 |
JAVA: Inheritance |
| << JAVA: Object Oriented Programming |
| JAVA: Collections >> |

Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
Lesson
5
Inheritance
In general,
inheritance is used to implement a
"is-a" relationship. Inheritance
saves code rewriting for
a
client
thus promotes
reusability.
In
java parent or base class is
referred as super
class
while child or derived class
is known as sub
class.
Comparison
with C++
Java
only supports single
inheritance. As a result a class
can only inherit from
one class at one
time.
Keyword
extends
is
used instead of ":" for
inheritance.
All
functions are virtual by
default
All
java classes inherit from
Object class (more on it
later).
To
explicitly call the super
class constructor, use super
keyword.
It's important to remember
that
call
to super class constructor must be
first line.
Keyword
super is also used to call
overridden methods.
Example
Code: using inheritance
We'll
use three classes to get familiar
you with inheritance. First
one is Employee class. This
will act
as
super class. Teacher class
will inherit from Employee
class and Test class is
driver class that
contains
main
method. Let's look at them one by
one
class
Employee{
protected
int id;
protected
String name;
//parameterized
constructor
public
Employee(int id, String
name){
this.id
= id;
this.name
= name;
}
//default
constructor
public
Employee(){
//
calling parameterized constructor of
same (Employee)
//
class by using keyword
this
this
(10, "not set");
}
//setters
public
void setId (int id)
{
this.id
= id;
32

Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
}
public
void setName (String name)
{
this.name
= name;
}
//getters
public
int getId () {
return
id;
}
public
String getName () {
return
name;
}
//
displaying employee object on
console
public
void display(){
System.out.println("in
employee display method");
System.out.println("Employee
id:" + id + " name:" + name);
}
//overriding
object's class toString
method
public
String toString() {
System.out.println("in
employee toString method");
return
"id:" + id + "name:" +
name;
}
}//end
class
The
Teacher class extends from
Employee class. Therefore
Teacher class is a subclass
of
Employee.
The teacher class has an
additional attribute i.e.
qualification.
class
Teacher
extends Employee{
private
String qual;
//default
constructor
public
Teacher () {
//implicit
call to superclass default
construct
qual
= "";
}
//parameterized
constructor
public
Teacher(int i, String n, String
q){
//call
to superclass param const
must be first line
super(i,n);
qual
= q;
}
//setter
public
void setQual (String
qual){
this.qual
= qual;
}
//getter
public
String getQual(){
33

Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
return
qual;
}
//overriding
display method of Employee
class
public
void display(){
System.out.println("in
teacher's display
method");
super.display();
//call
to superclass display method
System.out.println("Teacher
qualification:" + qual);
}
//overriding
toString method of Employee
class
public
String toString() {
System.out.println("in
teacher's toString
method");
String
emp = super.toString();
return
emp +" qualification:" +
qual;
}
}//end
class
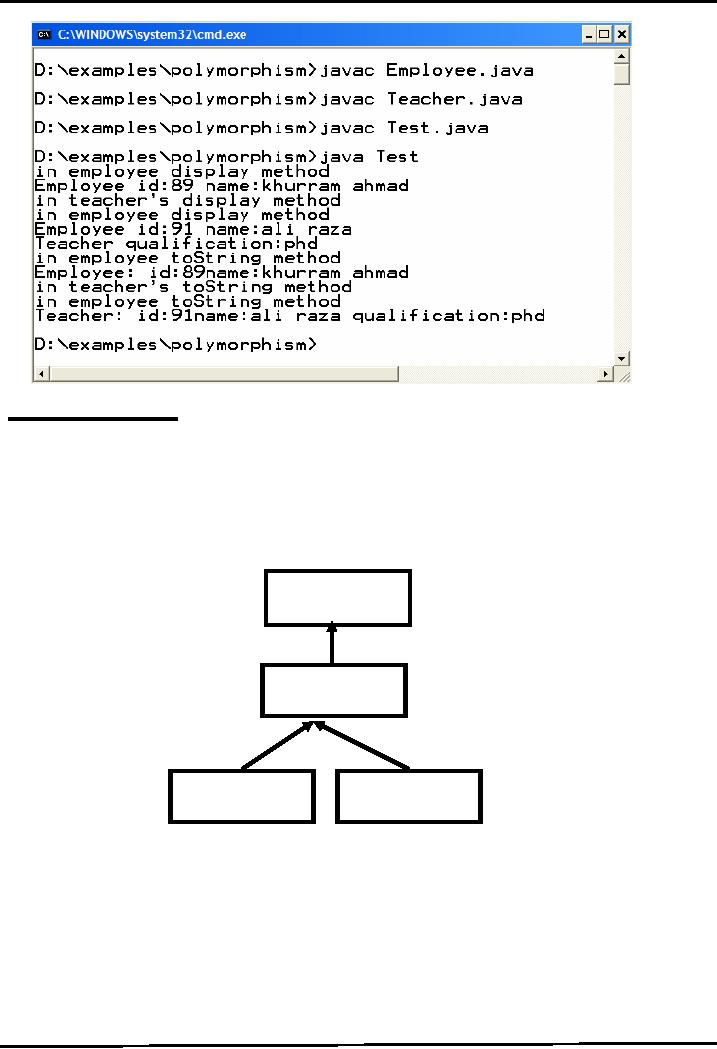
Objects
of Employee & Teacher class
are created inside main
method in Test class. Later calls
are made
to
display and toString method using
these objects.
class
Test{
public
static void main (String
args[]){
System.out.println("making
object of employee");
Employee
e = new Employee(89, "khurram
ahmad");
System.out.println("making
object of teacher");
Teacher
t = new Teacher (91, "ali
raza", "phd");
e.display();
//call to Employee class
display method
t.display();
//call to Teacher class
display method
//
calling employee class toString method
explicitly
System.out.println("Employee:
" +e.toString());
//
calling teacher class
toString implicitly
System.out.println("Teacher:
" + t);
} //end of
main
}//end
class
Output
34
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
Object
The Root Class
The
Od Java classes. For user
defined classes, its not
necessary to mention the Object
class as a
super
class, java doesbject class in
Java is a superclass for all
other classes defined in
Java's class
libraries,
as well as for user-define it
automatically for
you.
The
class Hierarchy of Employee
class is shown below. Object
is the super class of
Employee
class
and Teacher is a subclass of
Employee class. We can make
another class Manager that
can also
extends
from Employee class.
Object
Employe
Teacher
Manager
Polymorphism
"Polymorphic"
literally means "of multiple
shapes" and in the context of
OOP, polymorphic
means
"having multiple
behavior".
A parent
class reference can point to the
subclass objects because of is-a
relationship. For example a
Employee
reference can point
to:
o
Employee Object
35

Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
o
Teacher Object
o
Manager Object
A
polymorphic method results in different
actions depending on the object being
referenced
o
Also known as late
binding or run-time
binding
Example
Code: using polymorphism
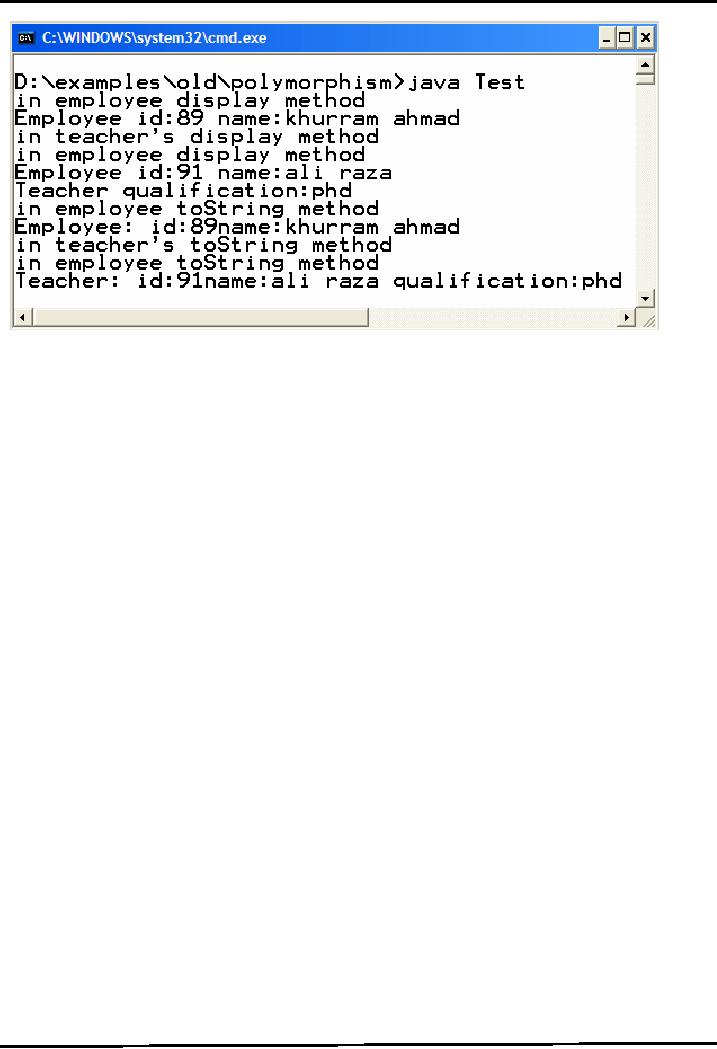
This
Test class is the modification of last
example code. Same Employee
& Teacher classes
are
used.
Objects of Employee & Teacher class
are created inside main
methods and calls are made
to
display
and toString method using these
objects.
class
Test{
public
static void main (String
args[]){
//
Make employee references
Employee
ref1, ref2;
//
assign employee object to first employee
reference
ref1
= new Employee(89, "khurram
ahmad");
//
is-a relationship,
polymorphism
ref2 =
new Teacher (91, "ali raza",
"phd");
//call
to Employee class display
method
ref1.display();
//call
to Teacher class display
method
ref2.display();
//
call to Employee class
toString method
System.out.println("Employee:
" +ref1.toString());
//
call to Teacher class
toString method
System.out.println("Teacher:
" + ref2.toString());
} //end of
main
}//end
class
Output
36
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
Type
Casting
In computer
science, type
conversion or typecasting
refers
to changing an entity of one datatype
into
another.
Type casting can be categorized into
two types
1.
Up-casting
Converting
a smaller data type into
bigger one
Implicit
we don't have to do something special
No
loss of information
Examples
of
-- Primitives
int a
= 10;
double
b = a;
-- Classes
Employee
e = new Teacher( );
2.
Down-casting
Converting
a bigger data type into
smaller one
Explicit
need to mention
Possible
loss of information
Examples
of
37

Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
-- Primitives
double
a = 7.65;
int b
= (int)
a;
-- Classes
Employee
e = new Teacher( ); // up-casting
Teacher
t = (Teacher)
e; //
down-casting
References:
Java
tutorial:
http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/java/javaOO/
Stanford
University
Example
code, their explanations and
corresponding figures for handout 5-1,5-2
are taken from
the
book JAVA A Lab Course by
Umair Javed. This material is
available just for the
use
of VU
students of the course Web Design and
Development and not for any
other
commercial
purpose without the consent of
author.
38
Table of Contents:
- JAVA FEATURES
- Java Virtual Machine & Runtime Environment
- Learning Basics of JAVA
- JAVA: Object Oriented Programming
- JAVA: Inheritance
- JAVA: Collections
- JAVA: Intro to Exceptions
- JAVA: Streams
- JAVA: Modification of Address Book Code
- JAVA: Graphical User Interfaces
- JAVA: Event Handling
- JAVA: More Examples of Handling Events
- JAVA: Problem in Last Code Example
- Java Database Connectivity
- JAVA: More on JDBC
- JAVA: Result Set
- JAVA: Meta Data
- Java Graphics
- JAVA: How to Animate
- JAVA Applets
- JAVA: Socket Programming
- JAVA: Serialization
- JAVA: Multithreading 1
- JAVA: Multithreading 2
- JAVA Web Application Development
- Java Servlets
- JAVA: Creating a Simple Web Application in Tomcat
- JAVA: Servlets Lifecycle
- JAVA: More on Servlets
- JAVA: Dispatching Requests
- JAVA: Session Tracking 1
- JAVA: Session Tracking 2
- JAVA: AddressBook Case Study Using Sevlets
- Java Server Pages 1
- JavaServer Pages 2
- Java Server Pages 3
- JAVA: JSP Action Elements and Scope
- JAVA: JSP Custom Tags
- JAVA: MVC + Case Study
- JAVA: MVC Model 2 Architecture
- JAVA: Layers and Tiers
- JAVA: Expression Language
- JAVA: JavaServer Pages Standard Tag Library (JSTL)
- JAVA: Client Side Validation & JavaServer Faces (JSF)
- JAVA: JavaServer Faces