 |
ILLUSTRATIONS: Ccarrying Forward of Balances |
| << types of vouchers, Carrying forward the balance of an account |
| Opening Stock, Closing Stock >> |
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Lesson-14
We
have demonstrated the carrying
forward of balances in lecture-13.
Another solved example is
given
below:
ILLUSTRATION
Following
is the trial balance of Rahil & co.
for the month ended January
31, 2002.
Rahil &
co..
Trial
Balance As On ( January 31,
2002)
Title
of Account
Code
Dr.
Rs.
Cr.
Rs.
Cash
Account
01
30,000
Accrued
expense Account
02
10,000
Bank
Account
03
50,000
Loan
Account
04
100,000
Furniture
Account
05
20,000
Office
Equipment
06
10,000
Debtors
account
07
12,000
Creditors
account
08
10,000
Sales
account
09
20,000
Purchase
account
10
18,000
Total
140,000
140,000
During
the month, following entries
took place:
No.
Date
Particulars
01
Feb
07
They
purchased stationery worth of Rs.
3,000
02
Feb
10
They paid
their first installment of loan Rs.
12,000
03
Feb
12
They
received a cheque from a
customer of Rs. 5,000
04
Feb
13
They paid a
cheque of Rs. 8,000 to a
creditor
05
Feb
15
Purchased
goods of Rs 6,000 & paid through
cheque
06
Feb
17
Accrued
expenses of Rs. 5,000 are
paid.
07
Feb
20
They
purchased furniture of Rs.
2,000
08
Feb
21
Sold
goods for cash
Rs.5,000
09
Feb
22
Purchased
goods on credit Rs.
5,000
10
Feb
23
Office
equipment of Rs. 5,000 is
Purchased
101
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
11
Feb
25
Staff
salaries are paid by cheque
Rs. 15,000
12
Feb
28
Utility
expenses of Rs. 3,000 are
accrued.
Leger
accounts of Rahil & co. during the
month will show following
picture:
Cash
Account
Account
code # 1
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
1-2-02
Balance
c/f
01
30,000
7-2-02
Stationery
10
3,000
21-2-02
Sold
goods
09
5,000
purchased
10-2-02
Loan
paid
04
12,000
17-2-02
Accrued
expenses
02
paid
5,000
Furniture
05
2,000
purchased
23-2-02
Office
equipment
06
5,000
purchased
Balance
c/d
8,000
Total
35,000
Total
35,000
Accrued
Expenses Account
Account
code # 2
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
17-2-02
Accrued
01
5,000
1-1-02
Balance
c/f
10,000
expenses
paid
Expenses
accrued
3,000
Balance
c/d
8,000
Total
13,000
Total
13,000
Bank
Account Account code #
3
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
Balance
c/f
50,000
13-2-02
Paid
to creditors
08
8,000
12-2-02
Cheque
received
15-2-02
Goods
purchased
10
6,000
07
5,000
25-2-02
Salaries
paid
11
15,000
Balance
c/d
26,000
Total
55,000
Total
55,000
Loan
Account Account code #
4
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
102
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
10-2-02
Installment
paid
01
12,000
Balance
c/f
100,000
Balance
c/d
88,000
Total
100,000
Total
100,000
Furniture
Account
Account
code # 5
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
10-2-02
Balance
c/f
20,000
23-2-02
20-2-02
Furniture
01
2,000
purchased
Balance
c/d
22,000
Total
22,000
Total
22,000
Office
Equipment Account
Account
code # 6
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
Balance
c/f
10,000
23-2-02
Office
01
5,000
Equipment
purchased
Balance
c/d
15,000
Total
15,000
Total
15,000
Debtors
Account
Account
code # 7
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
Balance
c/f
12,000
12-2-02
Cheque received
03
5,000
Balance
c/d
7,000
Total
12,000
Total
12,000
Creditors
Account
Account
code # 8
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
103
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
13-2-02
Paid
to creditors
03
8,000
Balance
c/f
10,000
22-2-02
Goods
purchased
10
5,000
Balance
c/d
7,000
Total
15,000
Total
15,000
Sales
Account Account code #
9
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
Balance
c/f
20,000
21-2-02
Goods
sold
01
5,000
Balance
c/d
25,000
Total
25,000
Total
25,000
Purchases
Account
Account
code # 10
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
Balance
c/f
18,000
15-2-02
Goods
03
6,000
purchased
07
5,000
22-2-02
Goods
purchased
Balance
c/d
29,000
Total
29,000
Total
29,000
Salaries
Account
Account
code # 11
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
25-2-02
Salaries
paid
03
15,000
Balance
c/d
15,000
Total
15,000
Total
15,000
Stationery
Account
Account
code # 12
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
104
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
25-2-02
Stationery
01
3,000
purchased
Balance
c/d
3,000
Total
3,000
Total
3,000
Utility
Expenses Account
Account
code # 13
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
Accrued
utility
02
3,000
28-2-02
expenses
Balance
c/d
3,000
Total
3,000
Total
3,000
The
trial balance at the end of the
month is as follows:
Rahil &
co..
Trial
Balance As On ( January 31,
2002)
Title
of Account
Code
Dr.
Rs.
Cr.
Rs.
Cash
Account
01
8,000
Accrued
expense Account
02
8,000
Bank
Account
03
26,000
Loan
Account
04
88,000
Furniture
Account
05
22,000
Office
Equipment
06
15,000
Debtors
account
07
7,000
Creditors
account
08
7,000
Sales
account
09
25,000
Purchase
account
10
29,000
Salaries
Account
11
15,000
Stationery
Account
12
3,000
Utility
Expenses Account
13
3,000
Total
128,000
128,000
Difference
between expenses &
Purchases
� If
business purchases items for
its own use (items
that are not meant to be
resold) are charged
to
expense
account.
� If
business purchases items for
resale purposes are charged
to purchases account.
STOCK
105

Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
�
Stock
is the quantity of unutilized or unsold
goods lying with the
organization.
�
Stock
is termed as "the value of
goods available to the business
that are ready for
sale". For
accounting
purposes, stock is of two
types
Type
of Stock
�
In
trading concern, Stock
consists of goods that are
purchased for the purpose of
resale, but not
sold
in that accounting period.
Trading concern is that organization,
which purchases items
for
resale
purposes.
�
In manufacturing
concern(an organization that converts
raw material into finished
product by
putting
it in a process), stock consists
of:
o Raw
material
o Work
in process
o Finished
goods
Raw
material
Raw
material is the basic part of an item,
which is processed to make a
complete item.
Work
in process
In manufacturing
concern, raw material is put
in a process to convert it into
finished goods. At the end
of
the
year, some part of raw
material remains under process.
i-e. it is neither in shape of raw
material nor in
shape
of finished goods. Such
items are taken in stock as
work in process.
Finished
goods
Finished
goods contain items that are
ready for sale, but could
not be sold in that
accounting period.
Stock
Account
�
Stock
Account is Debited
with
the Value
of the Goods
Purchased
�
Stock
account is Credited
with
the Purchase
Price of the Goods Sold /
Issued for Production.
�
Stock
Account shows the cost /
purchase value of unsold
goods.
106
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
In
manufacturing concern, entries
for stock are:
Purchase
of stock
Debit:
Stock
Account
Credit:
Cash/Supplier
/Creditors Account
When
the stock is purchased, stock
account gets the benefit, so it is
debited & cash or supplier
account
provides the
benefit, so it is credited.
Payment
to creditors
Debit:
`
Supplier /
Creditors account
Credit:
Cash
account
Consumption
of goods
Debit:
Cost
of goods sold
Credit:
Stock
Account
Cost
of goods sold
Cost
of goods sold is different in
both form of organization
� In
trading concern, cost of
goods sold is the value of
goods unsold(goods stands
for the items
purchased
for resale purpose)
� In
manufacturing concern, cost of goods
sold is the value of raw
material consumed plus any
other
manufacturing
cost. e.g., salaries of
labour cost of machinery
etc.
Stock
and cost of goods sold in
manufacturing concern
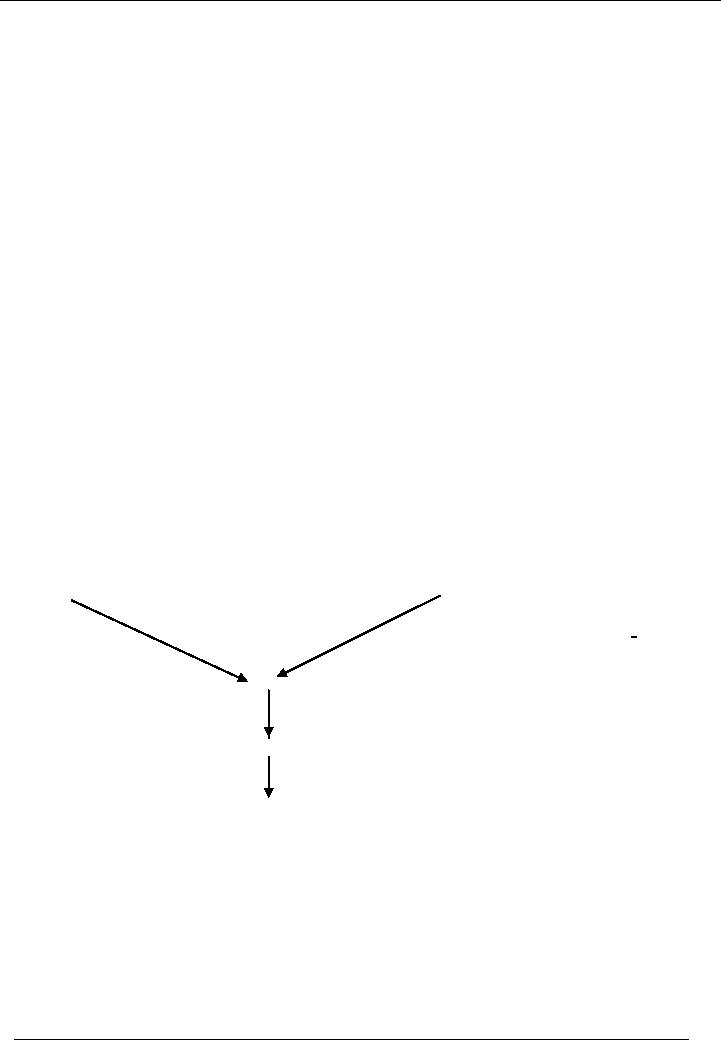
Raw
Material Stock
Other
Costs Accounts
Work
in Process Account
Finished
Goods Account
Cost
of Goods Sold
Account
In manufacturing
concern, Raw material stock
is put into process. For
accounting purposes, all
value of
stock
and other manufacturing costs
are charged to work in
process account. When the
process is completed
and
the goods are prepared, all
the value of work in process is
charged to finished goods
account. The
business
sells finished goods for the
whole accounting year. At the
end of the year, goods that
are unsold are
deducted
from cost of goods sold
account.
107
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Financial Accounting
- Basic Concepts of Business: capital, profit, budget
- Cash Accounting and Accrual Accounting
- Business entity, Single and double entry book-keeping, Debit and Credit
- Rules of Debit and Credit for Assets, Liabilities, Income and Expenses
- flow of transactions, books of accounts, General Ledger balance
- Cash book and bank book, Accounting Period, Trial Balance and its limitations
- Profit & Loss account from trial balance, Receipt & Payment, Income & Expenditure and Profit & Loss account
- Assets and Liabilities, Balance Sheet from trial balance
- Sample Transactions of a Company
- Sample Accounts of a Company
- THE ACCOUNTING EQUATION
- types of vouchers, Carrying forward the balance of an account
- ILLUSTRATIONS: Ccarrying Forward of Balances
- Opening Stock, Closing Stock
- COST OF GOODS SOLD STATEMENT
- DEPRECIATION
- GROUPINGS OF FIXED ASSETS
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 1
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 2
- REVALUATION OF FIXED ASSETS
- Banking transactions, Bank reconciliation statements
- RECAP
- Accounting Examples with Solutions
- RECORDING OF PROVISION FOR BAD DEBTS
- SUBSIDIARY BOOKS
- A PERSON IS BOTH DEBTOR AND CREDITOR
- RECTIFICATION OF ERROR
- STANDARD FORMAT OF PROFIT & LOSS ACCOUNT
- STANDARD FORMAT OF BALANCE SHEET
- DIFFERENT BUSINESS ENTITIES: Commercial, Non-commercial organizations
- SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
- Financial Statements Of Manufacturing Concern
- Financial Statements of Partnership firms
- INTEREST ON CAPITAL AND DRAWINGS
- DISADVANTAGES OF A PARTNERSHIP FIRM
- SHARE CAPITAL
- STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 1
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 2
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED, QUOTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES