 |
COST OF GOODS SOLD STATEMENT |
| << Opening Stock, Closing Stock |
| DEPRECIATION >> |

Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Lesson-16
COST
OF GOODS SOLD
STATEMENT
In manufacturing
concern, separate books are maintained to
keep the record of every
single work done in
manufacturing
process to ascertain cost incurred on
production of goods. This
record gives
information
about
total cost incurred on manufacturing
process and per unit
cost of goods manufactured.
When goods
are
produced, these are sold to
the customers of the business and
goods unsold are taken into
stock. At the
end of
the financial year, manufacturing concern
prepares a statement which gives the
brief summary of the
whole
process.
This
statement shows the value of
raw material consumed, amount
spent on labour and other
factory
expenses,
finished goods produced and
goods unsold (in stock).
Such statement is called `cost
of goods
sold
statement'. Manufacturing
concerns, while presenting financial
statements, also present
cost of goods
sold
statement.
Standard
format of cost of goods sold
statement is given below:
Raw
Material:
O/S
Raw Material
+
Purchases
+ Cost
Incurred to Purchase RM
- C/S
Raw Material
Cost
of Material Consumed
Conversion
Cost:
+
Direct Labour Cost
+
Factory Overheads
Total
Factory Cost
Work
in Process
+ O/S
of WIP
- C/S
of WIP
Cost
of Goods Manufactured
Finished
Goods
+ O/S
of Finished Goods
- C/S
of Finished Goods
Cost
of Good Sold
Cost
of material consumed is the
cost of material used for
consumption that has been
put in the
production
process. This head shows the
raw material left unused
from the previous year(opening
stock),
raw
material purchased in the current year,
expenses incurred in bringing the
purchased material into
the
business
premises and raw material
that is not used in the current
year(closing stock).
Over
Heads are
the other costs incurred in relation of
manufacturing of goods.
Examples
are factory utilities, supervisor
salaries, equipment repairs
etc.
Total
factory cost is the
cost of material consumed
plus labour and over
heads. In other words it is
the
total
cost incurred in the factory.
Cost
of goods manufactured is
total factory cost plus
opening stock of work in
process less closing
stock
of
work in process.
Cost
of goods sold is the
cost of goods manufactured
plus opening stock of
finished goods less
closing
stock
of finished goods.
Prime/Basic
Cost = Cost
of Direct Material Consumed +
Direct Labour cost
121

Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Conversion
cost
it is
the cost incurred to convert
raw material to finished
goods.
Conversion
cost =
Labour cost + factory
overhead
Example
�
Using the
following data calculate the
Cost of Goods Sold of XYZ
Co.
Stock
levels
O/S
Rs.
C/S
Rs.
Raw
material
100,000
85,000
Work
in process
90,000
95,000
Finished
goods
150,000
140,000
Purchase
of raw material during the
period Rs. 200,000
Paid
to labour Rs. 180,000 out of
which Rs. 150,000 used on
production.
Other
production costs Rs.
50,000
Solution
XYZ
Co.
Cost
of Goods Sols
Statement
For
the period ended-------
Raw
Material:
Opening
Stock Raw Material
100000
+
Purchases
200000
+ Cost
Incurred to Purchase RM
0
-
Closing Stock Raw
Material
(85000)
Cost
of Material Consumed
215000
Conversion
Cost
+
Labour Cost
150000
+Factory
overhead
50000
200000
Total
Factory Costs
415000
Work
in process
+ O/S
of WIP
90000
+ C/S
of WIP
(95000)
Cost
of Goods Manufactured
410000
Finished
Goods
+ O/S
of Finished Goods
150000
+ C/S
of Finished Goods
(140000)
Cost
of Goods Sold
420000
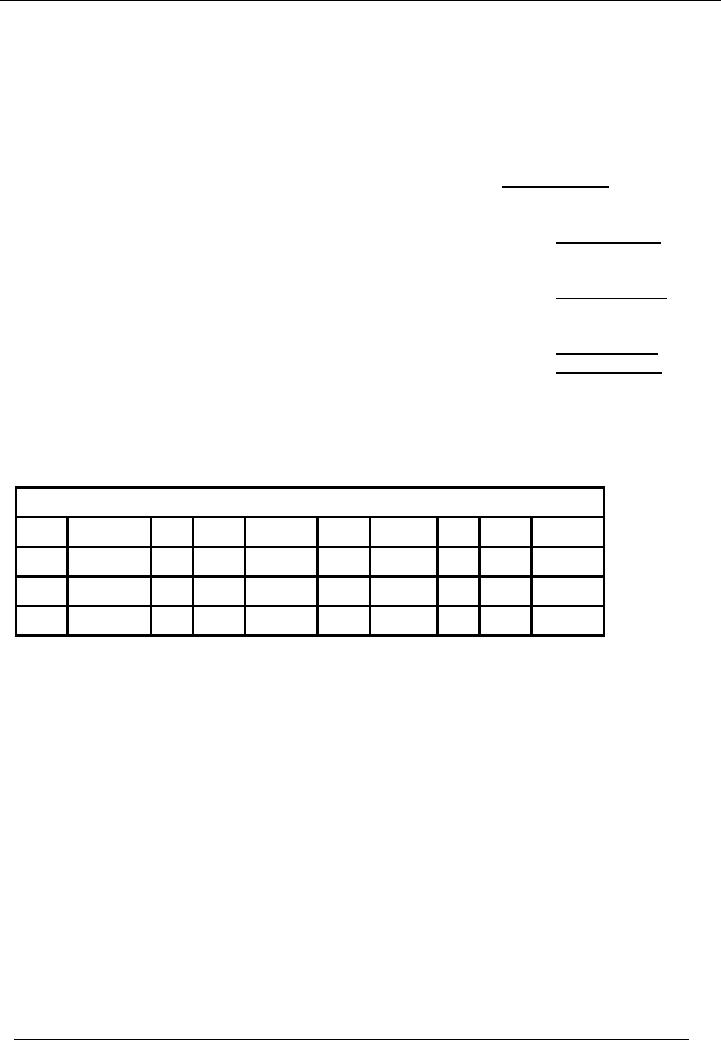
ILLUSTRATION
Following
information of Ahmad & Company is
given. Prepare a cost of goods
sold statement.
Stock
levels
O/S
Rs.
C/S
Rs.
Raw
material
150,000
115,000
Work
in process
50,000
55,000
Finished
goods
120,000
100,000
Purchase
of raw material during the
period Rs. 100,000
Transportation
charges of items purchased
Rs. 5,000
122
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Paid
to labour Rs.
100,000.
Other
production costs(FOH) Rs.
80,000
SOLUTION
Raw
Material:
Opening
Stock Raw Material
150,000
+
Purchases
100,000
+ Cost
Incurred to Purchase RM
5,000
-
Closing Stock Raw
Material
(115,000)
Cost
of Material Consumed
140,000
Conversion
Cost:
+
Labour
100,000
+
Factory Overheads
80,000
Total
Factory Cost
320,000
Work
in Process:
+ O/S
of WIP
50,000
- C/S
of WIP
(55,000)
Cost
of Goods Manufactured
315,000
Finished
Goods:
+ O/S
of Finished Goods
120,000
- C/S
of Finished Goods
(100,000)
Cost
of Good Sold
335,000
STOCK
CARD
Stock
card is used to keep the
record of what has come in
stock and what has gone
out of it. Standard
format
of stock card is given below:
Stock
Account Item 01
Date
Receipts
Qty
Rate
Amount
Date
Issues
Qty
Rate
Amount
Stock
card has two
parts.
� Receipt
side
� Issue
side
Both
sides have similar columns
that include:
� Nature
of item to be kept in stock
� Quantity
of items
� Rate
at which it was
purchased
� Total
value of items
Receipt
side is used to record data
of items coming in the stock
and issue side is used to
record information
of
goods issued for manufacturing
process.
VALUATION
OF STOCK
Any
manufacturing organization purchases different
material through out the
year. The prices of
purchases
may be
different due to inflationary
conditions of the economy. The question
is, what item should be issued
first
& what item should be issued later
for manufacturing. For this purpose, the
organization has to make a
123

Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
policy
for issue of stock. All the
issues for manufacturing and
valuation of stock are
recorded according to
the
policy of the organization. Mostly these
three methods are used
for the valuation of
stock:
� First in
first out (FIFO)
� Last
in first out (LIFO)
� Weighted
average
FIRST
IN FIRST OUT
(FIFO)
The
FIFO method is based on the assumption
that the first merchandise
purchased is the first
merchandised
issued.
The FIFO uses actual
purchase cost. Thus, if
merchandise has been
purchased at several
different
costs,
the inventory (stock) will
have several different cost
prices. The cost of goods
sold for a given
sales
transaction
may involve several
different cost
prices.
CHARACTERISTICS
�
This
is widely used method for determining
values of cost of goods sold
and closing stock.
�
In the
FIFO method, oldest available
purchase costs are
transferred to cost of goods
sold. That
means
the cost if goods sold has a
lower value and the
profitability of the organization
becomes
higher.
�
As the current
stock is valued at recent
most prices, the current assets of the
company have the
latest
assessed values.
LAST
IN FIRST OUT
(LIFO)
As the
name suggests, the LIFO method is
based on the assumption that the
recently purchased
merchandise
is issued first. The LIFO
uses actual purchase cost.
Thus, if merchandise has
been purchased at
several
different costs, the inventory
(stock) will have several
different cost prices. The
cost of goods sold
for
a given
sales transaction may
involve several different
cost prices.
CHARACTERISTICS
�
This is
alternatively used method for determining
values of cost of goods sold
and closing stock.
�
In the
LIFO method recent available
purchase costs are
transferred to cost of goods
sold. That
means
the cost of goods sold has a
higher value and the profitability of the
organization becomes
lower.
�
As the current
stock is valued at oldest
prices, the current assets of the company
have the oldest
assessed
values.
WEIGHTED
AVERAGE METHOD
When
weighted average method is in use, the
average cost of all units in
inventory, is computed after every
purchase.
This average cost is computed by
dividing the total cost of
goods available for sale by
the number
of units in
inventory. Under the average
cost assumption, all items
in inventory are assigned the
same per
unit
cost. Hence, it does not
matter which units are sold;
the cost of goods sold is
always based on current
average
unit cost.
CHARACTERISTICS
�
Under
the average cost assumption,
all items in inventory are
assigned same per unit
cost (the
average
cost). Hence it does not
matter which units are sold
first. The cost of goods
sold is always
on the current
average unit cost.
124
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
�
Since
all inventories are assigned
same cost, this method does
not make any effect on
the
profitability
and does not
increase/decrease any asset in the
financial statements.
� This
is the alternatively used method for determining
values of cost of goods sold
and closing stock.
Example
� Receipts:
01 Jan
20--,
10 units @
Rs. 150 per
unit
02 Jan
20--,
15 units @
Rs. 200 per
unit
10 Jan
20--,
20 units @
Rs. 210 per
unit
� Issues:
05 Jan
20--,
05
units
06 Jan
20--,
10
units
15 Jan
20--,
15
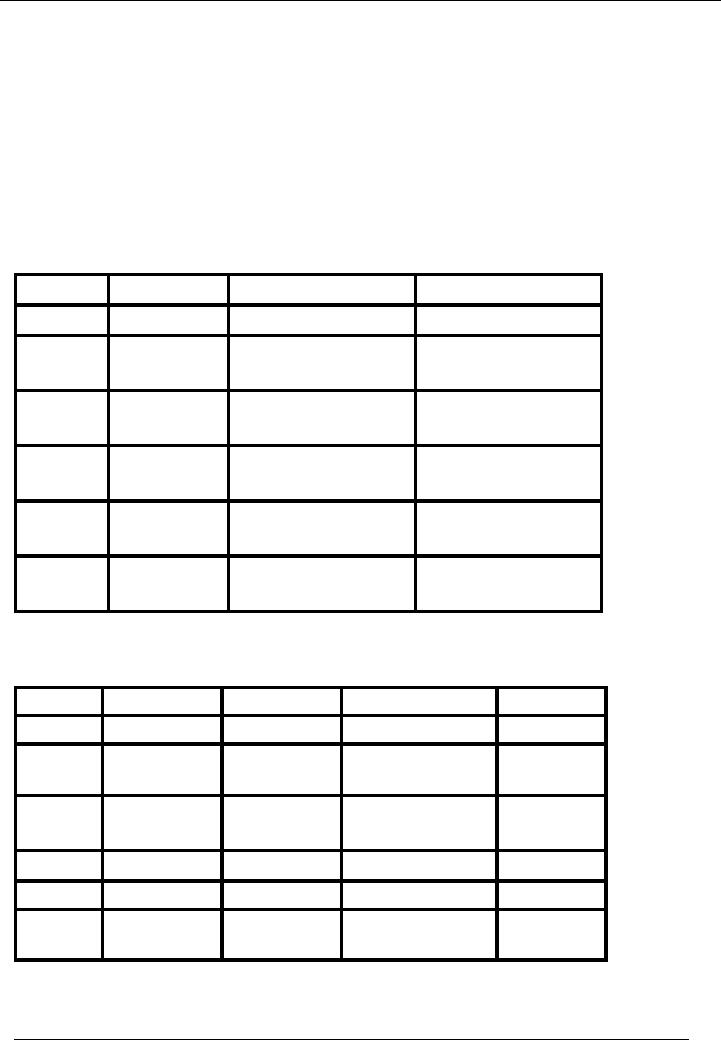
FIFO
Method of Stock
Valuation
Date
Receipts
Issues
Value
of Stock
01-01-20--
10 @
Rs. 150
10 x
150 = 1500 1500
02-01-20--
15 @
Rs. 200
10 x
150 = 1500
15 x
200 = 3000 4500
05-01-20--
5 @
150 = 750
750
5 x
150 = 750
15 x
200 = 3000 3750
06-01-20--
5 @
150 = 750
0 x
150 =
0
5 @
200 = 1000 1750
10 x
200 = 2000 2000
10-01-20--
20 @
Rs. 210
10 x
200 = 2000
20 x
210 = 4200 6200
15-01-20--
10 @
200 = 2000
0 x
200 =
0
5 @
210 = 1050 3050
15 x
210 = 3150 3150
Weighted
Average Method of Stock
Valuation
Date
Receipts
Issues
Value
of Stock
Average
Cost
01-01-20--
10x150
= 1500
1500
1500/10=150
02-01-20--
15x200
= 3000
1500 +
3000 = 4500
4500/25=180
05-01-20--
5x180
= 900
4500
900 = 3600
3600/20=180
06-01-20--
10x180
= 1800
3600
1800 = 1800
1800/10=180
10-01-20--
20x210
= 4200
1800 +
4200 = 6000
6000/30=200
15-01-20--
15x200
= 3000
6000
3000 = 3000
3000/15=200
Effects
of Valuation Method on Profit
FIFO
Method
125

Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
�
Cost
of Sales
= 750
+ 1750 + 3050 =
5,550
Gross
Profit
= 7500
5550
=
1,950
Weighted
Average Method
� Cost
of Sales
= 900
+ 1800 + 3000 =
5,700
Gross
Profit
= 7500
5700
=
1,300
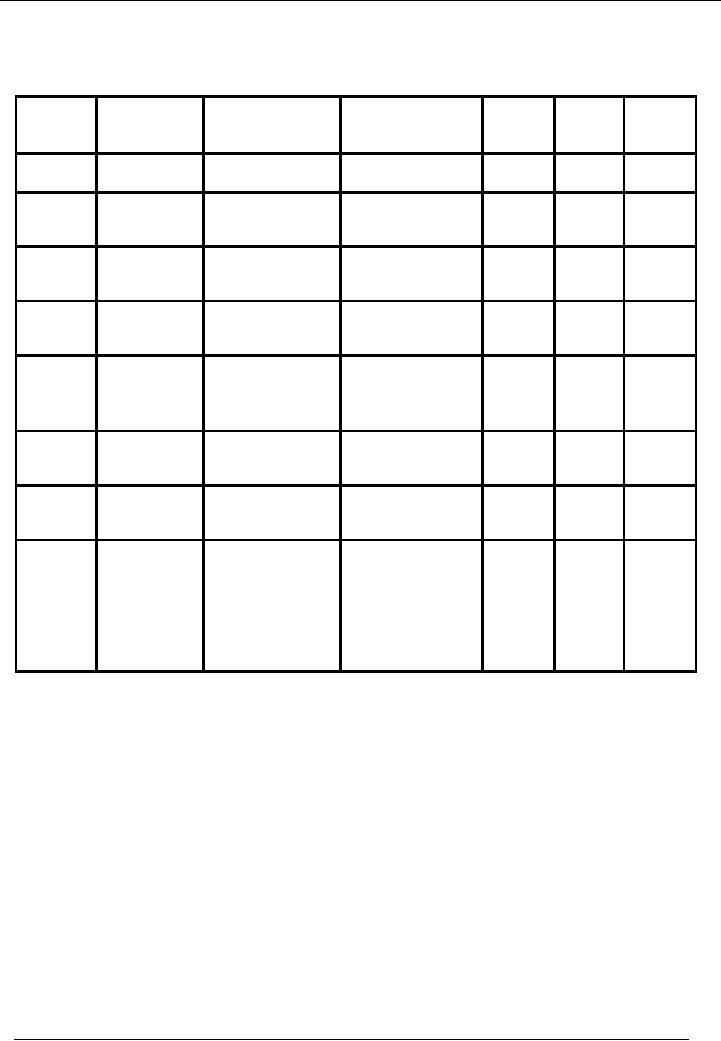
ILLUSTRATION
Hamid
& company is a manufacturing concern.
Following is the receipts & issues
record for the month
of
May,
2002
Date
Receipts
Issues
May
7
200
units @ Rs. 50/unit
May
9
60
units
May
13
150
units @ Rs. 75/unit
May
18
100
units @ Rs. 60/unit
May
22
150
units
May
24
100
units
May
27
100
units @ Rs. 50/unit
May
30
200
units
Calculate
the value of closing stock
by
� FIFO
Method
� Average
Method
126
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
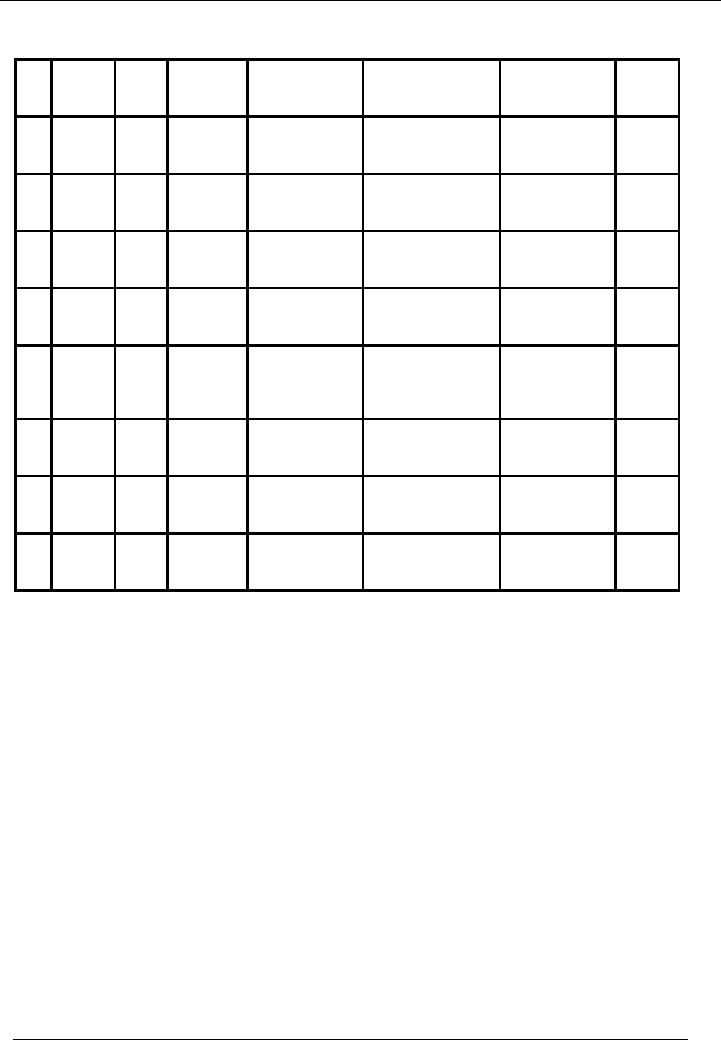
SOLUTION
Valuation
of stock by FIFO method
Date
Receipts
Issues
Value
of Stock
Total
Remaining Net
Amount
No. of
Balance
units
May
7
200
units @ Rs.
200 x
50 = 10,000
10,000
200
10,000
50/unit
May
9
60
units
@
Rs.
60 x 50 =
3,000
(3,000)
140
7,000
50/unit
May
13
150
units @ Rs.
75 x
150 = 11,250
11,250
290
18,250
75/unit
May
18
100
units @ Rs.
60 x
100 = 6,000
6,000
390
24,250
60/unit
May
22
140
units @ Rs.
50 x
140 = 7,000
(7,750)
240
16,500
50/unit
10 units
@ Rs.
10 x 75 =
750
75/unit
May
24
100
units @ Rs.
75 x
100 =7,500
(7,500)
140
9,000
75/unit
May
27
100
units @ Rs.
50 x
100 = 5,000
5,000
240
14,000
50/unit
May
30
40 units
@ Rs.
75 x 40 =
3,000
(12,000)
40
2,000
75/unit
100
units @ Rs.
60 x
100 = 6,000
60/unit
60 units
@ Rs.
50 x 60 =
3,000
50/unit
127
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Valuation
of stock by weighted average
method:
Date
Receipts Issues
Value
of
Total
Total
Units
Average
Net
Stock
Amount(Rs.)
Cost(Rs.)/unit
Balance(
Rs.)
May
200 units
200 x
50
10,000
200
50
10,000
7 @
Rs.
=
50/unit
10,000
May
60 units 60 x
50
(3,000)
140
7,000
9
=
3,000
May
150 units
150 x
75
7,000+11250
140+150
18250/290
18,250
13
@
Rs.
=
=
=
=
75/unit
11,250
18250
290
62.9
May
100 units
100 x
60
18250+6000
290+100
24250/390
24,250
18
@
Rs.
=
=
=
=
60/unit
6,000
24250
390
62.2
May
150
150 x
62.2
(9,330)
390-150
14,920
22
units
=
=
9330
240
May
100
100 x
62.2
(6,220)
240-100
8,700
24
units
=
=
6220
140
May
100 units
100 x
50
8,700+5,000
140+100
13700/240
13,700
27
@
Rs.
=
=
=
=
50/unit
5,000
13,700
240
57.1
May
200
200 x
57.1
(11,420)
240-200
2,280
30
units
=
=
11,420
40
LIFO
METHOD WILL BE DISCUSSED AT SOME LATER
STAGE
128
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Financial Accounting
- Basic Concepts of Business: capital, profit, budget
- Cash Accounting and Accrual Accounting
- Business entity, Single and double entry book-keeping, Debit and Credit
- Rules of Debit and Credit for Assets, Liabilities, Income and Expenses
- flow of transactions, books of accounts, General Ledger balance
- Cash book and bank book, Accounting Period, Trial Balance and its limitations
- Profit & Loss account from trial balance, Receipt & Payment, Income & Expenditure and Profit & Loss account
- Assets and Liabilities, Balance Sheet from trial balance
- Sample Transactions of a Company
- Sample Accounts of a Company
- THE ACCOUNTING EQUATION
- types of vouchers, Carrying forward the balance of an account
- ILLUSTRATIONS: Ccarrying Forward of Balances
- Opening Stock, Closing Stock
- COST OF GOODS SOLD STATEMENT
- DEPRECIATION
- GROUPINGS OF FIXED ASSETS
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 1
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 2
- REVALUATION OF FIXED ASSETS
- Banking transactions, Bank reconciliation statements
- RECAP
- Accounting Examples with Solutions
- RECORDING OF PROVISION FOR BAD DEBTS
- SUBSIDIARY BOOKS
- A PERSON IS BOTH DEBTOR AND CREDITOR
- RECTIFICATION OF ERROR
- STANDARD FORMAT OF PROFIT & LOSS ACCOUNT
- STANDARD FORMAT OF BALANCE SHEET
- DIFFERENT BUSINESS ENTITIES: Commercial, Non-commercial organizations
- SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
- Financial Statements Of Manufacturing Concern
- Financial Statements of Partnership firms
- INTEREST ON CAPITAL AND DRAWINGS
- DISADVANTAGES OF A PARTNERSHIP FIRM
- SHARE CAPITAL
- STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 1
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 2
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED, QUOTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES