 |
Partnership Accounts Changes in partnership firm |
| << ESSENTIALS OF PARTNERSHIP |
| COMPANY ACCOUNTS 1 >> |

Advance
Financial Accounting
(FIN-611)
VU
Lesson
# 19
Partnership
Accounts
Changes
in partnership firm
Subsequent to
the formation of a partnership
firm, a different accounting
treatment is required
when
any of the following changes
occur in the constitution of
the partnership
(Partnership
deed)
these changes might occur
because of the following
reasons:
� Admission
of a new partner
� Retirement
of an existing partner
� Death
of a partner
Admission of a
new partner
A new
partner may be admitted for
different reasons such as
personal influence, need of
more
capital, or
special skills.
At the
time of admission of a new
partner, certain adjustments
are necessary in the books
of
accounts;
among those calculation of good will is
very important.
Goodwill
Goodwill
may arise from such
attributes of a business as good
reputation, good customer
relationship,
strategic location, skill of
its employees, dynamic
management, durability of
its
products,
effective advertisement, patented
manufacturing process, outstanding
credit rating,
training
program of the employees, and good
relationship with suppliers and
employees, etc.
Goodwill
may be described as the
aggregate of those intangible attributes
of a business that
contribute
to the superior earning
capacity of the business. Goodwill is
the outcome of an
impression
created in the mind of each
customer and related persons.
Valuation
of Goodwill
Methods to
be adopted in valuing goodwill will
depend upon the
circumstances of each
particular
case. At the time of
valuation of goodwill, the
partnership deed should be
examined
and
valuation should be done in uch a
manner as must have been
agreed upon by the
partners.
Goodwill
Calculation methods
1. Average
profit method
2. Super
profit method
3. Market
capitalization method
Average
Profit Method
Under
this method, at first,
average profit is calculated on
the basis of the past
few years'
profits. At
the time of calculating
average profit, precaution
must be taken in respect of
any
abnormal
items of profit or loss which
may affect future profit. It
should be mentioned
that
average
profit is based on simple
average method.
After
calculating average profit, it is
multiplied by a number (times) 3, or 4,
or 5, what ever, as
agreed.
The product will be the
value of the
goodwill.
For
example:
Goodwill is
three times of the average
profit of previous five
years.
Let's
suppose:
Average
profit = 100 / 5 = 20
Goodwill =
20 x 3 = 60
86
Advance
Financial Accounting
(FIN-611)
VU
Solved
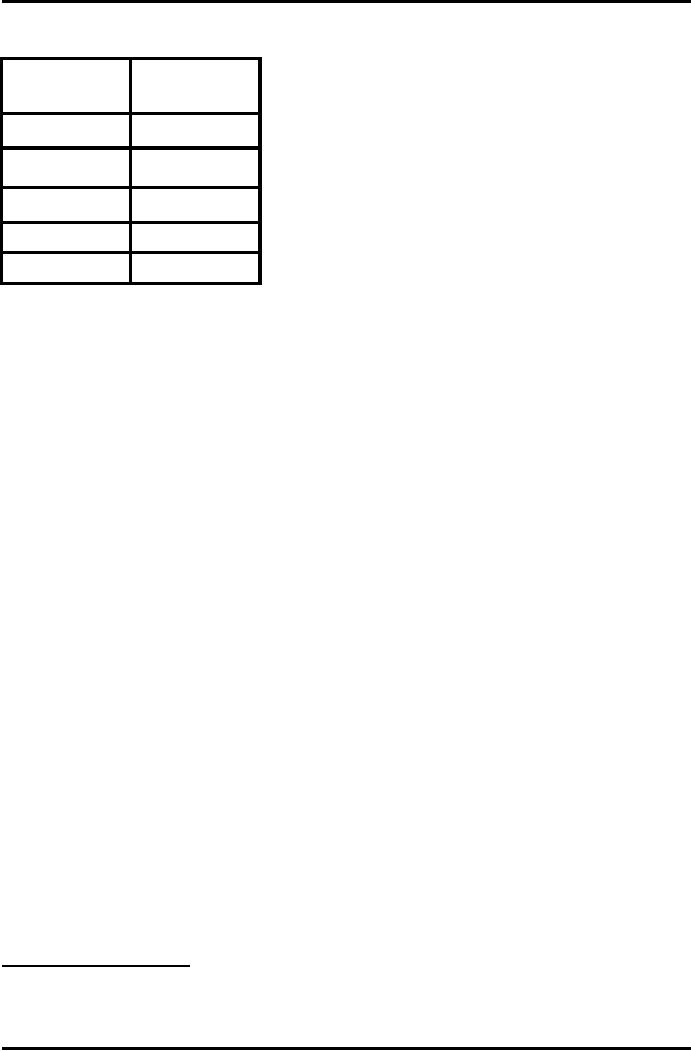
Problem No 1:
Years
Profit
1st
year
20,000
2nd
year
40,000
3rd
year
50,000
4th
year
70,000
Total
180,000
Goodwill of
the firm is equal to the
three years purchase of the last
four years average
profits:
Average
profit = 180,000 / 4 = Rs. 45,0000
Goodwill =
45,000 x 3 = 135,000
Super
Profit Method
Super profit
is the excess of actual
profit (average profit) over
the normal profit of an
entity. A
common
method of valuation of goodwill is
the super profit method. A
business unit may
possess
some advantages which enable it to make
extra profits over and above
the amount that
would be
earned if the capital of the
business was invested elsewhere
with similar risks.
These
extra
profits, generally expressed as super
profits, can be valued, and goodwill is
the value of
the
few years' purchase of super
profit.
In this
method, super profits are
taken as the basis for
calculating goodwill in place of
average
profit.
Certain
steps are followed in
calculating goodwill under super
profit method, these are
as
under:
1. Calculate
Capital of the firm
2. Calculate
normal profit by multiplying
firm's capital with normal
rate of return
3. Calculate
average profit of the
firm
4. Calculate
super profit by subtracting normal
profit from the average
profit
5. Multiply
the super profit by the
number of year's purchase (number of
times)
6. The
product will be called
goodwill.
Let's
suppose:
Normal
profit = 200,000 x 18% =
36,000
Super profit
= Average profit Normal
profit
= 45,000
36,000 = 9,000
Goodwill
= 9,000 x 3
= 27,000
Market
Capitalization Method
Under
this method the value of
the firm is first determined
based on the market
capitalization
rate using
the following
formula:
Average
profit of the firm x
100
% of market
rate of return
87

Advance
Financial Accounting
(FIN-611)
VU
The above
formula will give an estimate of the
firm's value in the market.
By subtracting the
book
value of the net assets
(owners' equity/capital) of the
firm from the above
calculated
value we
shall get the amount of
goodwill.
Suppose
average profit of the firm
is Rs. 45,000 and the market
rate of return is 18% and
the
capital
(net assets) of the firm is
Rs. 200,000.
Then
the good will of the firm will be
calculated as under:
Goodwill
= 45,000 /
18 x 100 = 250,000
= 250,000
-200,000
=
50,000
Accounting
treatment of goodwill
Since the
goodwill of a partnership firm
belongs to the old partners
and no one else, it is
apparent
that some adjustments must
be made to the Capital
accounts of the old partners
upon
the
admission of a new partner so
that the incoming partner
will not take a share of
the
goodwill
belonging to old partners
without payment. The amount
that the incoming
partner
pays for
goodwill is known as premium
for goodwill. This goodwill
can be treated in the books
of account
in any of the following
manner:
Goodwill
Raised
Scenario-1
When
the incoming partner cannot
bring cash as premium for
goodwill
Here,
the capital accounts of the
old partners are
artificially inflated towards
the right of the
goodwill,
without any cash
contribution. The idea is
that if the business were
sold immediately
after
the admission of the new
partner and the goodwill and
other assets realized their
book
value,
the old partners would
automatically receive cash
for their share of the
goodwill since
the
amounts attributable to them in
respects of the goodwill are
now included in their
respective
capital
accounts.
In this
case, goodwill account is to be
raised in the books of account at
its full value by
debiting
the
goodwill account and crediting
the old partners' capital
accounts in old
ratio.
Journal
Entry
Goodwill
A/c 135,000
A's
capital A/c
81,000
B's
capital A/c
45,000
Working
A's
share = 135,000 x 3/5 =
81,000
B's
share = 135,000 x 2/5 =
54,000
Important
Note
Following
should be taken in to account
when doing the above
treatment for
goodwill:
1. If
goodwill already appears in
the Balance Sheet which is
equal to full value of
goodwill so
calculated, then no entry is
required to be passed.
2. if
goodwill already appears in
the Balance Sheet which is
less than the full value
of
goodwill
then goodwill is to be raised
for the balance (full value
of goodwill calculated
less
goodwill already appearing in the
Balance sheet)
88

Advance
Financial Accounting
(FIN-611)
VU
3. if
goodwill already appears in
the Balance sheet which is
more than the full value
of
goodwill,
then excess goodwill is to be
written off. The journal
entry will be as under:
Old
partners' capital
accounts
Dr
Goodwill
accounts
Cr
(Being
the value of the goodwill
written down to its
calculated value)
Goodwill
Raised & Written-Off
Scenario-2
When
the incoming partner cannot
bring anything as premium for
goodwill but no goodwill
is
to
appear in the books:
Since the
value of the goodwill
constantly changes and partners
may not wish that an
account
should
remain in the books,
goodwill is raised in the books
first and, thereafter it is
written off.
Journal
Entry (Goodwill
raised)
Goodwill
A/c 135,000
A's
capital A/c
81,000
B's
capital A/c
45,000
Journal
Entry (Goodwill raised & written
off )
A's
capital A/c
67,500
B's
capital A/c
45,000
C's
capital A/c
22,500
Goodwill
A/c
135,000
A's
benefit
Old
ratio (Cr) 81,000
New
ratio (Dr)67,500
(Cr)
13,500
B's
benefit
Old
ratio (Cr) 54,000
New
ratio (Dr)45,000
(Cr)
9,000
A's
benefit + B's benefit
13,500 +
9,000 = 22,500
C's
share = 22,500
C's
share = 135,000 x 1/6 =
22,500
Goodwill
Brought in Cash
Scenario-3
When
the required amount of premium for
goodwill is brought in by the incoming
partner and
the
money is retained in the business to
increase the cash resources:
In this
situation, premium for
goodwill is to be shared by the
old partners in the
sacrificing
ratio.
The sacrificing ratio is to be
calculated by deducting the
new ratio from the
old ratio for
each
partner. It should be noted
that when the profit
sharing ratio between the
old partners does
not change
as between themselves, this
old profit sharing ratio is
their sacrificing
ratio.
Goodwill
brought in cash
89

Advance
Financial Accounting
(FIN-611)
VU
Bank
A/c 22,500
C's
premium for goodwill A/c
22,500
Distribution
of goodwill (sacrifice ratio)
C's
premium for goodwill A/c
22,500
A's
capital A/c
13,500
B's
capital A/c
9,000
A's
share = 22,500 x 3/5 =
13,500
B's
share = 22,500 x 2/5 =
9,000
Goodwill
Brought in Cash &
Withdrawn
Scenario-4
When
the required amount of premium for
goodwill is brought in by the new
partners and this
amount is
immediately withdrawn by the old
partners:
Goodwill
brought in cash
Bank
A/c 22,500
C's
premium for goodwill A/c
22,500
Distribution
of goodwill (sacrifice ratio)
C's
premium for goodwill A/c
22,500
A's
capital A/c
13,500
B's
capital A/c
9,000
Goodwill
withdrawn
A's
capital A/c 13,500
B's
capital A/c 9,000
Bank
A/c
22,500
90
Table of Contents:
- ACCOUNTING FOR INCOMPLETE RECORDS
- PRACTICING ACCOUNTING FOR INCOMPLETE RECORDS
- CONVERSION OF SINGLE ENTRY IN DOUBLE ENTRY ACCOUNTING SYSTEM
- SINGLE ENTRY CALCULATION OF MISSING INFORMATION
- SINGLE ENTRY CALCULATION OF MARKUP AND MARGIN
- ACCOUNTING SYSTEM IN NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATIONS
- NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATIONS
- PREPARATION OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATIONS FROM INCOMPLETE RECORDS
- DEPARTMENTAL ACCOUNTS 1
- DEPARTMENTAL ACCOUNTS 2
- BRANCH ACCOUNTING SYSTEMS
- BRANCH ACCOUNTING
- BRANCH ACCOUNTING - STOCK AND DEBTOR SYSTEM
- STOCK AND DEBTORS SYSTEM
- INDEPENDENT BRANCH
- BRANCH ACCOUNTING 1
- BRANCH ACCOUNTING 2
- ESSENTIALS OF PARTNERSHIP
- Partnership Accounts Changes in partnership firm
- COMPANY ACCOUNTS 1
- COMPANY ACCOUNTS 2
- Problems Solving
- COMPANY ACCOUNTS
- RETURNS ON FINANCIAL SOURCES
- IASB’S FRAMEWORK
- ELEMENTS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
- EVENTS AFTER THE BALANCE SHEET DATE
- PROVISIONS, CONTINGENT LIABILITIES AND CONTINGENT ASSETS
- ACCOUNTING POLICIES, CHANGES IN ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES AND ERRORS 1
- ACCOUNTING POLICIES, CHANGES IN ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES AND ERRORS 2
- BORROWING COST
- EXCESS OF THE CARRYING AMOUNT OF THE QUALIFYING ASSET OVER RECOVERABLE AMOUNT
- EARNINGS PER SHARE
- Earnings per Share
- DILUTED EARNINGS PER SHARE
- GROUP ACCOUNTS
- Pre-acquisition Reserves
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Minority Interest
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Inter Company Trading (P to S)
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Fair Value Adjustments
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Pre-acquistion Profits, Dividends
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Profit & Loss
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Minority Interest, Inter Co.
- GROUP ACCOUNTS: Inter Co. Trading (when there is unrealized profit)
- Comprehensive Workings in Group Accounts Consolidated Balance Sheet