 |
JAVA: JavaServer Faces |
| << JAVA: Client Side Validation & JavaServer Faces (JSF) |

Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
Lesson
45
JavaServer
Faces
In the last
lecture, we have covered the basic nutshells of
JSF. Having a belief on
"learning by doing", in
this
lecture another example is also
given to show you the capabilities of
JSF.
Example
Code: Addition of Two
Numbers
The
example code ("AddNumbers") is
given along with the
handout. It is strongly advised that
you must
see
the lecture video in order to
learn the making plus
working of this
example.
This
example demonstrates the usage of
value and method binding expressions,
managed beans, and
how
to
use page navigation
technique using IDE
etc.
Web
Services
In the
remaining handout, we'll
take an overview of web services'
potential, their types and
working
model.
Resources are given at the end
for those who are interested
in learning new
technologies.
Introduction
Web
services are Web-based enterprise
applications that use open,
XML-based standards and
transport
protocols
to exchange data with
calling clients.
Web Service is
becoming one of those overly
overloaded buzzwords these days.
Due to their increasing
popularity,
Java platform Enterprise Edition
(J2EE) provides the APIs and
tools you need to create
and
deploy
interoperable web services
and clients.
Web
service, Definition by W3C
W3C
recently has come up with a
decent definition of web
services. According to W3C, "A Web
service is
a
software application identified by a
URI, whose interfaces and binding
are capable of being
defined,
described and
discovered by XML artifacts and supports
direct interactions with
other software
applications
using
XML based messages via internet-based
protocols".
Distributed
Computing Evolution
Let's
think a little bit on how
distributed computing technology
has evolved.
In the
beginning, things were built and
deployed typically in the form of
client and server model in
which
clients
talk to a single server, for
example, remote procedure calls (RPC).
The
second phase can be called
web-based computing in which
many clients talk to many
servers through
the net. In
this phase, communicating
partners still have to go through
some pre-arrangement in terms of
what
common object model they have to
use or what common communication
protocol they have to
agree
upon.
Finally,
the web services model in
which service users and service providers
can be dynamically
connected.
And
the pretty much every
computing device and application
participates as both service user and
service
provider.
357
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
Characteristics of
Web services
Web
services are XML-based
throughout. Pretty much
everything in the domain of Web services
is defined
in XML.
For example, the format of the
data being exchanged between service user
and service provider is
defined
in XML or the description of web service is
defined in XML.
Because
the only contract that has to be
agreed upon between service user and
service provider is syntax
and
semantics of XML messages, as long as
valid messages can be
generated and understood, it does
not
matter what programming language is used.
So a web service is said to be
programming language
independent.
Web
services can be dynamically
located and invoked. And
typically they will be
accessed and
invoked
over both internet and
intranet.
Interoperable
Connect
across heterogeneous networks
using ubiquitous web-based
standards
Economical
Recycle
components, no installation and tight
integration of software
Automatic
No human
intervention required even for
highly complex
transactions
Accessible
Legacy
assets & internal apps
are exposed and accessible
on the web
Available
Services
on any device, anywhere,
anytime
Scalable
No
limits on scope of applications and
amount of heterogeneous
applications
Types
of Web service
Data
providers
For
example, a service providing stock
quotes
Business-to-business
process integration
For
example, purchase
orders
Enterprise
application integration
Different
applications work together
simply by adding a webservice
wrapper
Comparison
between Web page & Web
service
Just
to give you a sense on the
difference between a web page and a
web service, consider the
following
table:
Web
page
Web
Service
Has a
UI
No
GUI
Interacts
with user
Interacts
with application
Works
with web browser
client
Works
with any type of
client
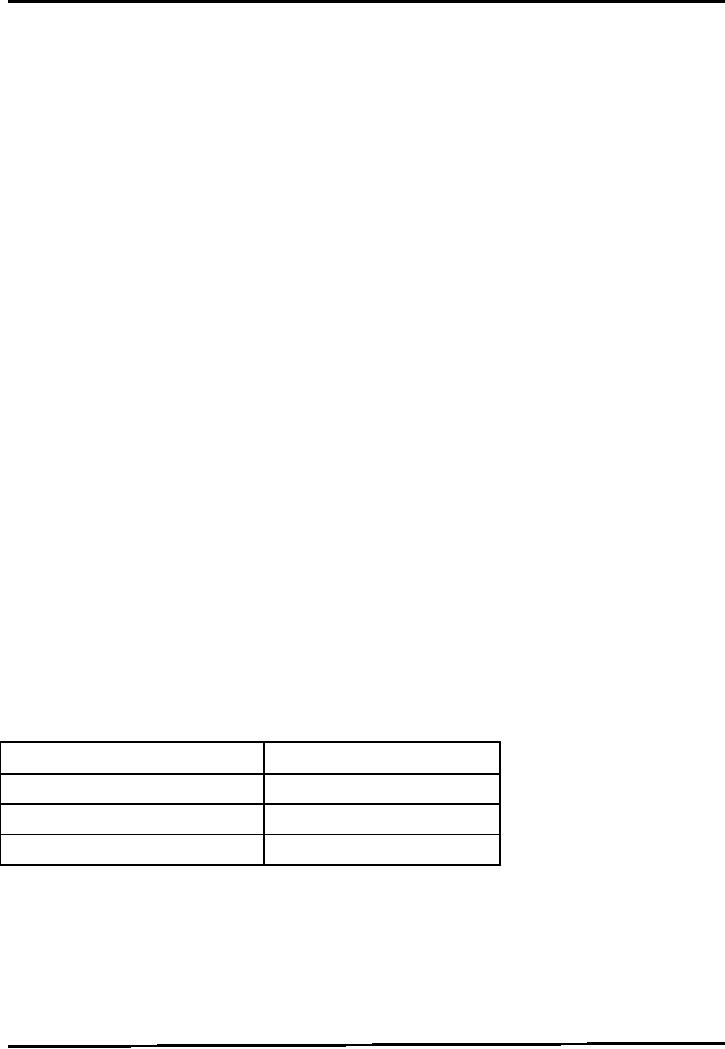
Web
service Architectural
Components
Following
are the core building blocks
of web service architecture.
Service
Description how do clients know
how it works (which functions, parameters
etc.)?
At the
minimum, you need a standard
way of describing a web service
that is universally
understood by
all potential service users and service
providers. This is important
because without
commonly
agreed upon description of service, a
service provider might have to produce
individually
tailored
way of describing its service to
all its potential service
users.
358
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
Web
beybeb 752.1 (6pV26
392.71/TT6 1 Tf25.225 0 TD-79985
162.599976 P8 cm/i126l 392.5.0011
TcL3l6d2
359
Table of Contents:
- JAVA FEATURES
- Java Virtual Machine & Runtime Environment
- Learning Basics of JAVA
- JAVA: Object Oriented Programming
- JAVA: Inheritance
- JAVA: Collections
- JAVA: Intro to Exceptions
- JAVA: Streams
- JAVA: Modification of Address Book Code
- JAVA: Graphical User Interfaces
- JAVA: Event Handling
- JAVA: More Examples of Handling Events
- JAVA: Problem in Last Code Example
- Java Database Connectivity
- JAVA: More on JDBC
- JAVA: Result Set
- JAVA: Meta Data
- Java Graphics
- JAVA: How to Animate
- JAVA Applets
- JAVA: Socket Programming
- JAVA: Serialization
- JAVA: Multithreading 1
- JAVA: Multithreading 2
- JAVA Web Application Development
- Java Servlets
- JAVA: Creating a Simple Web Application in Tomcat
- JAVA: Servlets Lifecycle
- JAVA: More on Servlets
- JAVA: Dispatching Requests
- JAVA: Session Tracking 1
- JAVA: Session Tracking 2
- JAVA: AddressBook Case Study Using Sevlets
- Java Server Pages 1
- JavaServer Pages 2
- Java Server Pages 3
- JAVA: JSP Action Elements and Scope
- JAVA: JSP Custom Tags
- JAVA: MVC + Case Study
- JAVA: MVC Model 2 Architecture
- JAVA: Layers and Tiers
- JAVA: Expression Language
- JAVA: JavaServer Pages Standard Tag Library (JSTL)
- JAVA: Client Side Validation & JavaServer Faces (JSF)
- JAVA: JavaServer Faces