 |
Java Virtual Machine & Runtime Environment |
| << JAVA FEATURES |
| Learning Basics of JAVA >> |
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
Lesson
2
Java
Virtual Machine & Runtime
Environment
Basic
Concept
When
you write a program in C++
it is known as source code.
The C++ compiler converts
this source code
into
the machine code of underlying system
(e.g. Windows) If you want to
run that code on Linux
you need
to
recompile it with a Linux
based compiler. Due to the
difference in compilers, sometimes
you need to
modify
your code.
Java
has introduced the concept of WORA
(write once run anywhere).
When you write a java
program it is
known
as the source code of java.
The java compiler does
not compile this source
code for any
underlying
hardware
system; rather it compiles it for a
software system known as JVM
(This compiled code is
known
as
byte code). We have different JVMs
for different systems (such
as JVM for Windows, JVM for
Linux
etc).
When we run our program the
JVM interprets (translates) the compiled
program into the language
understood by the
underlying system. So we write
our code once and the JVM
runs it everywhere
according
to the underlying system.
This
concept is discussed in detail
below
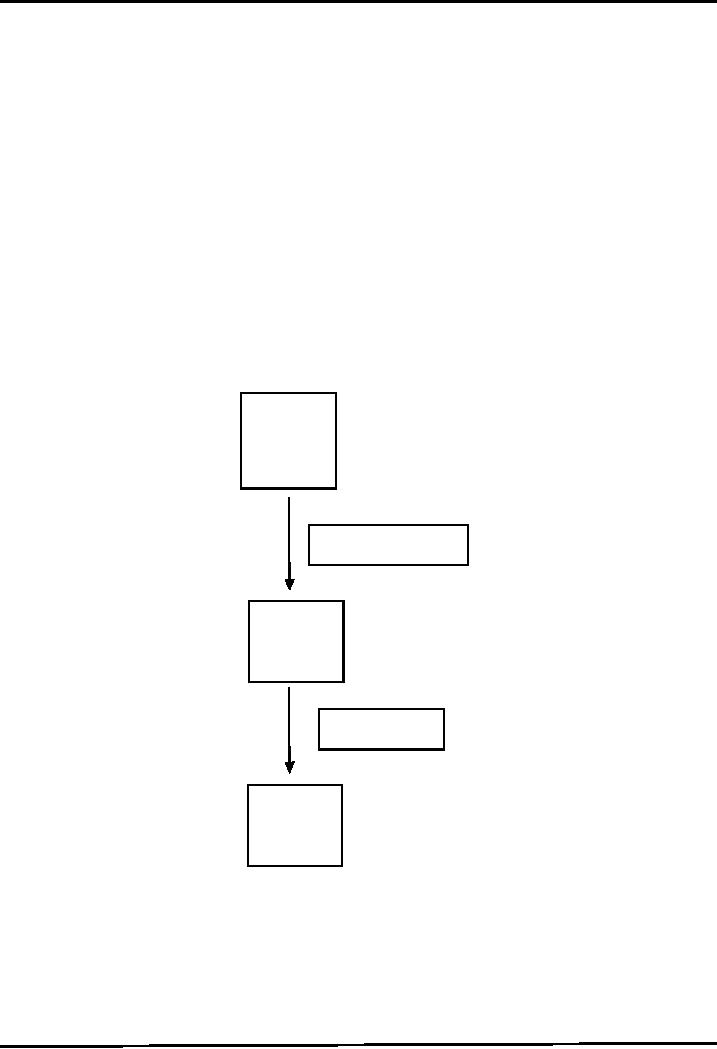
JAVA
Source
Code
Java
Compiler javac
Java
Byte
Code
Java
Interpreter
Machine
Code
Bytecode
Java
programs (Source code) are
compiled into a form called
Java bytecodes.
The
Java compiler reads Java
language source (.java) files,
translates the source
into
Java
bytecodes, and places the bytecodes
into class (.class)
files.
The
compiler generates one class
file for each class
contained in java source
file.
5
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
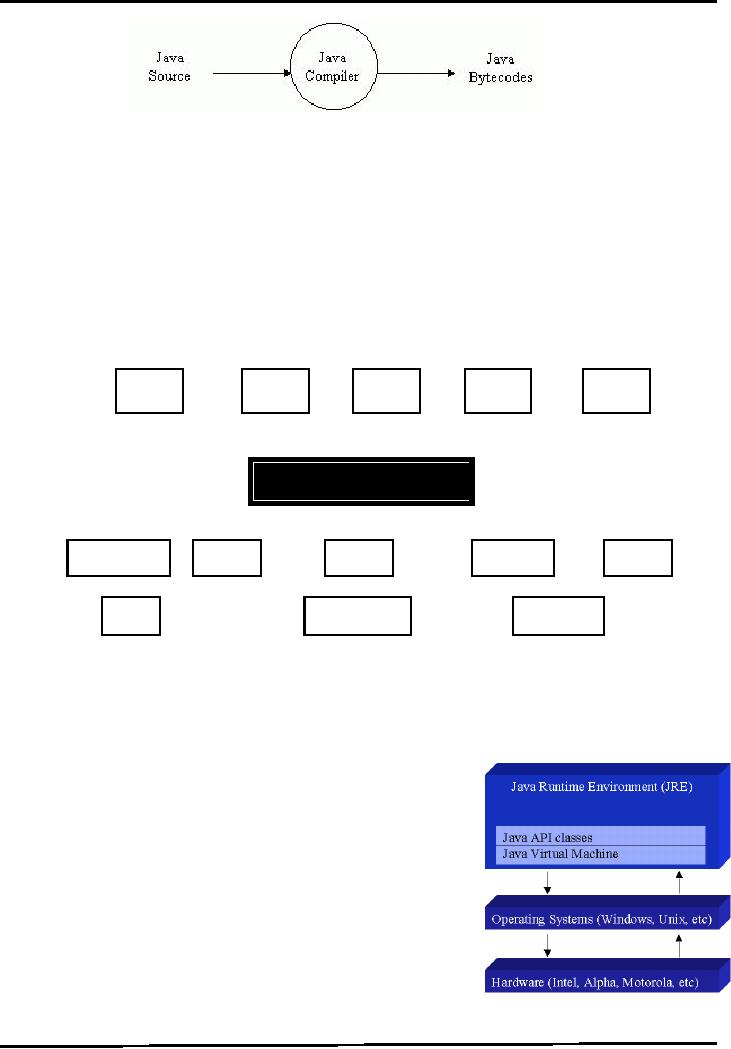
Java
Virtual Machine
(JVM)
The
central part of java
platform is java virtual
machine
Java
bytecode executes by special software known as a
"virtual machine".
Most
programming languages compile
source code directly into
machine code, suitable for
execution
The
difference with Java is that
it uses bytecode - a special type of machine
code.
The
JVM executes Java bytecodes, so
Java bytecodes can be
thought of as the machine language of
the
JVM.
App1
App2
App3
App4
App5
Java
Virtual Machine
Windows
Linux
OS
X
Solaris
Linux
Intel
PowerPC
SPARC
�
JVM
are available for almost all
operating systems.
�
Java
bytecode is executed by using any
operating system's JVM. Thus achieve
portability.
Java
Runtime Environment
(JRE)
The
Java Virtual Machine is a
part of a large system i.e.
Java Runtime
Environment
(JRE).
Each
operating system and CPU
architecture requires different
JRE.
The
JRE consists of set of
built-in classes, as well as a
JVM.
Without
an available JRE for a given
environment, it is impossible to
run
Java software.
References
Java
World: http://www.javaworld.com
6

Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
Inside
Java: http://www.javacoffeebreak.com/articles/inside_java
Java
Program Development and Execution
Steps
Java
program normally go through
five phases. These
are
1.
Edit,
2.
Compile,
3.
Load,
4.
Verify
and
5.
Execute
We
look over all the above
mentioned phases in a bit
detail. First consider the following
figure that
summarizes
the all phases of a java
program.
Phase
1: Edit
Phase
1 consists of editing a file.
This is accomplished with an editor
program. The programmer
types a
java program using the
editor like notepad, and make corrections
if necessary.
When
the programmer specifies that the file in the
editor should be saved, the
program is stored on a
secondary
storage device such as a
disk. Java program file
name ends with a
7

Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
.java
extension.
On
Windows platform, notepad is a simple
and commonly used editor
for the beginners. However
java
integrated
development environments (IDEs) such as
NetBeans, Borland JBuilder, JCreator
and
IBM's
Ecllipse have built-in editors that
are smoothly integrated into
the programming environment.
Phase
2: Compile
In
Phase 2, the programmer gives the command
javac to compile the program. The
java compiler
translates
the java program into
bytecodes, which is the language understood by the
java interpreter.
To
compile a program called
Welcome.java, type
javac
Welcome.java
at the
command window of your
system. If the program compiles
correctly, a file
called
Welcome.class
is produced. This is the file containing
the bytecodes that will be
interpreted
during
the execution phase.
Phase
3: Loading
In
phase 3, the program must
first be placed in memory before it can
be executed. This is done by the
class
loader,
which takes the .class file
(or files) containing the
bytecodes and transfers it to
memory.
The
.class file can be loaded
from a disk on your system
or over a network (such as
your local
university
or company network or even the
internet).
Applications
(Programs) are loaded into
memory and executed using the java
interpreter
via
the command java. When
executing a Java application
called Welcome, the command
Java
Welcome
Invokes
the interpreter for the Welcome
application and causes the
class loader to load
information
used
in the Welcome program.
Phase
4: Verify
Before
the bytecodes in an application are
executed by the java interpreter,
they are verified by
the
bytecode
verifier in
Phase 4. This ensures that
the bytecodes for class that
are loaded form the
internet
(referred
to as downloaded
classes) are
valid and that they do not
violate Java's security
restrictions.
Java
enforces strong security because
java programs arriving over
the network should not be
able to
cause
damage to your files and
your system (as computer viruses
might).
Phase
5: Execute
Finally
in phase 5, the computer, under the
control of its CPU,
interprets the program one bytecode at
a
time.
Thus performing the actions specified by the
program.
Programs
may not work on the first
try. Each of the preceding
phases can fail because of
various errors.
This
would cause the java program to
print an error message. The
programmer would return to
the
edit phase, make the
necessary corrections and proceed through
the remaining phases again
to
determine id the
corrections work properly.
8
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
References:
JavaTM
How to Program 5th edition by
Deitel & Deitel
Sun
Java online tutorial: http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/java/index.html
Installation
and Environment
Setting
Installation
�
Download
the latest version j2se5.0 (java 2
standard edition) from http://java.sun.com
or get it
from any other source
like CD.
Note:
j2se
also called jdk (java
development kit). You can
also use the previous versions
like
jdk
1.4 or 1.3 etc. but it is
recommended that you use
either jdk1.4 or
jdk5.0
�
Install
j2se5.0 on your system
Note:
For
the rest of this handout,
assume that j2se is
installed in C:\Program
Files\Java\jdk1.5.0
Environment
Setting
Once
you successfully installed the j2se, the
next step is environment or path
setting. You
can
accomplish this in either of two
ways.
�
Temporary
Path Setting
Open the
command prompt from Start �
Programs � Accessories �
Comman
Prompt.
The command prompt screen
would be opened in front of
you.
Write
the command on the command prompt
according to the following
format
path
= < java installation directory\bin
>
So,
according to handout, the command
will look like
this
path
= C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.5.0\bin
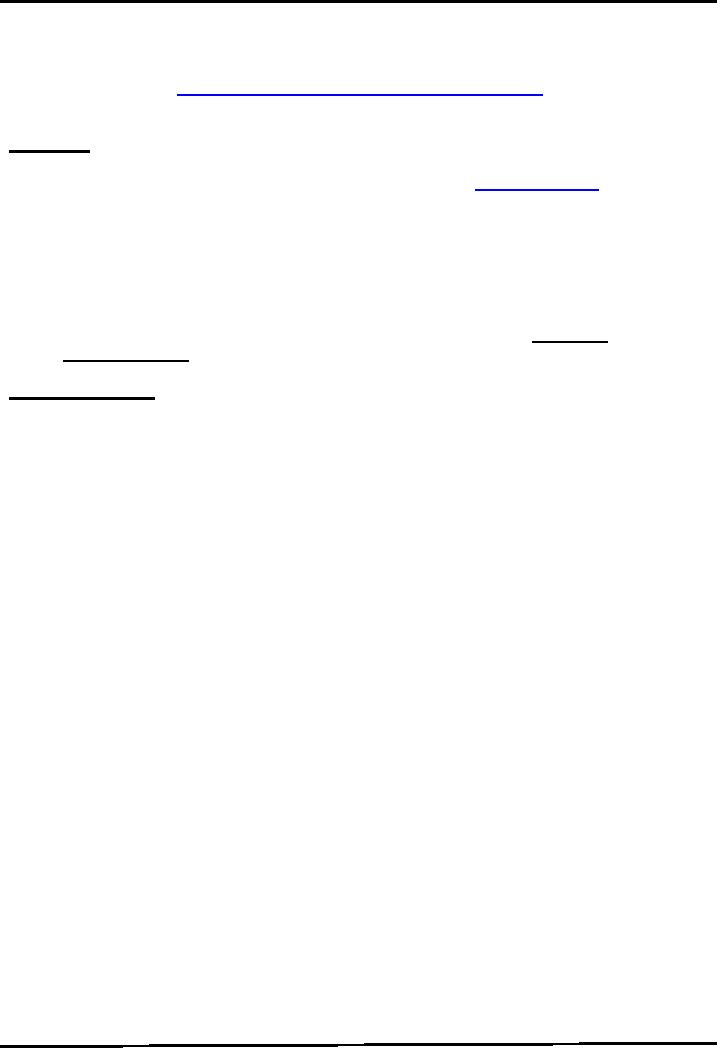
To
Test whether path has
been set or not, write
javac and press ENTER. If the
list ofn b
options
displayed as shown in the below figure
means that you have
successfully
completed the
steps of path
setting.
The
above procedure is illustrates in the given
below picture.
9
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
Note:
The
issue with the temporary
path setting is you have to
repeat the above explained
procedure
again and again each time
you open a new command
prompt window. To avoid
this
overhead, it is
better to set your path
permanently
�
Permanent
Path Setting
In
Windows NT (XP, 2000), you
can set the permanent environment
variable.
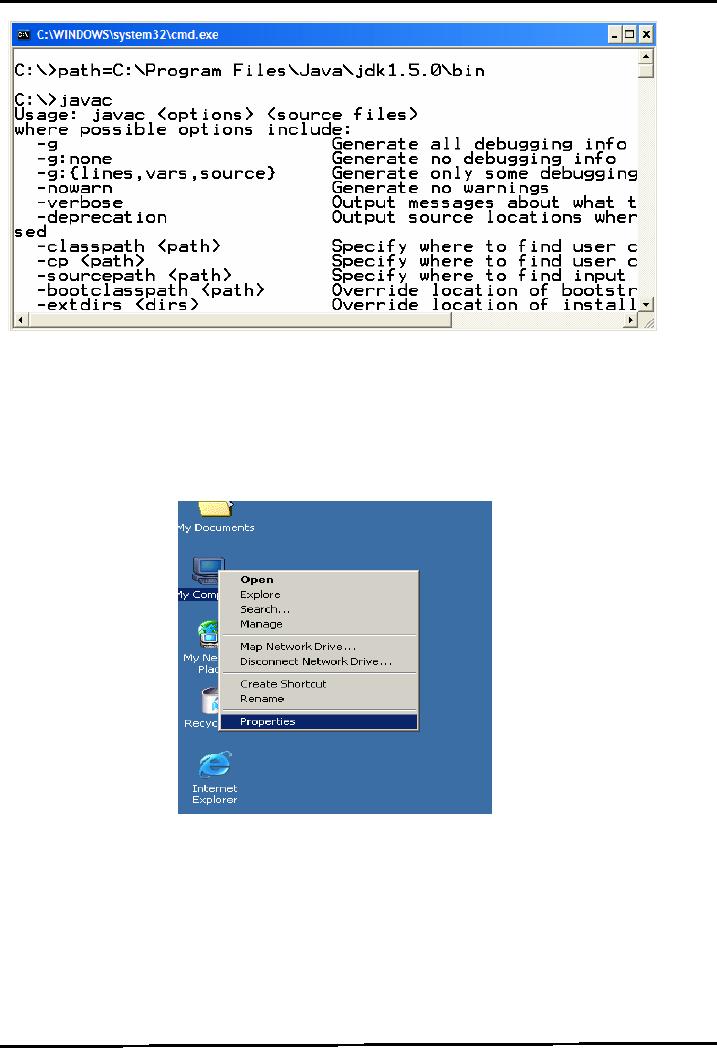
Right
click on my
computer icon
click on properties as shown
below
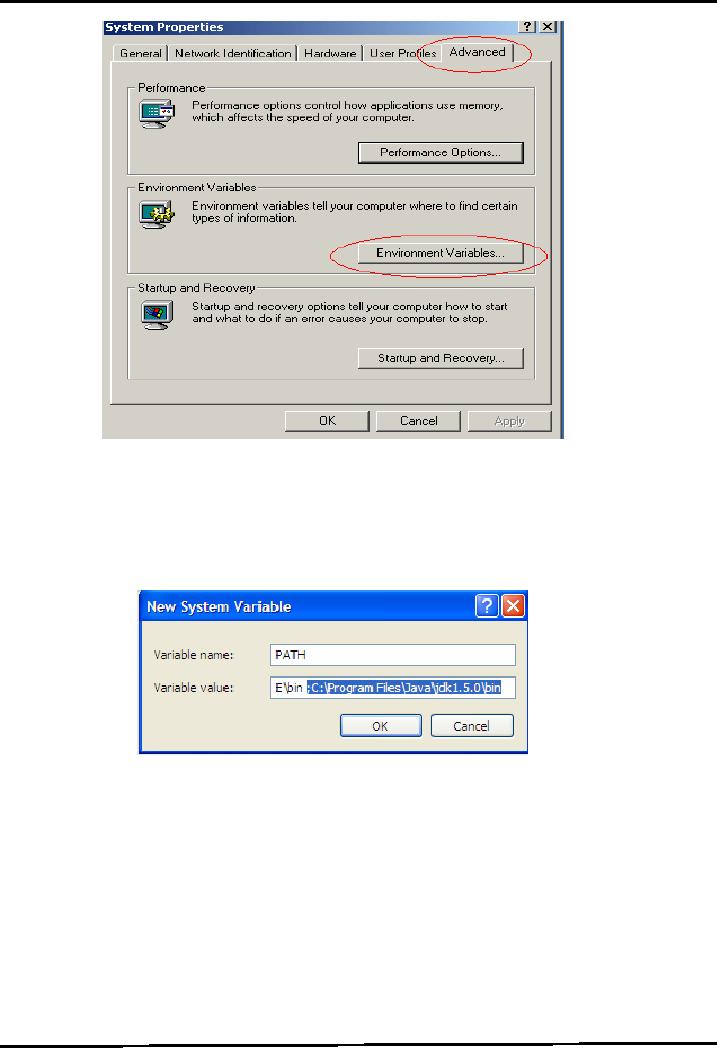
A
System Properties frame would appeared as
shown in the picture
10
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
Select
the advanced tab followed by clicking the
Environment Variable button.
The
Environment
variables frame would be displayed in
front of you
Locate
the Path variable in the System or
user variables, if it is present there,
select it by
single
click. Press Edit button.
The following dialog box
would be appeared.
�
Write;
C:\Program
Files\Java\jdk1.5.0\bin at the
end of the value field.
Press OK
button.
Remember to write semicolon (;)
before writing the path for
java installation
directory
as illustrate in the above figure
�
If
Path variable does not
exist, click the New button.
Write variable name
"PATH",
variable value C:\Program
Files\Java\jdk1.5.0\bin and
press OK button.
�
Now
open the command prompt and write
javac,
press enter button. You see
the list of
options
would be displayed.
�
After
setting the path permanently,
you have no need to set the
path for each new
opened
command
prompt.
11

Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
References
Entire
material for this handout is
taken from the book JAVA A
Lab Course by Umair Javed.
This
material
is available just for the
use of VU students of the course Web
Design and Development and
not
for any other commercial
purpose without the consent of
author.
First
Program in Java
Like
any other programming language, the
java programming language is used to
create applications.
So,
we start from building a
classical "Hello World"
application, which is generally
used as the first
program
for learning any new
language.
HelloWorldApp
1. Open notepad
editor from Start
�
ProgarmFiles
�
Accessories� Notepad.
2.
Write the following code
into it.
Note:
Don't
copy paste the given below
code. Probably it gives errors
and you can't able to remove
them
at the
beginning stage.
1.
/*
The HelloWorldApp class implements an
application that
2.
simply
displays "Hello World!" to the standard
output.
3.
*/
4.
public
class HelloWorldApp {
5.
public
static void main(String[]
args) {
6.
//Display
the string. No global
main
7.
System.out.println("Hello
World");
8.
}
9.
}
3. To
save your program, move to
File menu and choose save as
option.
4.
Save your program as
"HelloWorldApp.java" in some directory.
Make sure to add double
quotes
around
class name while saving
your program. For this example
create a folder known
as
"examples"
in D: drive
Note:
Name of
file must match the name of
the public class in the file
(at line 4). Moreover,
it
is
case sensitive. For example, if your
class name is MyClass, than
file name must be
MyClass.
Otherwise the
Java compiler will refuse to
compile the program.
For
the rest of this handout, we
assume that program is saved
in D:\examples directory.
HelloWorldApp
Described
Lines
1-3
Like
in C++, You can add
multiple line comments that
are ignored by the
compiler.
Lines
4
Line
4 declares the class name as
HelloWorldApp. In java, every
line of code must reside
inside
class.
This is also the name of our
program (HelloWorldApp.java). The
compiler creates the
12
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
HelloWorldApp.class
if this program successfully gets
compiled.
Lines
5
Line
5 is where the program execution starts.
The java interpreter must
find this defined
exactly
as given or it will refuse to
run the program. (However you
can change the name
of
parameter
that is passed to main. i.e.
you can write String[]
argv or String[] some Param
instead of
String[]
args)
Other
programming languages, notably C++
also use the main( )
declaration as the starting point
for
execution.
However the main function in
C++ is global and reside
outside of all classes where
as
in
Java the main function must
reside inside a class. In
java there are no global
variables or
functions.
The various parts of this
main function declaration
will be covered at the end of
this
handout.
Lines
6
Again
like C++, you can
also add single line
comment
Lines
7
Line
7 illustrates the method call. The
println( ) method is used to print
something on the
console. In
this example println( ) method
takes a string argument and writes it to
the standard
output
i.e. console.
Lines
8-9
Line
8-9 of the program, the two braces,
close the method main( ) and the
class
HelloWorldApp
respectively.
Compiling
and Running
HelloWorldApp
1. Open the
command prompt from Start
�
Program
Files � Accessories.
OR
alternatively
you can write cmd
in the
run command window.
2.
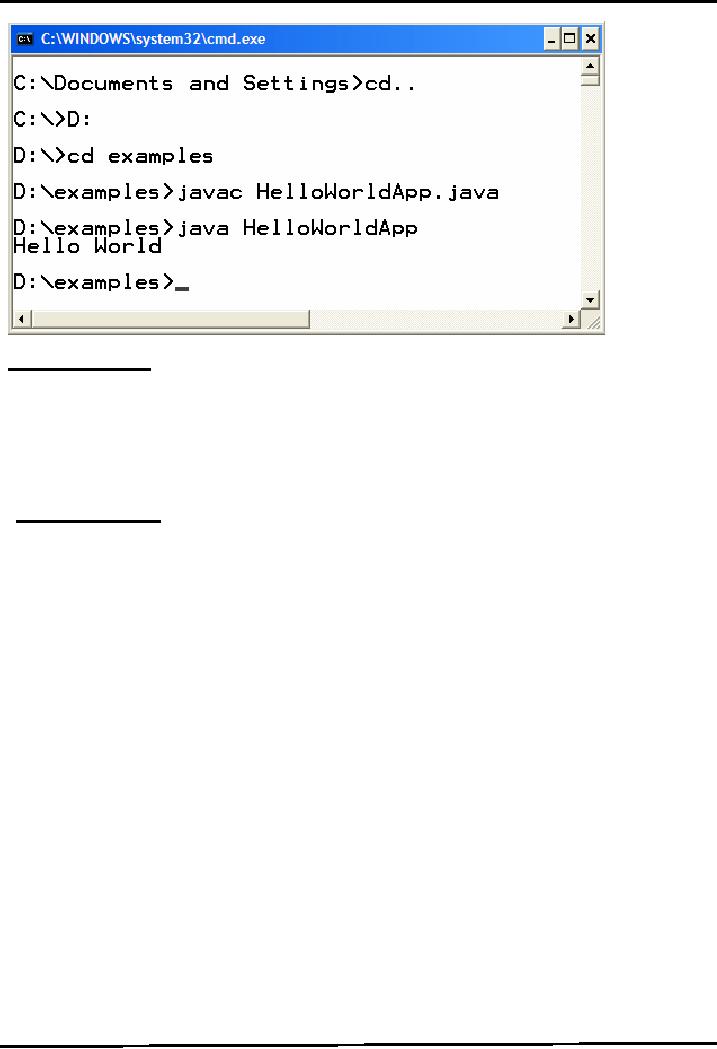
Write cd..
to
came out from any
folder, and cd [folder name] to move
inside the specified
directory.
To move from one drive to another,
use [Drive Letter]: See
figure given below
3.
After reaching to the folder or
directory that contains your source
code, in our case
HelloWorldApp.java.
4.
Use "javac"
on the
command line to compile the
source file (".java"
file).
D:\examples>
javac HelloWorld.java
5. If
program gets successfully compiled, it
will create a new file in
the same directory
named
HelloWorldApp.class
that contains the byte-code.
6.
Use "java" on the command
line to run the compiled
.class file. Note ".class"
would be added with
the
file name.
D:\examples>
java HelloWorld
7.
You can see the Hello
World would
be printed on the console. Hurrah! You
are successful in
writing,
compiling and executing your
first program in java ☺
13
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
Points
to Remember
Recompile
the class after making
any changes
Save
your program before
compilation
Only
run that class using
java command that contains the
main method, because
program
executions
always starts form
main
An
Idiom Explained
You
will see the following line
of code often:
public
static void main(String args[]) {
...}
�
About main()
"main"
is the function from which
your program starts
Why
public?
Since
main method is called by the JVM that is
why it is kept public so
that it is
accessible
from outside. Remember
private methods are only
accessible from within
the
class
Why
static?
Every
Java program starts when the
JRE (Java Run Time
Environment) calls the
main
method of that program. If main is not
static then the JRE have to create an
object
of the
class in which main method is
present and call the main method on
that object (In
OOP
based languages method are
called using the name of
object if they are not
static).
It is
made static so that the JRE
can call it without creating
an object.
Also
to ensure that there is only one
copy of the main method per
class
Why
void?
14

Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
�
Indicates
that main ( ) does not
return anything.
What
is String args[] ?
Way
of specifying input (often
called command-line arguments) at startup
of application.
More
on it latter
References
Entire
material for this handout is
taken from the book JAVA A
Lab Course by Umair Javed.
This
material
is available just for the
use of VU students of the course Web
Design and Development and
not
for
any other commercial purpose
with out the consent of
author.
15
Table of Contents:
- JAVA FEATURES
- Java Virtual Machine & Runtime Environment
- Learning Basics of JAVA
- JAVA: Object Oriented Programming
- JAVA: Inheritance
- JAVA: Collections
- JAVA: Intro to Exceptions
- JAVA: Streams
- JAVA: Modification of Address Book Code
- JAVA: Graphical User Interfaces
- JAVA: Event Handling
- JAVA: More Examples of Handling Events
- JAVA: Problem in Last Code Example
- Java Database Connectivity
- JAVA: More on JDBC
- JAVA: Result Set
- JAVA: Meta Data
- Java Graphics
- JAVA: How to Animate
- JAVA Applets
- JAVA: Socket Programming
- JAVA: Serialization
- JAVA: Multithreading 1
- JAVA: Multithreading 2
- JAVA Web Application Development
- Java Servlets
- JAVA: Creating a Simple Web Application in Tomcat
- JAVA: Servlets Lifecycle
- JAVA: More on Servlets
- JAVA: Dispatching Requests
- JAVA: Session Tracking 1
- JAVA: Session Tracking 2
- JAVA: AddressBook Case Study Using Sevlets
- Java Server Pages 1
- JavaServer Pages 2
- Java Server Pages 3
- JAVA: JSP Action Elements and Scope
- JAVA: JSP Custom Tags
- JAVA: MVC + Case Study
- JAVA: MVC Model 2 Architecture
- JAVA: Layers and Tiers
- JAVA: Expression Language
- JAVA: JavaServer Pages Standard Tag Library (JSTL)
- JAVA: Client Side Validation & JavaServer Faces (JSF)
- JAVA: JavaServer Faces