 |
Java Server Pages 1 |
| << JAVA: AddressBook Case Study Using Sevlets |
| JavaServer Pages 2 >> |
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
Lesson
34
Java
Server Pages
As we concluded in
our discussion on JSP, JSP
is a text based document capable of
returning either static
or
dynamic content to a client's browser.
Static content and dynamic content can be
intermixed. The
examples
of static content are HTML, XML & Text
etc. Java code, displaying
properties of JavaBeans
and
invoking
business logic defined in
custom tags are all
examples of dynamic
content.
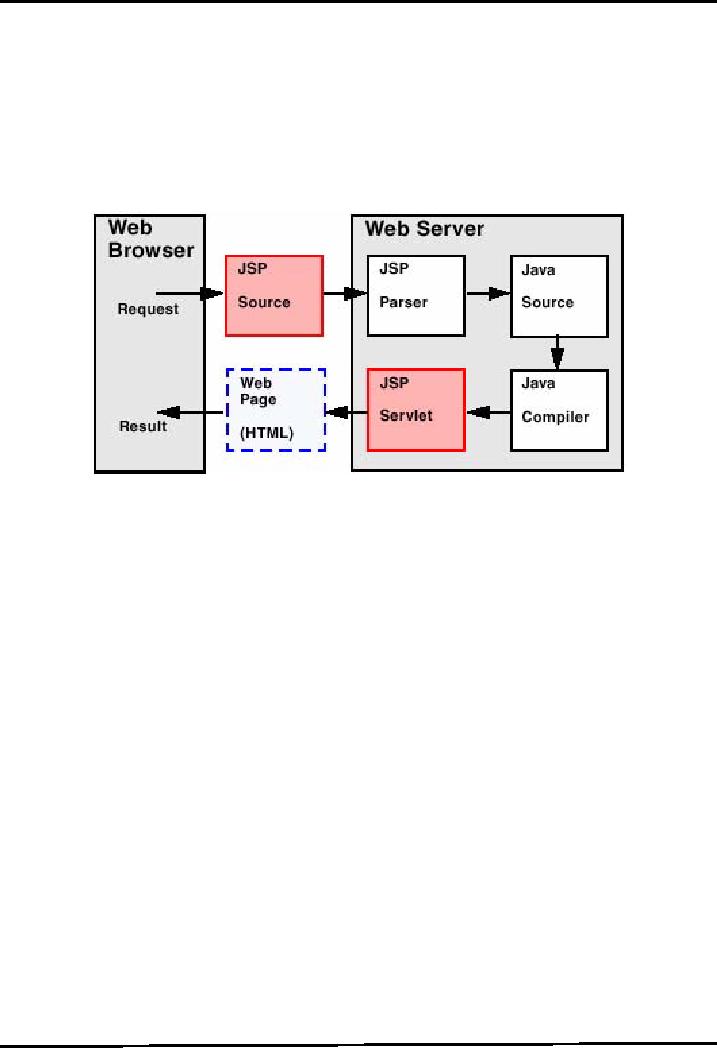
First
run of a JSP
Figure
below shows what phases a
JSP passed through before
displaying result.
The
web browser makes a request to
JSP source code. This
code is bifurcated into HTML and
java code by
the
JSP parser. The java
source code is compiled by the
Java compiler resulting in
producing a servlet
equivalent
code of a JSP. The servlet
code is intermixed with HTML and
displayed to the user. It is
important
to note that a JSP only
passes through all these
phases when it is invoked
for the first time or
when
the changes have been made to
JSP. Any later call to JSP
does not undergo of
compilation phase.
Benefits
of JSP
Convenient
� We
already know java and HTML. So
nothing new to be learned to work
with JSP.
� Like
servlets (as seen, ultimately a
JSP gets converted into a
servlet), provides an
� extensive
infrastructure for
Tracking
sessions
Reading
and sending HTML headers
Parsing and
decoding HTML form
data
Every
request for a JSP is handled
by a simple JSP java thread as
JSP gets converted into a
servlet. Hence,
the
time to execute a JSP document is
not dominated by starting a
process.
Portable
Like
Servlets, JSP is also a specification
and follows a well standardized
API. The JVM which is used
to
execute
a JSP file is supported on many
architectures and operating
systems.
Inexpensive
There
are number of free or
inexpensive Web Servers that
are good for commercial
quality
websites
JSP
vs. Servlet
Let's
compare JSP and Servlet
technology by taking an example
that simply plays current
date.
First
have a look on JSP that is
displaying a current date. This
page more looks like a HTML
page except
254

Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
of
two strangely written lines
of codes. Also there are no
signs of doGet(), doPost().
<%@
page import="java.util.*"
%>
<html>
<body>
<h3>
Current Date is:<%= new
Date()%>
</h3>
</body>
</html>
Now,
compare the JSP code above
with the Servlet code given
below that is also
displaying the current
date.
//File:
SearchPersonServlet.java
import
java.io.*;
import
java.net.*;
import
javax.servlet.*;
import
avax.servlet.http.*;
import
java.util.*;
public
class SearchPersonServlet extends
HttpServlet {
protected
void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse
response)throws
ServletException,
IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter
out = response.getWriter();
out.println(
"<html>"
+ "<body>" + "<h3>" +
"Current Date is:" + new
Date() +
"</h3>"
+ "</body>" +
"</html>"
);
//
Handles the HTTP GET
method.
protected
void doGet(HttpServletRequest
request,HttpServletResponse response)throws
ServletException,
IOException {
processRequest(request,
response);
}
//
Handles the HTTP POST
method.
protected
void doPost(HttpServletRequest
request,HttpServletResponse response)throws
ServletException,
IOException {
processRequest(request,
response); }
}
Clearly,
a lot of code is needed to be
written in the case of servlet
example to perform a basic
job.
Besides
HTML, a JSP may contain the
following elements.
Directive
Elements
Provides global control of
JSP ......................... <%@
%>
Scripting
Elements
JSP comments
............................................. <%----%>
declarations
............................................. <%!
%>
�
Used to declare
instance variables &
methods
expressions .............................................
<%=
%>
�
A
java code fragment which
returns String
scriptlets
............................................. <%
%>
�
Blocks
of java code
255

Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
Action
Elements
Special
JSP tags ...........................................
<jsp:
..... />
We'll
discuss in detail all the
ingredients of JSP. This
handout will cover only
scripting elements,
remaining
ones will be discussed in next
handouts.
Scripting
Elements
Comments
Comments
are ignored by JSP-to-servlet
translator. Two types of
comments are possibly used
in
JSP.
HTML
comment:
These
comments are shown in
browser, means on taking
view source of the web
page;
these
sorts of comments can be read. Format of
HTML comments is like
to:
<!--
comment text-->
JSP
comment:
These
comments are not displayed
in browser and have format
like:
<%--
comment text --%>
Expressions
The
format of writing a Java expression
is: <%= Java expression
%>
These
expressions are evaluated,
after converted to strings placed into
HTML page at the place it occurred
in
JSP page Examples of writing
Expressions are:
<h2>
Time: <%= new
java.util.Date() %> </h2>
will
print current data &
time after converting it to
String
<h2>
Welcome: <%= request.getParameter("name")%>
</h2>
will
print the name
attribute
Scriptlets
The
format of writing a scriptlet
is: <%= Java code
%>
After
opening up the scriptlet
tag, any kind of java
code can be written inside
it. This code is
inserted
verbatim into corresponding
servlet.
Example
of writing a scriptlet
is:
<%
String
n = request.getParameter("name");
out.println("welcome
" + n);
%>
The
above scriptlet reads the name
attribute and prints it after
appending "welcome"
Declarations
The
format of writing a declaration tag
is: <%! Java code
%>
This
tag is used to declare variables and
methods at class level. The
code written inside this tag
is
inserted
verbatim into servlet's
class definition.
Example
of declaring a class level
(attribute) variable
is:
<%!
private
int someField = 5; %>
%>
Example
of declaring a class level method
is:
<%!
256

Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
public
void someMethod ( ...... ) {
................
}
Code
Example: Using scripting
elements
The
next example code consists on
two JSP pages namely
first.jsp and second.jsp. The user
will
enter
two numbers on the first.jsp
and after pressing the calculate
sum button, able to see the
sum
of entered
numbers on second.jsp
first.jsp
This
page only displays the two
text fields to enter numbers
along with a button.
<html>
<body>
<h2>Enter
two numbers to see their
sum</h1>
<!--the
form values will be posted to
second.jsp -->
<form
name = "myForm" action="second.jsp"
>
<h3>
First Number
</h3>
<input
type="text" name="num1" />
<h3>
Second Number
</h3>
<input
type="text" name="num2"
/><br/><br/>
<input
type="submit" value="Calculate Sum"
/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
second.jsp
This
page retrieves the values posted by
first.jsp. After converting the
numbers into integers, displays
their
sum.
<html>
<body>
<!--
JSP to sum two numbers
-->
<%--
Declaration--%>
<%!
//
declaring a variable to store
sum
int
res;
// method helps in
calculating the sum
public
int sum(int op1, int
op2) {
return
op1 + op2;
}
%>
<%--
Scripltet--%>
<%
String
op1 = request.getParameter("num1");String
op2 =
request.getParameter("num2");
int
firstNum = Integer.parseInt(op1);
int
secondNum = Integer.parseInt(op2);
//
calling method sum(), declared above in
declartion tag
res =
sum(firstNum, secondNum);
%>
257

Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
<%--
expression used to display
sum --%>
<h3>Sum
is: <%=res%>
</h3>
</body>
</html>
Writing
JSP scripting Elements in XML
Now
days, the preferred way
for composing a JSP pages is
using XML. Although writing
JSP
pages
in old style is still
heavily used as we had shown
you in the last example.
Equivalent XML
tags
for writing scripting
elements are given
below:
Comments:
No
equivalent tag is defined
Declaration:
<jsp:declartion>
</jsp:declaration>
Expression:
<jsp:expression>
</jsp:expression>
Scriptlet:
<jsp:scriptlet>
</jsp:scriptlet>
It's
important to note that every
opening tag also have a closing tag
too. The second.jsp of
last
example
is given below in XML
style.
<?
xml version="1.0"
encoding="UTF-8"?>
<jsp:root
xmlns:jsp="http://java.sun.com/JSP/Page"
version="2.0">
<!--
to change the content type or response
encoding change thefollowing
line-->
<jsp:directive.page
contentType="text/xml;charset=UTF-8"/>
<!--
any content can be specified
here, e.g.: -->
<jsp:element
name="text">
<jsp:body>
<jsp:declaration>
int
res;
public
int sum(int op1, int
op2) {
return
op1 + op2;
}
</jsp:declaration>
<jsp:scriptlet>
String
op1 = request.getParameter("num1");
String
op2 = request.getParameter("num2");
int
firstNum = Integer.parseInt(op1);
int
secondNum = Integer.parseInt(op2);
res =
sum(firstNum, secondNum);
</jsp:scriptlet>
<jsp:text>
Sum is:
</jsp:text>
<jsp:expression>
res </jsp:expression>
</jsp:body>
</jsp:element>
</jsp:root>
References
Java
A Lab Course by Umair
Javed
Core Servlets
and JSP by Marty
Hall
258
Table of Contents:
- JAVA FEATURES
- Java Virtual Machine & Runtime Environment
- Learning Basics of JAVA
- JAVA: Object Oriented Programming
- JAVA: Inheritance
- JAVA: Collections
- JAVA: Intro to Exceptions
- JAVA: Streams
- JAVA: Modification of Address Book Code
- JAVA: Graphical User Interfaces
- JAVA: Event Handling
- JAVA: More Examples of Handling Events
- JAVA: Problem in Last Code Example
- Java Database Connectivity
- JAVA: More on JDBC
- JAVA: Result Set
- JAVA: Meta Data
- Java Graphics
- JAVA: How to Animate
- JAVA Applets
- JAVA: Socket Programming
- JAVA: Serialization
- JAVA: Multithreading 1
- JAVA: Multithreading 2
- JAVA Web Application Development
- Java Servlets
- JAVA: Creating a Simple Web Application in Tomcat
- JAVA: Servlets Lifecycle
- JAVA: More on Servlets
- JAVA: Dispatching Requests
- JAVA: Session Tracking 1
- JAVA: Session Tracking 2
- JAVA: AddressBook Case Study Using Sevlets
- Java Server Pages 1
- JavaServer Pages 2
- Java Server Pages 3
- JAVA: JSP Action Elements and Scope
- JAVA: JSP Custom Tags
- JAVA: MVC + Case Study
- JAVA: MVC Model 2 Architecture
- JAVA: Layers and Tiers
- JAVA: Expression Language
- JAVA: JavaServer Pages Standard Tag Library (JSTL)
- JAVA: Client Side Validation & JavaServer Faces (JSF)
- JAVA: JavaServer Faces