 |
types of vouchers, Carrying forward the balance of an account |
| << THE ACCOUNTING EQUATION |
| ILLUSTRATIONS: Ccarrying Forward of Balances >> |
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Lesson-13
LEARNING
OBJECTIVE
After
studying this lecture, you should be able
to:
� Understand
different types of
vouchers.
� How
to book entry in voucher.
� Carrying
forward the balance of an
account.
VOUCHER
In
book keeping, voucher is the first
document to record an entry. Normally three
types of vouchers are
used.
i-e.:
� Receipt
voucher
� Payment
voucher
� Journal
voucher
RECEIPT
VOUCHER
Receipt
voucher is used to record cash or bank
receipt. Receipt vouchers
are of two types.
i-e.
� Cash
receipt voucher
� Bank
receipt voucher
Cash
receipt voucher denotes receipt of
cash; bank receipt voucher indicates
receipt of cheque or
demand
draft.
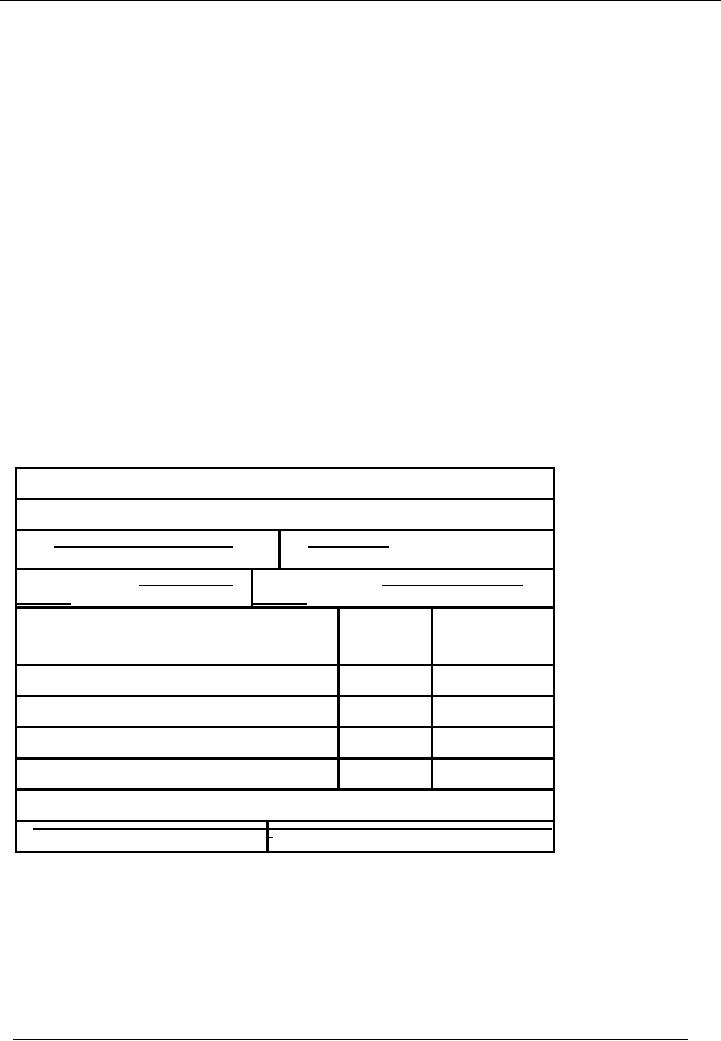
Standard format of cash
receipt voucher is given below:
Name of the
Organization
Bank
Receipt / Cash Receipt OR
Receipt
Voucher
Date:
No:
Description
/ Title:
Cash /
Bank code:
Description
/
Code
Credit
Title
of Account
#
Amount
Total:
Narration:
Prepared
By:
Checked
By:
94
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
PAYMENT
VOUCHER
Payment
voucher is used to record a payment of
cash or cheque. Payment
vouchers are of two types.
i.e.
� Cash
Payment voucher
� Bank
Payment voucher
Cash
Payment voucher denotes Payment of
cash, bank Payment voucher indicates
payment by cheque or
demand
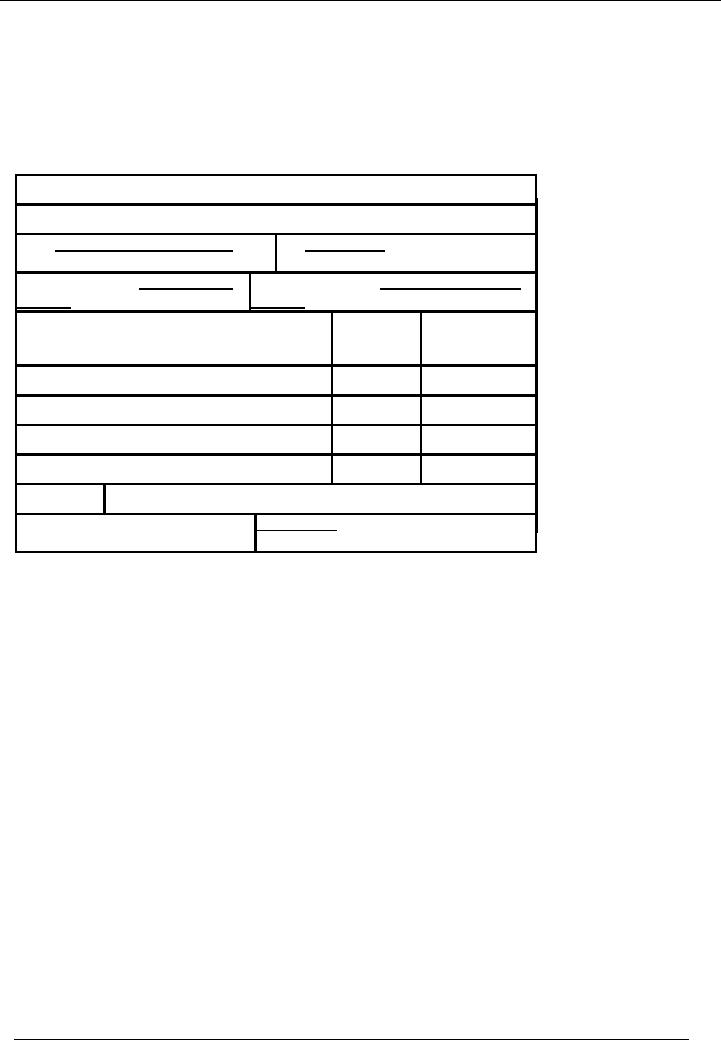
draft. Standard format of
cash Payment voucher is given
below:
Name of the
Organization
Bank
Payment / Cash Payment OR
Payment
Voucher
No:
Date:
Description
/ Title:
Cash /
Bank code:
Description
/
Code
Credit
Title
of Account
#
Amount
Total:
Naration
Prepared
By:
Checked
By:
95
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
JOURNAL
VOUCHER
Journal
voucher is used to record transactions
that do not affect cash or bank.
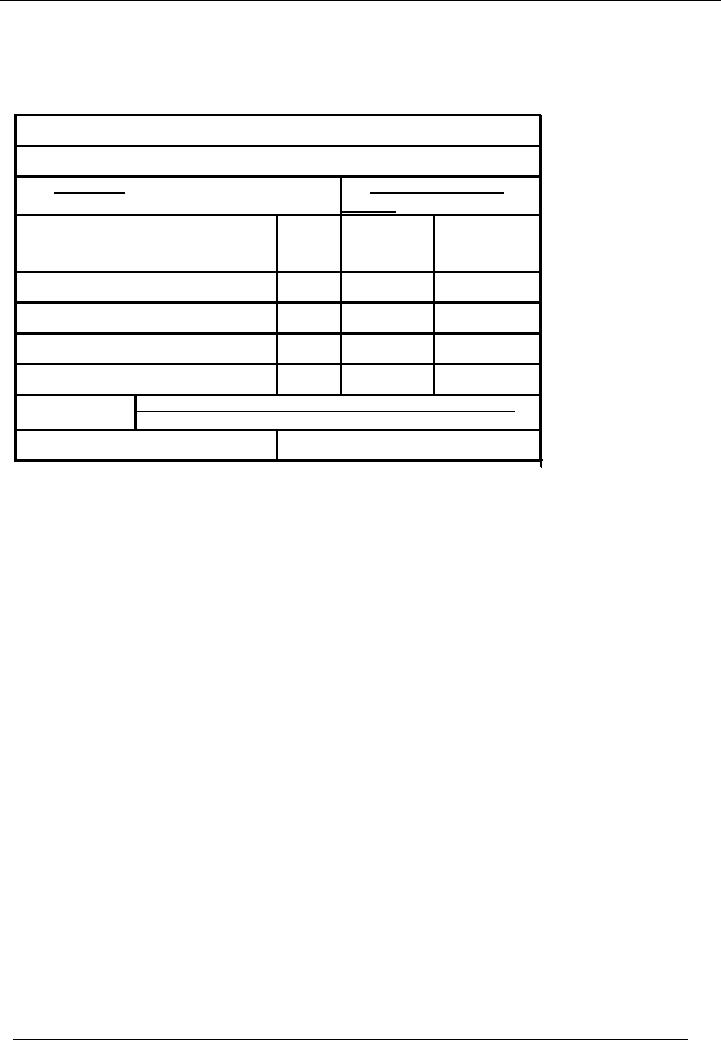
Standard format of
journal
voucher is given
hereunder:
Name Of
Organization
Journal
Voucher
Date:
No:
Description
Code
Debit
Credit
Amount
#
Amount
Total:
Narration:
Prepared
By:
Checked
by:
HOW TO
CARRY FORWARD A
BALANCE
It is
already mentioned that in `T'
account, at the end of accounting
period, if one side is
greater than the
other
side, balancing figure will
be written on the lesser side as
balance. For instance, if amount on
debit side
is
greater than the amount on credit side,
the balancing figure is written on the
credit side as balance & it is
known
as Debit
Balance. On the
other hand, if amount on the credit side
is greater than that of amount
on
the
debit side, the balance is
shown on the debit side. It is
called the Credit
Balance.
At the
start of next accounting
period, these balances are
carried forward. Debit
balance is written on the
credit
side, but it is the excess of
debit side over the credit
side, when it is carried
forward, it is written on the
debit
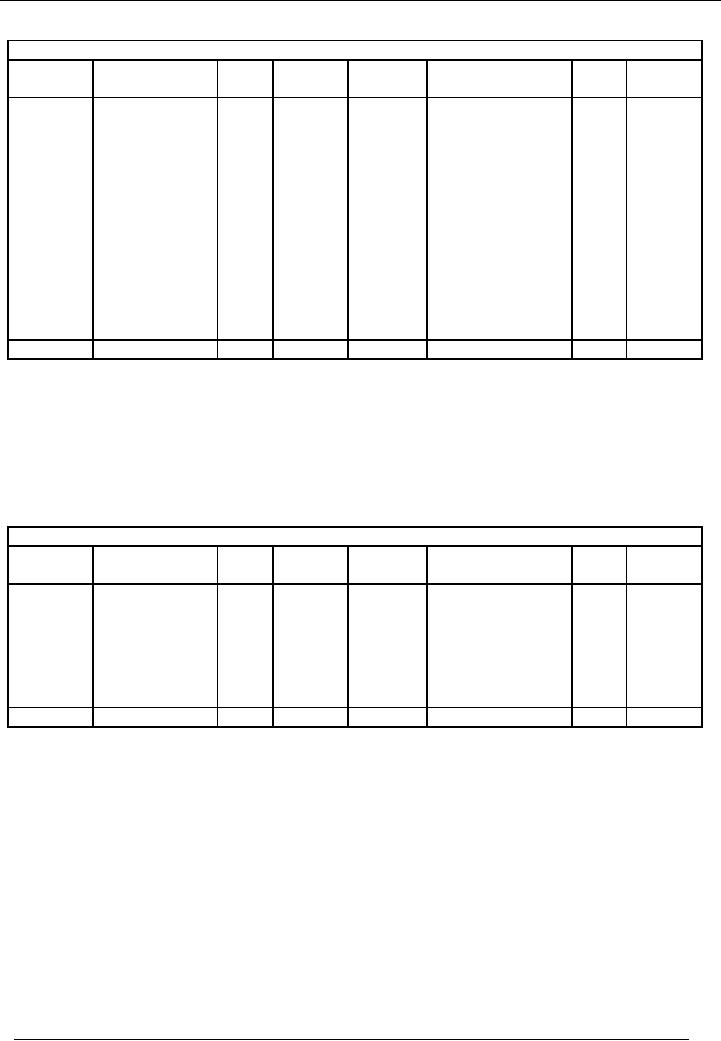
side. For example, ledger
account of cash is given below:
96
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Cash
Account
Account
code # 1
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
1-3-02
Commenced
02
150,000
5-3-02
Office
furniture
03
2,000
business
purchased
13-3-02
Goods
sold
07
12,000
7-3-02
Goods
purchased
04
9,000
250
21-3-02
Received
from
10-3-02
Carriage
paid
05
7,000
debtors
08
25,000
21-3-02
Paid
to creditors
06
2,500
23-3-02
Paid
salaries
09
3,000
25-3-02
Paid
rent
10
29-3-02
Paid
for stationery
11
2,000
BALANCE
161,250
Total
187,000
Total
187,000
This
cash account is showing the
balance of Rs. 161,250 on the credit
side. This balance is excess
of debit
side
over the credit side and, therefore, is
called the debit
balance. When
it is carried
forward it is
written
on the
debit side because debit
side of the cash account is
greater & Rs. 161,250 is the
balancing amount of
the
debit side of cash account.
So, it is an asset & it will be
used for further expenses in
the forth coming
period.
This
is another example of accrued
expenses:
Accrued
Expenses Account
Account
code # 13
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
31-3-02
Accrued
utility
12
5,000
bills
BALANCE
5,000
Total
5,000
Total
5,000
In this
account, balance is written on the
debit side & it is called the credit
balance. As this balance
represents
excess of credit side over
debit side, when it is carried
forward it is
again written on the credit
side.
It can
also be explained like
this:
� Debit
balance when carried forward, is written
on the debit side
� Credit
balance when carried forward, is written
on the credit
side
This
is further explained with the help of the
following solved
illustration:
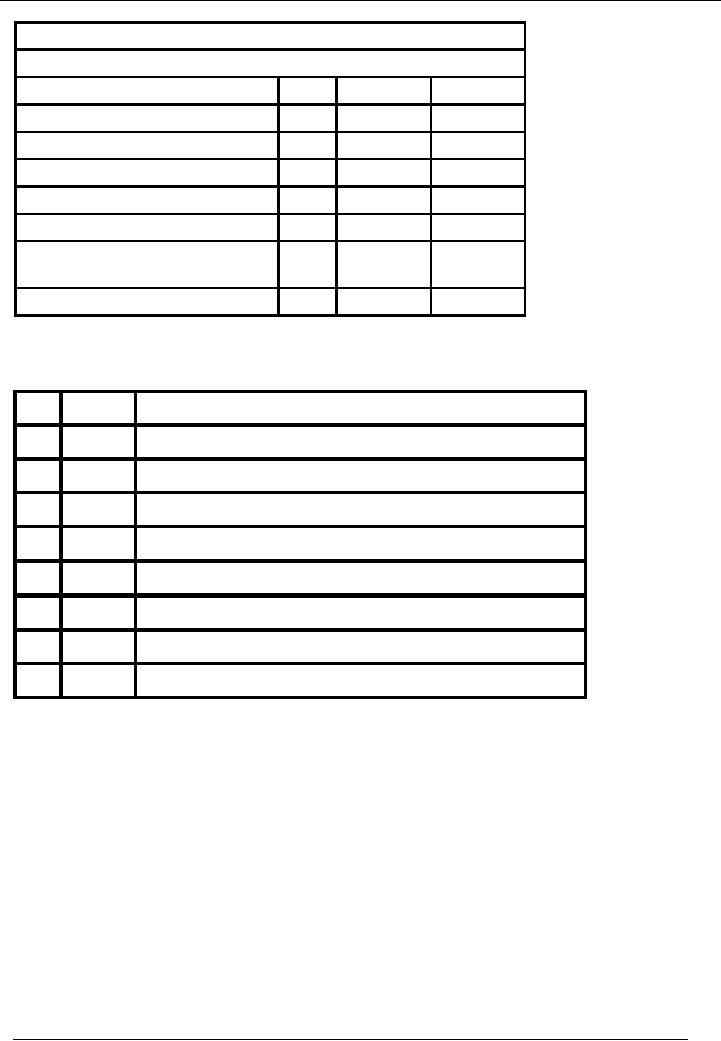
ILLUSTRATION
Following
is the trial balance of Saeed &
sons for the month ended
January 31, 2002
97
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Saeed
& Sons.
Trial
Balance As On ( January 31,
2002)
Title
of Account
Code
Dr.
Rs.
Cr.
Rs.
Cash
Account
01
55,000
Accrued
expense Account
02
10,000
Bank
Account
03
25,000
Loan
Account
04
100,000
Furniture
Account
05
20,000
Office
Equipment
06
10,000
Total
110,000
110,000
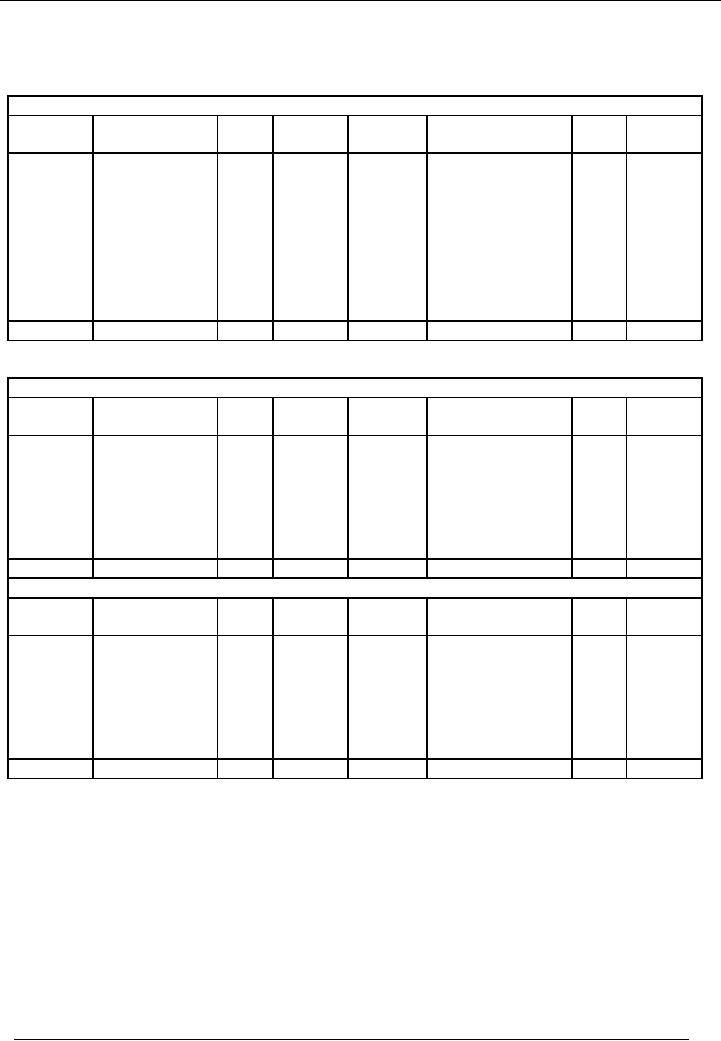
In the
month of February, following
transactions took
place:
No.
Date
Particulars
01
Feb
07
They
purchased stationery worth of Rs.
5,000
02
Feb
10
They paid
their first installment of loan Rs.
10,000
03
Feb
12
They
received a cheque from a
customer of Rs. 5,000
04
Feb
17
Accrued
expenses of Rs. 5,000 are
paid.
05
Feb
20
They
purchased furniture of Rs.
1,000
06
Feb
23
Office
equipment of Rs. 2,000 is
sold
07
Feb
25
Staff
salaries are paid by cheque
Rs. 10,000
08
Feb
28
Sold
goods for cash
Rs.2,000
98
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
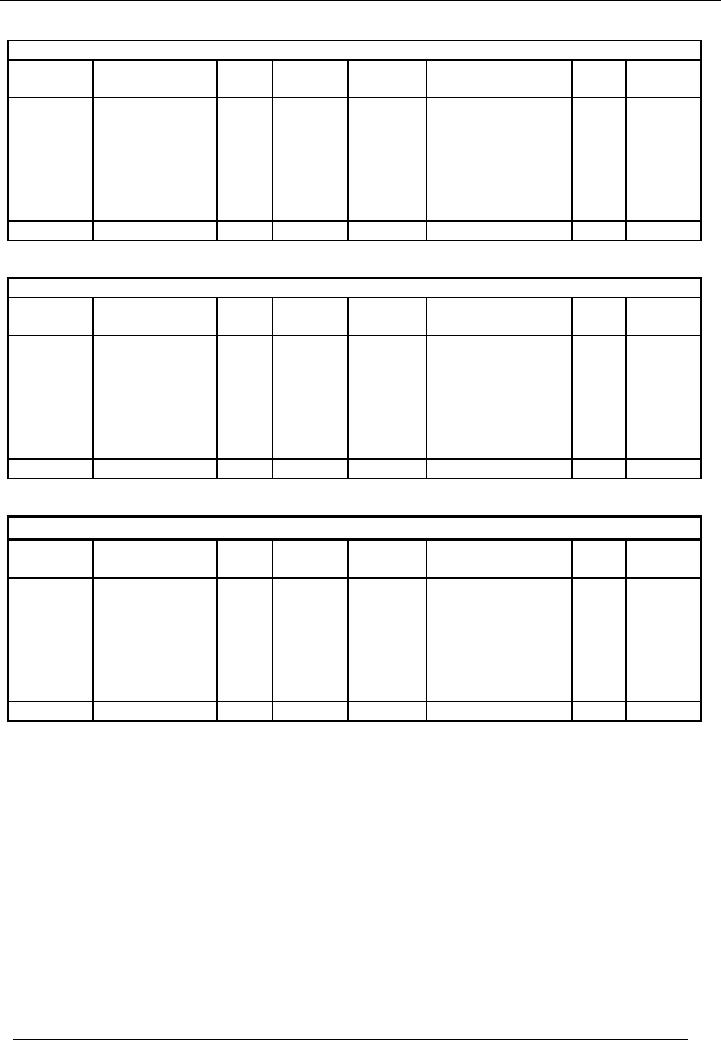
SOLUTION
The
ledger accounts of Saeed &
Sons will bear the following
changes:
Cash
Account
Account
code # 1
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
1-2-02
Balance
c/f
55,000
7-2-02
Stationery
10
5,000
23-2-02
Sold
office
06
2,000
purchased
equipment
10-2-02
Loan
paid
04
10,000
28-2-02
Sold
goods
01
2,000
17-2-02
Accrued
expenses
02
paid
5,000
Furniture
05
purchased
1,000
Balance
c/d
38,000
Total
59,000
Total
59,000
Accrued
Expenses
Account
code # 2
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
17-2-02
Accrued
01
5,000
1-1-02
Balance
c/f
10,000
expenses
paid
Balance
c/d
5,000
Total
10,000
Total
10,000
Bank
Account
Account
code # 3
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
17-2-02
Balance
c/f
01
25,000
25-2-02
Salaries
paid
10,000
12-2-02
Cheque
received
07
5,000
Balance
c/d
20,000
Total
30,000
Total
30,000
99
Financial
Accounting (Mgt-101)
VU
Loan
Account
Account
code # 4
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
10-2-02
Installment
paid
01
10,000
Balance
c/f
100,000
Balance
c/d
90,000
Total
100,000
Total
100,000
Furniture
Account
Account
code # 5
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
10-2-02
Balance
c/f
20,000
23-2-02
20-2-02
Furniture
01
1,000
purchased
Balance
c/d
21,000
Total
21,000
Total
21,000
Office
Equipment Account
Account
code # 6
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
Date
Particulars
Code
Amount
#
Rs.
(Dr.)
#
Rs.
(Cr.)
10-2-02
Balance
c/f
10,000
Office
Equipment
01
2,000
sold
Balance
c/d
8,000
Total
10,000
Total
10,000
Balance
c/f is balance carried forward &
balance c/d is balance Carried
down.
100
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Financial Accounting
- Basic Concepts of Business: capital, profit, budget
- Cash Accounting and Accrual Accounting
- Business entity, Single and double entry book-keeping, Debit and Credit
- Rules of Debit and Credit for Assets, Liabilities, Income and Expenses
- flow of transactions, books of accounts, General Ledger balance
- Cash book and bank book, Accounting Period, Trial Balance and its limitations
- Profit & Loss account from trial balance, Receipt & Payment, Income & Expenditure and Profit & Loss account
- Assets and Liabilities, Balance Sheet from trial balance
- Sample Transactions of a Company
- Sample Accounts of a Company
- THE ACCOUNTING EQUATION
- types of vouchers, Carrying forward the balance of an account
- ILLUSTRATIONS: Ccarrying Forward of Balances
- Opening Stock, Closing Stock
- COST OF GOODS SOLD STATEMENT
- DEPRECIATION
- GROUPINGS OF FIXED ASSETS
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 1
- CAPITAL WORK IN PROGRESS 2
- REVALUATION OF FIXED ASSETS
- Banking transactions, Bank reconciliation statements
- RECAP
- Accounting Examples with Solutions
- RECORDING OF PROVISION FOR BAD DEBTS
- SUBSIDIARY BOOKS
- A PERSON IS BOTH DEBTOR AND CREDITOR
- RECTIFICATION OF ERROR
- STANDARD FORMAT OF PROFIT & LOSS ACCOUNT
- STANDARD FORMAT OF BALANCE SHEET
- DIFFERENT BUSINESS ENTITIES: Commercial, Non-commercial organizations
- SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
- Financial Statements Of Manufacturing Concern
- Financial Statements of Partnership firms
- INTEREST ON CAPITAL AND DRAWINGS
- DISADVANTAGES OF A PARTNERSHIP FIRM
- SHARE CAPITAL
- STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- Financial Statements of Limited Companies
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 1
- CASH FLOW STATEMENT 2
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED, QUOTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES
- FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF LISTED COMPANIES