 |
GROUPINGS OF FIXED ASSETS |
| << DEPRECIATION |
| CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 1 >> |

Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Lesson-18
DEPRECIATION
It is a
systematic allocation of the cost of a
depreciable asset to expense
over its useful
life".
GROUPINGS
OF FIXED ASSETS
Major
groups of Fixed
Assets:
� Land
� Building
� Plant
and Machinery
� Furniture
and Fixtures
� Office
Equipment
� Vehicles
No depreciation is
charged for `Land'. In case of
`Leased Asset/Lease Hold
Land' the amount paid for it is
charged
over the life of the lease
and is called Amortization.
RECORDING
OF JOURNAL ENTRIES
Purchase
of fixed asset:
Debit:
Relevant
asset account
Credit:
Cash,
Bank or Payable Account
For
recording of depreciation, following two
heads of accounts are
used:
� Depreciation
Expense Account
� Accumulated
Depreciation Account
Depreciation
expense account contains the depreciation
of the current year. Accumulated depreciation
contains
the depreciation of the asset from the
financial year in which it
was bought. Depreciation of
the
following
years in which asset was
used, is added up in this account. In
other words, this head of
account
shows
the cost of usage of the asset up to the
current year. Depreciation account is
charged to profit &
loss
account
under the heading of Administrative
Expenses. In the balance sheet,
fixed assets are presented
at
written
down value. i-e.
WDV =
Actual cost of fixed asset
Accumulated Depreciation.
Journal
entry for the depreciation is given
below:
Debit:
Depreciation
Account
Credit:
Accumulated
Depreciation Account
METHODS
OF CALCULATING DEPRECIATION
There
are several
methods of calculating depreciation. At this
stage, we will discuss only
two of them
namely:
� Straight
line method
� Reducing
balance method
STRAIGHT
LINE METHOD
134
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
In this method, a
fixed amount is calculated by a formula.
That fixed amount is charged
every year
irrespective
of the written down value of the
asset. The formula for
calculating the depreciation is given
below:
Depreciation
= (cost Residual value) / Expected
useful life of the
asset
Residual
value is the
cost of the asset after the expiry of
its useful life.
REDUCING
BALANCE METHOD
In this method,
depreciation is calculated on written
down value. In the first
year, depreciation is calculated
on
cost. Afterwards written
down value is calculated by deducting
accumulated depreciation from the cost
of
that
asset(cost accumulated depreciation)
and depreciation is charged on that
value.
�
Cost
of Asset Price at which
the asset was initially
recorded.
�
Written
Down Value / Book Value
Cost minus Accumulated
Depreciation.
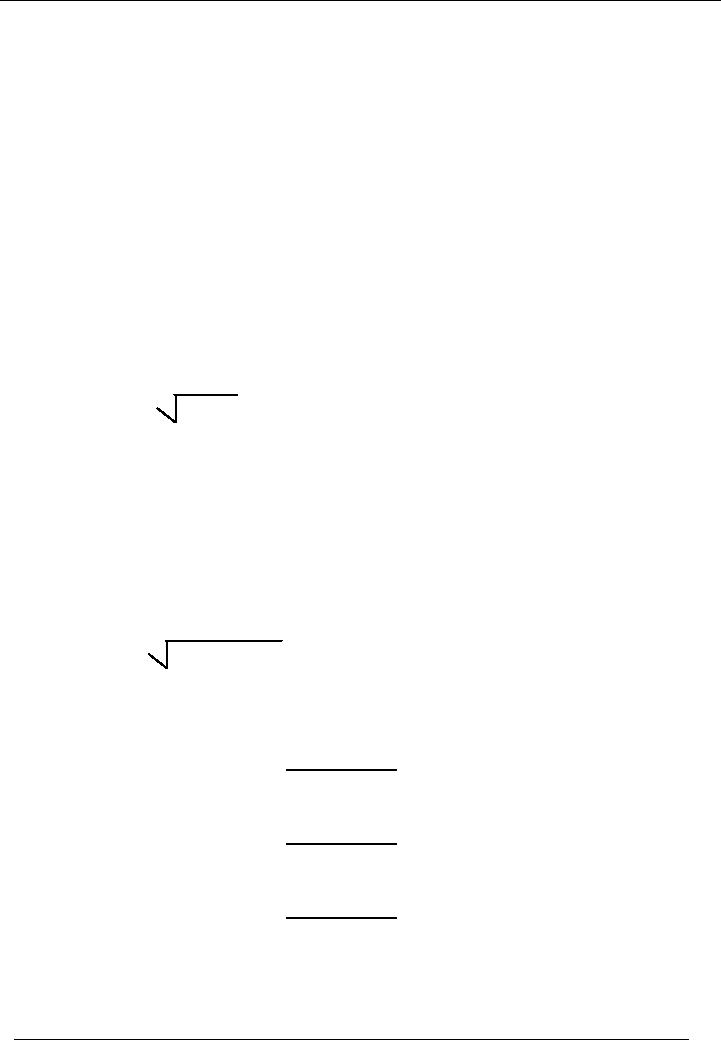
In
reducing balance method, a formula is
used for calculation of depreciation
rate. i e.
�
Rate =
1
n RV /
C
Where:
"RV" =
Residual Value
"C" =
Cost
"n" =
Life of Asset
Calculate
the rate if:
�
Cost
=
100,000
�
Residual
Value (RV)
=
20,000
�
Life
= 3
years
�
Rate =
1 3 20000/100000
=
42%
Year
1
Cost
100,000
Depreciation
100,000
x 42%
(42,000)
WDV
(Closing Balance)
58,000
Year
2
WDV
(Opening Balance)
58,000
Depreciation
58,000
x 42%
(24,360)
WDV
(Closing Balance)
33,640
Year
3
WDV
(Opening Balance)
33,640
Depreciation
33,640
x 42%
(14,128)
WDV
(Closing Balance)
19,511
Disposal of
Asset
Cost
of Asset
=
100,000
Life
of the Asset
= 5
Years
Depreciation
Method
=
Straight Line
135
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Residual
Value
=
Rs.10000
Sale
Price after Five
Years
=
Rs.15000
Depreciation
per year = (100000-10000) /
5
=
Rs.5000 per year
Total
Depreciation in Five
Years
=
18,000 x 5
=
90,000
Book
Value after Five
Years
=
100,000- 90,000
=
10,000
Profit
on Disposal
=
15,000 10,000
=
Rs.5000
Recording
of Disposal
Debit
Fixed
Asset Disposal A/c
100,000
Credit
Fixed
Asset Cost A/c
100,000
(With
the cost of asset)
Debit
Accumulated
Dep. A/c
90,000
Credit
Fixed
Asset Disposal A/c
90,000
(With
the depreciation accumulated to
date)
Debit
Cash /
Bank / Receivable A/c 15,000
Credit
Fixed
Asset Disposal A/c
15,000
(With
the price at which asset is
sold)
[Note:
one group to appear at a
time]
Disposal of
Asset Account
Fixed
Asset Disposal Account
DEBIT
CREDIT
Cost
Account
100,000
Acc.
Dep. Account
90,000
Cash
/ Bank
15,000
P & L
Account
5000
( Balancing
Figure)
Total
105000
Total
105000
POLICY
FOR DEPRECIATION
The
management of the business selects the
policy for charging depreciation. There
is no law binding on the
management.
The management is free to
choose method of depreciation and policy
of charging
depreciation.
Normally two policies are
commonly used:
� Depreciation
on the basis of use
� In the
year of purchase, full
year's depreciation is charged; where
as, in the year of sale
no
depreciation is
charged.
Now it
is up to the management to decide, what method
and what policy is better and effective
for their
business.
136

Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
DISPOSAL
OF FIXED ASSET
When
depreciable asset is disposed
off at any time during the
financial year, an entry should be
made to give
effect of the
disposal. Since, the residual
value of asset is only
estimated, it is common for asset to be
sold at
price
that differs from its
book value at the date of
disposal. When asset is
sold, any profit or loss
is
computed by
comparing book value with the amount
received from sale. As you
know, book value is
obtained by
deducting accumulated depreciation from
original cost of the asset. A
sale price in excess of
the
book
value produces profit; a
sale price below the book
value produces loss. This
profit or loss should be
shown
in the profit & loss
account.
ENTRIES
FOR RECORDING
DISPOSAL
Debit
Fixed
Asset Disposal A/c
Credit
Fixed
Asset Cost A/c
(With
the cost of asset)
Debit
Accumulated
Dep. A/c
Credit
Fixed
Asset Disposal A/c
(With
the depreciation accumulated to
date)
Debit
Cash /
Bank / Receivable A/c
Credit
Fixed
Asset Disposal A/c
(With
the price at which asset is
sold)
Example
�
An
asset is purchased for Rs.
500,000 on Nov. 01,
2001.
�
Depreciation
rate is 10% p.a.
�
The
Asset is sold on Apr. 30,
2004.
�
Financial
Year is July 1 to June
30
Question
� Calculate
the WDV For both
policies
137
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Depreciation
is Charged on the Basis of
USe
Year
On
the Basis of Use
Rs.
1-11-2001
Cost
500,000
2001-2002
Dep.
500,000 x 10% x 8 / 12
(33,333)
30-6-2002
WDV
466,667
2002-2003
Dep.
466,666 x 10%
(46,667)
30-6-2003
WDV
420,000
2003-2004
Dep.
420,000 x 10% x 10 / 12
(35,000)
30-4-2004
WDV
385,000
Full
Dep. In the Year of
Purchase
Year
Full
Dep. in year of
Purchase
Rs.
1-11-2001
Cost
500,000
2001-2002
Dep.
500,000 x 10%
(50,000)
30-6-2002
WDV
450,000
2002-2003
Dep.
450,000 x 10%
(45,000)
30-6-2003
WDV
405,000
2003-2004
Dep.
00 in the year of
sale
00
30-6-2004
WDV
405,000
Contents
of Fixed Assets
Register
� Different
record for each class of
assets
� Date
of purchase
� Detailed
particulars of asset
� Location
of asset
� Record
of depreciation
ILLUSTRATION
Cost
of asset
Rs.
200,000
Life
of the asset
5
years
Depreciation
method
Straight
line
Residual
value
Rs.
20,000
Sale
price after 5 years
30,000
Calculate
profit/Loss on the sale of the
asset?
SOLUTION
138
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Written
down value = 200,000
20,000 = 180,000
Depreciation/year
= 180,000/5 = 36,000 (Straight
line method)
Particulars
Depreciation
Written
(Rs)
Down
Value
(Rs.)
200,000
Depreciable
cost
st year
(36,000)
164,000
Dep.
Of the 1
Dep.
Of the 2nd year
(36,000)
128,000
Dep.
Of the 3
(36,000)
92,000
rd year
(36,000)
56,000
Dep.
Of the 4th year
Dep.
Of the 5th year
(36,000)
20,000
Book
value after five
years
Rs.
20,000
Sale
price
Rs.
30,000
Profit
on sale
Rs.
10,000 (30,000
20,000)
Same
illustration is solved by reducing
balance method
Cost
of asset
Rs.
200,000
Residual
value
Rs.
20,000
Estimated
useful life
5
years
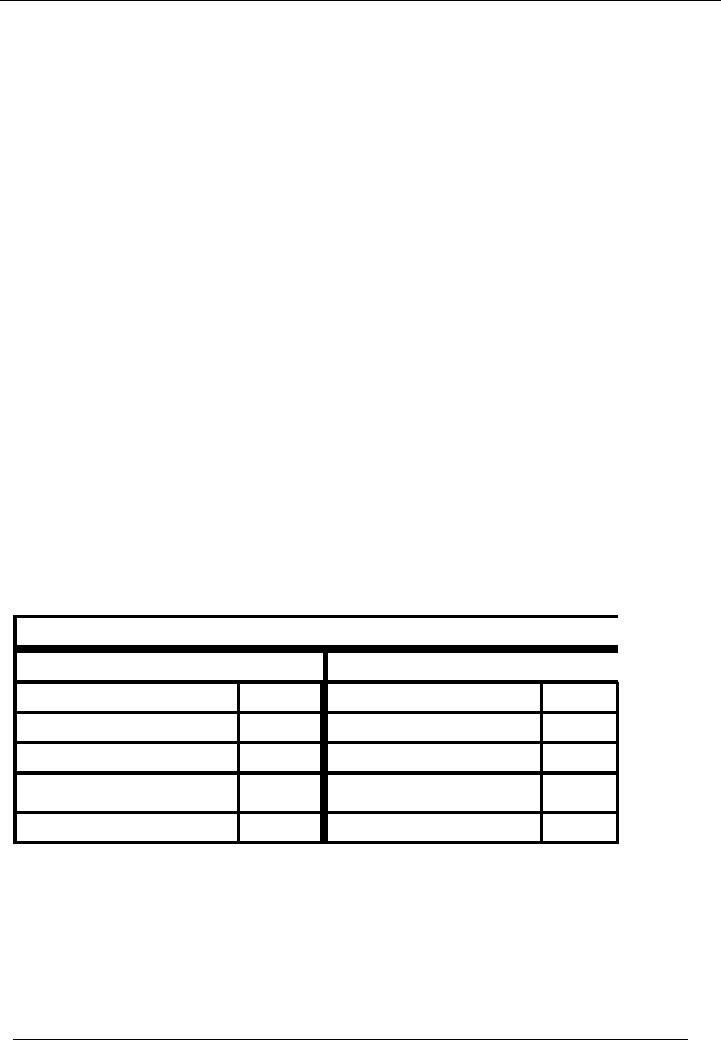
Calculation of
depreciation rate
____
Depreciation
Rate = 1 n√Rv/c
_____________
=1-
5√20,000/200,000
=
37%
Allocation
of depreciation is given below:
Particulars
Depreciation
Accumulated
Written
(Rs)
Depreciation
Down
(Rs.)
Value
(Rs.)
200,000
Depreciable
cost
Dep.
Of the 1st year
200,000
x 37%
74,000
74,000
126,000
Dep.
Of the 2nd year
126,000
x 37%
46,620
120,620
79,380
Dep.
Of the 3rd year
29,371
149,991
50,009
79,380
x 37%
Dep.
Of the 4th year
50,009
x 37%
18,503
168,494
31,506
Dep.
Of the 5th year
31,506
x 37%
11,657
180,151
19,849
Book
value after five
years
Rs.
19,849
Sale
price
Rs.
30,000
Profit
on sale
Rs.
10,151 (30,000
19,849)
139
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Financial Accounting
- Basic Concepts of Business: capital, profit, budget
- Cash Accounting and Accrual Accounting
- Business entity, Single and double entry book-keeping, Debit and Credit
- Rules of Debit and Credit for Assets, Liabilities, Income and Expenses
- flow of transactions, books of accounts, General Ledger balance
- Cash book and bank book, Accounting Period, Trial Balance and its limitations
- Profit & Loss account from trial balance, Receipt & Payment, Income & Expenditure and Profit & Loss account
- Assets and Liabilities, Balance Sheet from trial balance
- Sample Transactions of a Company
- Sample Accounts of a Company
- THE ACCOUNTING EQUATION
- types of vouchers, Carrying forward the balance of an account
- ILLUSTRATIONS: Ccarrying Forward of Balances
- Opening Stock, Closing Stock
- COST OF GOODS SOLD STATEMENT
- DEPRECIATION
- GROUPINGS OF FIXED ASSETS
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 1
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 2
- REVALUATION OF FIXED ASSETS
- Banking transactions, Bank reconciliation statements
- RECAP
- Accounting Examples with Solutions
- RECORDING OF PROVISION FOR BAD DEBTS
- SUBSIDIARY BOOKS
- A PERSON IS BOTH DEBTOR AND CREDITOR
- RECTIFICATION OF ERROR
- STANDARD FORMAT OF PROFIT & LOSS ACCOUNT
- STANDARD FORMAT OF BALANCE SHEET
- DIFFERENT BUSINESS ENTITIES: Commercial, Non-commercial organizations
- SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
- Financial Statements Of Manufacturing Concern
- Financial Statements of Partnership firms
- INTEREST ON CAPITAL AND DRAWINGS
- DISADVANTAGES OF A PARTNERSHIP FIRM
- SHARE CAPITAL
- STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 1
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 2
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED, QUOTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES