 |
EVENTS AFTER THE BALANCE SHEET DATE |
| << ELEMENTS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS |
| PROVISIONS, CONTINGENT LIABILITIES AND CONTINGENT ASSETS >> |

Advance
Financial Accounting
(FIN-611)
VU
LESSON
27
IAS 10
EVENTS AFTER THE BALANCE
SHEET DATE
Before
starting discussion on the IAS 10
that is about the events
that occur after
the
balance
sheet date, let us
differentiate between
the:
�
Draft
Financial Statements and
�
Published
Financial Statements
Draft
financial statements:
Draft
financial statements are one
that are prepared by the
accounts department,
audited
by the external auditors and put in front
of the board of directors for
approval.
Published
financial statements:
Published
financial statements are one
that has been approved by
the board of
directors
and has also been published
for issuance to the shareholders of
the company.
Here
we must also discuss different
dates that are pertinent to
the IAS 10
for
better
understanding.
�
Balance
Sheet Date
�
Date
of the Board of Director's
Meeting (BOD)
�
Date
of the Annual General Meeting
(AGM)
Balance
sheet date:
It is
the closing date on which
the balance sheet is
prepared. This is the
closing date of
the
accounting year.
Date
of BOD meeting:
It is
the date in which the
directors approve the
financial statements of the
company.
This
date is obviously after the
balance sheet date but
before the date of
annual
general
meeting (AGM). The BOD
meeting should be held at least 21
days before the
date
of the annual general
meeting. Because members of
the company should
receive
21
days notice of the AGM along
with the published financial
statements.
Date
of AGM:
It is
the date that should not be
after the expiry of four
months (in Pakistani
scenario
according
to the requirements of the
securities and exchange commission of
Pakistan-
SECP) and
six months (in international
scenario according to the
provisions of IAS-1)
133
Advance
Financial Accounting
(FIN-611)
VU
Note:
The
BOD holds meeting after
the balance sheet date but
before the annual
general
meeting.
Events
after the balance sheet
date
These
are those events, favorable
and unfavorable, that occur
between the balance
sheet
date and the date when the
financial statements are
authorized for issue. Two
types
of events can be
identified:
(a)
Those
events that provide evidence
of conditions that existed at
the
balance
sheet date (adjusting events
after the balance sheet
date); and
(b)
Those
events that are indicative
of conditions that arose
after the balance
sheet
date (non-adjusting events
after the balance sheet
date).
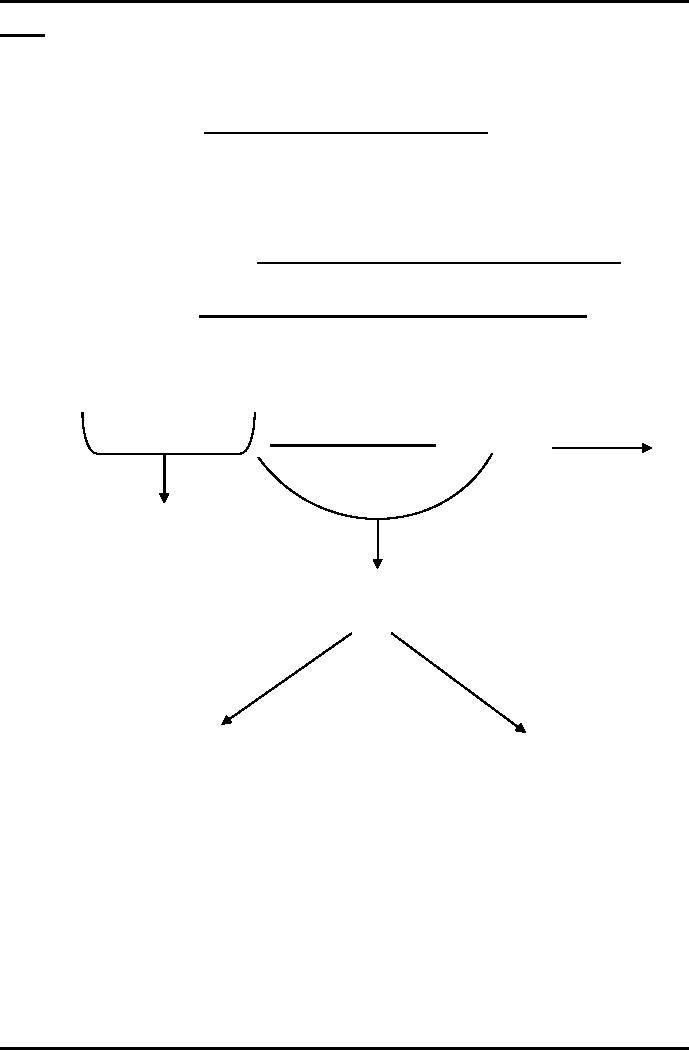
Following
figure will help to under stand
the events after the
balance sheet date;
31 Dec
2008
1 Jan
2008
25 March
2009
Accounting
Period
Events
after the balance
sheet
date.
Adjusting
events
Non-adjusting
events
In
this figure balance sheet
date is December 31, 2008 and
the date of BOD meeting
is
March
25, 2009. So the events
that occur in between these
two dates will be the
events
after
the balance sheet
date.
Explanation:
A
Good Stock costing Rs.
100,000 was written down to NRV of Rs.
97,500 at the
Balance
Sheet date. After the
Balance Sheet date it is
sold for Rs. 96,000.
The
condition of stock at the
balance sheet date has not
changed till sale and the
future
event
provides evidence regarding
the decline in its value.
Thus, it is an adjusting
event
after the balance sheet
date.
134

Advance
Financial Accounting
(FIN-611)
VU
On
the other hand, a Good
Stock costing Rs. 200,000
was written down to NRV of Rs.
197,000 at
the balance sheet date.
After the balance sheet date
the stock was
spoiled
and
sold for only Rs.10, 000 as
scrap.
In
this case the condition of
spoilage did not exist at the
balance sheet date.
This
spoilage
is indicative of condition that
arose after the balance
sheet date. So, this is
a
non-adjusting
event after the balance
sheet date.
Example-1:
Classify
the following events after
the balance sheet date as
adjusting or non-
adjusting:
(a)
Creative
Textile (Private) Limited
decided to takeover Saga
Sports (Private)
Limited
after the balance sheet
date.
(b)
QSA
Surgical announces a plan to discontinue
its Marala Branch after
the
balance
sheet date.
(c)
Sale
of inventory after the
balance sheet date below
its cost and also below
its
NRV (Inventory
was measured at NRV on the
Balance Sheet Date).
(d)
Changes
in tax rates after the
balance sheet date having a
significant effect on
current
and deferred tax assets and
liabilities.
(e)
A doubtful
customer defaults after the
balance sheet date;
provision for such
customer
has been made @
10%.
Asset
purchased on 27th
December
2004, invoice has been
received on 5th
(f)
January
2005. The year ends on
31st December
2004.
(g)
The
discovery of fraud that shows
that the financial
statements are
incorrect.
Solution:
Adjusting
events after the balance
sheet date.
(c),
(e), (f), (g)
Non-adjusting
events after the balance
sheet date.
(a),
(b), (d)
The
process involved in authorizing the
financial statements for issue will
vary
depending
upon the management structure,
statutory requirements and
procedures
followed
in preparing and finalizing the
financial statements.
In
some cases, an entity is
required to submit its
financial statements to
its
shareholders
for approval after the
financial statements have
been issued. In such
cases,
the financial statements are
authorized for issue on the
date of issue, not
the
date
when shareholders approve the
financial statements.
135

Advance
Financial Accounting
(FIN-611)
VU
Example-2:
The
management of an entity completes
draft financial statements for
the year to 31st
December
2005 on 28th January 2006. On
18th February 2006,
the board of
directors
reviews
the financial statements and
authorizes them for issue. The
entity announces
its
profit and selected other
financial information on 19th February 2006. The
financial
statements
are made available to
shareholders and others on 1st March 2006. The
shareholders
approve the financial
statements at their annual
meeting on 15th
April
2006 and
the approved financial
statements are then filed with a
regulatory body on
17th April 2006.
The
financial statements are authorized
for issue on 18th February 2006 (date of
board
authorization
for issue).
In
some cases, the management
of an entity is required to issue
its financial
statements
to a
supervisory board (made up
solely of non-executives) for approval.
In such cases,
the
financial statements are
authorized for issue when the
management authorizes
them for
issue to the supervisory
board.
Example-3:
On
18th February 2002,
the management of an entity
authorizes financial
statements
for
issue to its supervisory
board. The supervisory board
is made up solely of non-
executives
and may include representatives of
employees and other outside
interests.
The
supervisory board approves
the financial statements on
26th February 2002.
The
financial
statements are made
available to shareholders and others on
1st March 2002.
The
shareholders approve the
financial statements at their
annual meeting on 15th
April 2002 and
the financial statements are
then filed with a regulatory body on
17th
April
2002.
The
financial statements are authorized
for issue on 18th February 2002 (date of
management
authorization
for issue to the supervisory
board).
RECOGNITION
AND MEASUREMENT:
Adjusting
Events after the Balance
Sheet Date:
An
entity shall adjust the
amounts recognized in its
financial statements to
reflect
adjusting
events after the balance
sheet date.
Example-4:
A
customer was considered doubtful at
the balance sheet date. A
provision for such
customer
was made @ 50%. After the
balance sheet date, customer
was declared as
insolvent
based on his financial
position on year end.
Required:
What will be
the accounting
treatment?
Solution:
136

Advance
Financial Accounting
(FIN-611)
VU
This
is an adjusting event after
the balance sheet date and
should be recognized in
the
financial
statements. At the balance
sheet date, 100% provision
shall be made against
that
debtor i.e. provision is to be
increased by further 50%.
Example-5:
A
customer was doubtful at the
balance sheet date. A
provision for such customer
was
made
@ 5%. After the balance
sheet date, customer paid
85% of the total
amount.
Required:
What will be
the accounting
treatment?
Solution:
This
is an adjusting event. This
event shall be recognized in
the financial
statements.
At
the balance sheet, provision
shall be made @ 15% i.e.
Additional 10%
provision
shall
also be recorded.
Non-adjusting
Events after the Balance
Sheet Date:
An
entity shall not adjust the
amounts recognized in its
financial statements to
reflect
Non-adjusting
events after the balance
sheet date.
Example-6
An
asset, whose book value is
Rs. 89,000, was destroyed by
fire after the balance
sheet
date.
Required:
(i)
Identify
event type
(ii)
What will be
accounting treatment?
Solution:
(i)
This
is non-adjusting event as the
condition arose after the
balance sheet date.
(ii)
An
entity shall not recognize
such event in the financial
statement. It shall only
be
disclosed.
Examples
are:
a)
Decline
in market value of investments
between the balance sheet
date and the
date
when the financial statements
are authorized for
issue.
b)
Loss
of stock after the date of
financial statements.
The
following are the examples of
non-adjusting events after
the balance sheet
date
that
would generally result in
disclosure:
137
Advance
Financial Accounting
(FIN-611)
VU
(a)
A
major business takeover
after the balance sheet
date or disposing of a
major
subsidiary;
(b)
Announcing
a plan to discontinue an
operation;
(c)
Major
purchases of assets, classification of
assets as held for sale, other
disposals
of assets, or expropriation of major
assets by government;
(d)
The
destruction of a major production plant
by a fire after the balance
sheet
date;
(e)
Announcing,
or commencing the implementation
of, a major
restructuring;
(f)
Abnormally
large changes after the
balance sheet date in asset
prices or foreign
exchange
rates;
(g)
changes
in tax rates or tax laws
enacted or announced after
the balance sheet
date
that have a significant
effect on current and deferred
tax assets and liabilities;
(h)
Entering
into significant commitments or
contingent liabilities, for example,
by
issuing
significant guarantees; and
(i)
Commencing
major litigation arising,
solely out of events that occurred
after
the
balance sheet date.
Dividends
If an
entity declares dividends to
holders of equity instruments
after the balance
sheet
date,
the entity shall not
recognize those dividends as a
liability at the balance
sheet
date.
If
dividends are declared (i.e.
the dividends are
appropriately authorized and no
longer
at the discretion of the
entity) after the balance
sheet date but before
the
financial
statements are authorized for
issue, the dividends are not
recognized as a
liability
at the balance sheet date
because they do not meet the
criteria of a present
obligation
in
IAS-37.
Such dividends are disclosed
in the notes in accordance
with
IAS-1
Presentation of Financial
Statements.
Example-7:
Mobitel
Private Limited announces
dividend to its shareholders
amounting to
Rs.1,500,000
after the Balance Sheet
Date. The closing balance of
Retained Earnings is
Rs.
7,000,000 including above
dividend.
Required:
Effect
of the above on Financial
Statements.
Solution:
It
shall be disclosed in the
notes to the accounts as
follows:
Proposed
Dividend
Dividend
proposed for the year is
Rs.1,500,000.
138

Advance
Financial Accounting
(FIN-611)
VU
Going
Concern
An
entity shall not prepare its
financial statements on a going
concern basis if
management
determines after the balance
sheet date either that it
intends to liquidate
the
entity or to cease trading, or
that it has no realistic
alternative but to do so.
Deterioration
in operating results and financial
position after the balance
sheet date
may
indicate a need to consider
whether the going concern
assumption is still
appropriate.
If the going concern
assumption is no longer appropriate,
the effect is so
pervasive
that this Standard requires
a fundamental change in the
basis of accounting,
rather
than an adjustment to the amounts
recognized within the original
basis of
accounting.
Example-8:
Elahi
(Private) Limited is in the
course of finalizing its
financial statements for the
year
ended
30th June
2004.
Due to
market competition and loss of
customers, company intends to
cease its
business
and liquidate the
company.
Should
the company prepare
financial statement on a going
concern basis or not?
Solution:
The
company should not prepare
the financial statement on a
going concern basis.
It
must
also disclose the fact
that financial statements
are not prepared on a
going
concern
basis. The amounts appearing
in Financial Statements would also be
adjusted
appropriately
according to new basis of accounting
i.e. current market
values.
139
Table of Contents:
- ACCOUNTING FOR INCOMPLETE RECORDS
- PRACTICING ACCOUNTING FOR INCOMPLETE RECORDS
- CONVERSION OF SINGLE ENTRY IN DOUBLE ENTRY ACCOUNTING SYSTEM
- SINGLE ENTRY CALCULATION OF MISSING INFORMATION
- SINGLE ENTRY CALCULATION OF MARKUP AND MARGIN
- ACCOUNTING SYSTEM IN NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATIONS
- NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATIONS
- PREPARATION OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATIONS FROM INCOMPLETE RECORDS
- DEPARTMENTAL ACCOUNTS 1
- DEPARTMENTAL ACCOUNTS 2
- BRANCH ACCOUNTING SYSTEMS
- BRANCH ACCOUNTING
- BRANCH ACCOUNTING - STOCK AND DEBTOR SYSTEM
- STOCK AND DEBTORS SYSTEM
- INDEPENDENT BRANCH
- BRANCH ACCOUNTING 1
- BRANCH ACCOUNTING 2
- ESSENTIALS OF PARTNERSHIP
- Partnership Accounts Changes in partnership firm
- COMPANY ACCOUNTS 1
- COMPANY ACCOUNTS 2
- Problems Solving
- COMPANY ACCOUNTS
- RETURNS ON FINANCIAL SOURCES
- IASB’S FRAMEWORK
- ELEMENTS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
- EVENTS AFTER THE BALANCE SHEET DATE
- PROVISIONS, CONTINGENT LIABILITIES AND CONTINGENT ASSETS
- ACCOUNTING POLICIES, CHANGES IN ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES AND ERRORS 1
- ACCOUNTING POLICIES, CHANGES IN ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES AND ERRORS 2
- BORROWING COST
- EXCESS OF THE CARRYING AMOUNT OF THE QUALIFYING ASSET OVER RECOVERABLE AMOUNT
- EARNINGS PER SHARE
- Earnings per Share
- DILUTED EARNINGS PER SHARE
- GROUP ACCOUNTS
- Pre-acquisition Reserves
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Minority Interest
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Inter Company Trading (P to S)
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Fair Value Adjustments
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Pre-acquistion Profits, Dividends
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Profit & Loss
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Minority Interest, Inter Co.
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Inter Co. Trading (when there is unrealized profit)
- Comprehensive Workings in Group Accounts Consolidated Balance Sheet