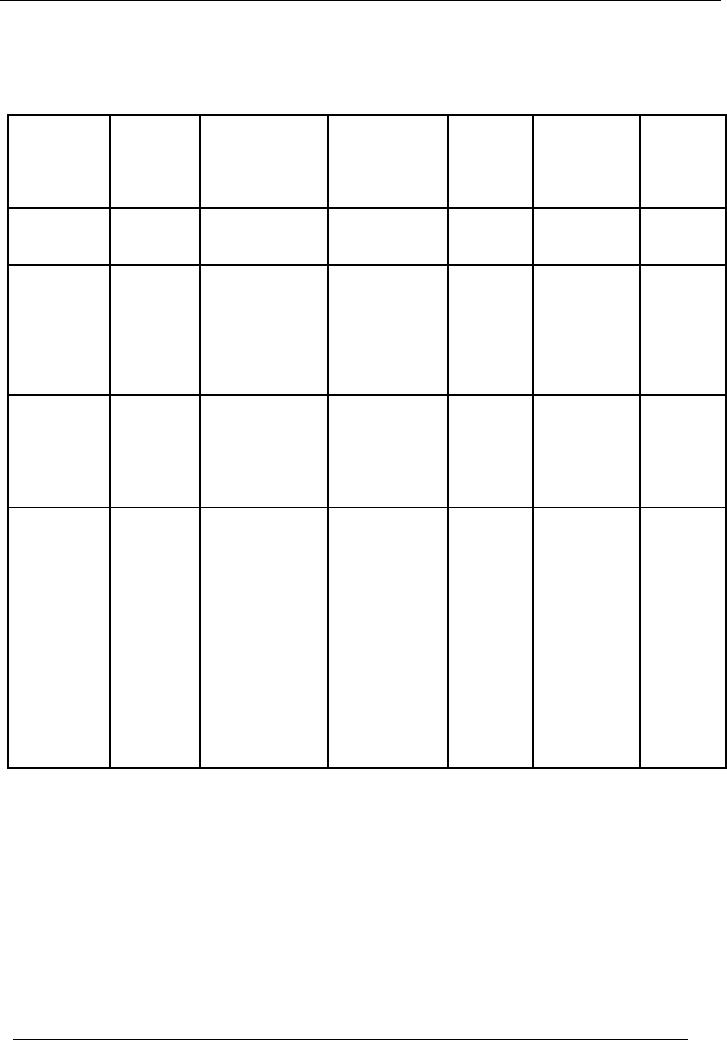
SOLUTION
Depreciation
on the basis of
use
Date
Purchase
Depreciation
Accumulated
Total
Written
Total
of
(Rs.)
depreciation
Accum.
Down
Value
Written
machine
(Rs.)
Dep.
(Rs.)
Down
(Rs.)
Value
(Rs.)
01-09-2000
100,000
Machine # 1
Machine
# 1
20,833
Machine
# 1
79,167
100,000
x 25%
20,833
79,167
x10/12=20,833
2001-2002
Machine
# 1
Machine
# 1
61,458
Machine
# 1
238,542
79,167x25%
40,625
59,375
= 19,792
31-01-2002
200,000
Machine # 2
Machine
# 2
Machine
# 2
200,000x25%x5/
20,833
179,167
12=20,833
2002-2003
Machine
# 1
Machine
# 1
121,094
Machine
# 1
178,906
59,375x25%
55,469
44,531
= 14,844
Machine
# 2
Machine
# 2
Machine
# 2
179,167x25%
65,625
134,375
=44,792
2003-2004
Machine
# 1
Machine
# 1
175,538
Machine
# 1
138,281
44,531x25%x
63,819
(36,181)
9/12=
8,350
(sold)
Machine
# 2
Machine
# 2
Machine
# 2
134,375x25%
99,219
100,781
= 33,594
01-07-2003
50,000
Machine # 3
Machine
# 3
Machine
# 3
50,000x25%
12,500
37,500
= 12,500
Figure in blue
color is the written down
value of machine # 1, which is
disposed of by the management.
142
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
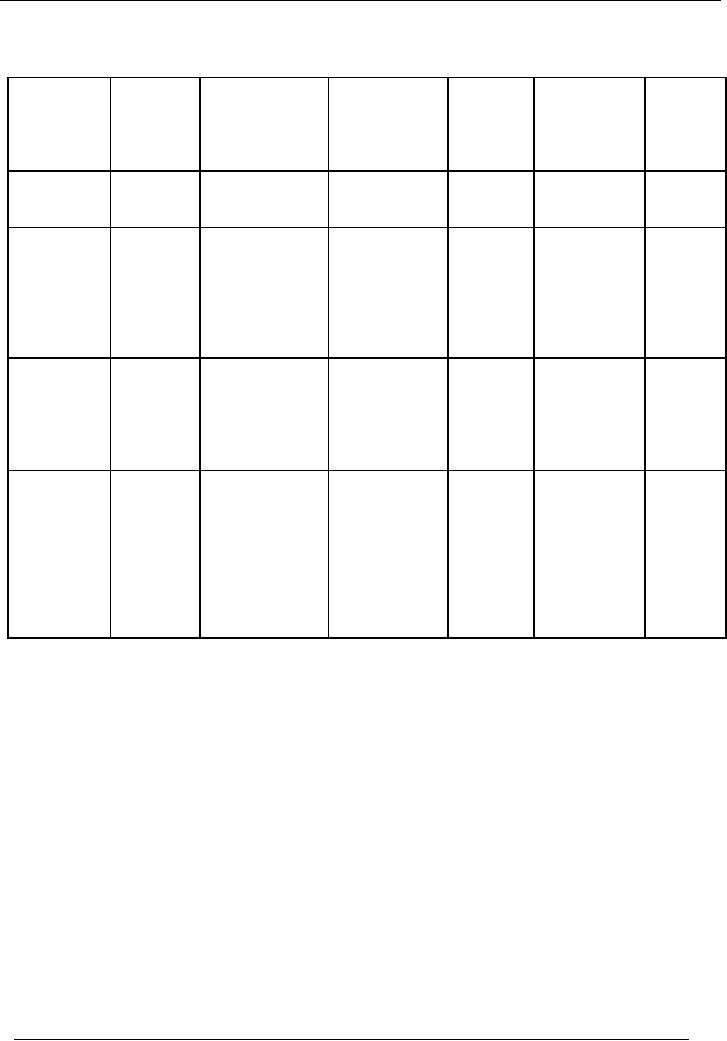
Full
year depreciation in the
year of purchase and no depreciation in
the year of sale:
Date
Purchase
Depreciation
Accumulated
Total
Written
Total
of
(Rs.)
depreciation
Accum.
Down
Value
Written
machine
(Rs.)
Dep.
(Rs.)
Down
(Rs.)
Value
(Rs.)
01-09-2000
100,000
Machine # 1
Machine
# 1
25,000
Machine
# 1
75,000
100,000
x 25%
25,000
75,000
=25,000
2001-2002
Machine
# 1
Machine
# 1
93,750
Machine
# 1
206,250
75,000x25%
43,750
56,250
= 18,750
31-01-2002
200,000
Machine # 2
Machine
# 2
Machine
# 2
200,000x25%
50,000
150,000
=50,000
2002-2003
Machine
# 1
Machine
# 1
145,313
Machine
# 1
154,687
56,250x25%
57,813
42,187
= 14,063
Machine
# 2
Machine
# 2
Machine
# 2
112,500
150,000x25%
87,500
=37,500
Machine
# 1 185,935
2003-2004
Machine
# 1
Machine
# 1
121,875
57,813
0
42,187
Machine
sold
(sold)
(sold)
Machine
# 2
Machine
# 2
Machine
# 2
112,500x25%
115,625
84,375
= 28,125
50,000
Machine # 3
Machine
# 3
01-07-2003
Machine
# 3
50,000x25%
12,500
37,500
= 12,500
143
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Financial Accounting
- Basic Concepts of Business: capital, profit, budget
- Cash Accounting and Accrual Accounting
- Business entity, Single and double entry book-keeping, Debit and Credit
- Rules of Debit and Credit for Assets, Liabilities, Income and Expenses
- flow of transactions, books of accounts, General Ledger balance
- Cash book and bank book, Accounting Period, Trial Balance and its limitations
- Profit & Loss account from trial balance, Receipt & Payment, Income & Expenditure and Profit & Loss account
- Assets and Liabilities, Balance Sheet from trial balance
- Sample Transactions of a Company
- Sample Accounts of a Company
- THE ACCOUNTING EQUATION
- types of vouchers, Carrying forward the balance of an account
- ILLUSTRATIONS: Ccarrying Forward of Balances
- Opening Stock, Closing Stock
- COST OF GOODS SOLD STATEMENT
- DEPRECIATION
- GROUPINGS OF FIXED ASSETS
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 1
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 2
- REVALUATION OF FIXED ASSETS
- Banking transactions, Bank reconciliation statements
- RECAP
- Accounting Examples with Solutions
- RECORDING OF PROVISION FOR BAD DEBTS
- SUBSIDIARY BOOKS
- A PERSON IS BOTH DEBTOR AND CREDITOR
- RECTIFICATION OF ERROR
- STANDARD FORMAT OF PROFIT & LOSS ACCOUNT
- STANDARD FORMAT OF BALANCE SHEET
- DIFFERENT BUSINESS ENTITIES: Commercial, Non-commercial organizations
- SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
- Financial Statements Of Manufacturing Concern
- Financial Statements of Partnership firms
- INTEREST ON CAPITAL AND DRAWINGS
- DISADVANTAGES OF A PARTNERSHIP FIRM
- SHARE CAPITAL
- STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 1
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 2
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED, QUOTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES