 |
JAVA: Result Set |
| << JAVA: More on JDBC |
| JAVA: Meta Data >> |
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
Lesson
16
Result
Set
This
handout will familiarize you
with another technique of inserting,
updating & deleting rows.
Before
moving
on, first we look at
ResultSet.
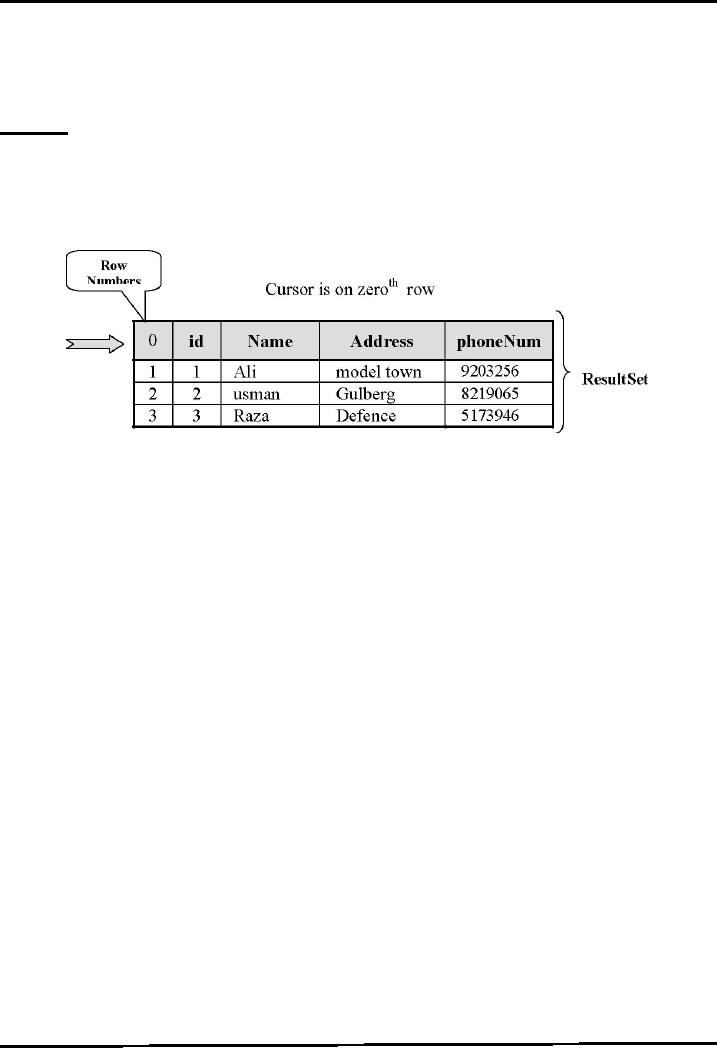
ResultSet
A ResultSet
contains the results of the SQL
query
Represented
by a table with rows and
columns
Maintains
a cursor pointing to its
current row of data.
Initially
the cursor positioned before the
row (0).
First
row has index 1
124

Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
-The
ResultSet is implicitly closed when the
associated Statement object
executes a new query
or
closed
by method call.
Updatable
and/or Scrollable ResultSet
It is possible to
produce ResultSet objects that are
scrollable and/or updatable
(since JDK 1.2)
With
the help of such ResultSet, it is possible to
move forward as well as
backward with in
RestultSetobject.
Another
advantage is, rows can be inserted, updated or deleted
by using updatable ResultSet
object.
Creating
Updatable & Scrollable
ResultSet
The
following code fragment,
illustrates how to make a ResultSet
object that is scrollable and
updatable.
String
sql = "SELECT * FROM
Person";
PreparedStatement
pStmt =
con.prepareStatement(sql,ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE,ResultSet.CONCUR_U
PDATABLE);
ResultSet
rs = pStmt.executeQuery( );
Two
constants have been used of ResultSet
class for producing a ResultSet rs
that is scrollable, will
not
show
changes made by others and
will be updatable
Useful
ResultSet's Methods (cont.)
The
methods discussed in this section
can only be used with
updatable/scrollable ResultSet
object.
. previous(
)
-Moves
the cursor to the previous row in the
ResultSet object, if available -Returns
true if
cursor
is on a valid row, false it is off the
result set. -Throws
exception if result type
is
TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY.
Example
Code 16.1: Use of previous(
), next( ) & various getters
methods
The
ResultSetEx.java shows the use of
previous, next and getters
methods. We are using the
same Person
table
of PersonInfo database, the one we had
created earlier in this
example and later on.
1
//
File ResultSetEx.java
2
import
java.sql.*;
3
public
class ResultSetEx {
4
public
static void main (String args[ ])
{
5
try
{
6
//Step
2: load driver
7
Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
8
//Step
3: define the connection
URL
9
String
url = "jdbc:odbc:personDSN";
10
//Step
4: establish the connection
11
Connection
con =
DriverManager.getConnection(url);
12
//Step 5:
creating PrepareStatement by passing
sql and
13
//ResultSet's
constants so that the ResultSet that
will
14
//produce
as a result of executing query
will be
15
//scrollable
& updatable
16
String
sql = "SELECT * FROM
Person";
17
PreparedStatement
pStmt = con.prepateStatement(sql,
18
ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE,
19
ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE);
20
//Step
6: execute the query
21
ResultSet
rs = pStmt.executeQuery();
22
//
moving cursor forward i.e.
first row
23
rs.next(
);
24
//
printing column "name" value
of current row
(first)
25
System.out.println("moving
cursor forward");
26
String
name = rs.getString("Name");
27
System.out.println(name);
125
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
28
//
moving cursor forward i.e.
on to second row
29
rs.next(
);
30
//
moving cursor backward i.e
to first row
31
rs.previous(
);
32
//
printing column "name" value
of current row
(first)
33
System.out.println("moving
cursor forward");
34
name
= rs.getString("Name");
35
System.out.println(name);
36
//Step
8: close the connection
37
con.close();
38
}catch(Exception
sqlEx){
39
System.out.println(sqlEx);
40
}
41
} // end
main
42
43
} //
end class
Compile
& Execute:
The
sample output is given
below:
Useful
ResultSet's Methods (cont.)
absolute(int)
-Moves
the cursor to the given row number in the
ResultSetobject.
-If
given row number is positive,
moves the cursor forward
with respect to beginning of the
result set.
-If the
given row number is negative, the
cursor moves to the absolute row
position with respect to
the
end of the
result set.
-For
example, calling absolute(-1)
positions the cursor on the last row;
calling absolute(-2) moves
the
cursor
to next-to-last row, and so
on.
-Throws
Exception if ResultSet type is
TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY
updaters
(for primitives, String and
Object)
-Used to update
the column values in the current row or
in insert row (discuss
later)
-Do
not update the underlying
database
-Each
update method is overloaded; one that
takes column name while
other takes column index.
For
example
String updater are available
as:
updateString(String
columnName, String
value)
updateString(String
columnIndex, String
value)
updateRow(
)
-Updates the
underlying database with new
contents of the current row of
this ResultSetobject
Example
Code 16.2: Updating values
in existing rows
The
following code example
updates the Name
column
in the second row of the ResultSet object
rs and
126

Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
then
uses the method updateRow to update the
Person table in
database.
This
code is the modification of the last one.
Changes made are shown in
bold face.
1
//
File ResultSetEx.java
2
import
java.sql.*;
3
public
class ResultSetEx {
4
public
static void main (String args[ ])
{
5
try
{
6
//Step
2: load driver
7
Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
8
//Step
3: define the connection
URL
9
String
url = "jdbc:odbc:personDSN";
10
//Step
4: establish the connection
11
Connection
con =
DriverManager.getConnection(url);
12
//Step
5: create PrepareStatement by passing
sql and
13
// ResultSet
appropriate fields
14
String
sql = "SELECT * FROM
Person";
15
PreparedStatement
pStmt = con.prepateStatement(sql,
16
ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE,
17
ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE);
18
//Step
6: execute the query
19
ResultSet
rs = pStmt.executeQuery();
20
//
moving cursor to second
row
21
rs.absolute(2);
nd
22
// update
address column of 2 row in
rs
23
rs.updateString("Address",
"model town");
24
// update the
row in database
25
rs.updateRow(
);
26
//Step
8: close the connection
27
con.close();
28
}catch(Exception
sqlEx){
29
System.out.println(sqlEx);
30
}
31
} // end
main
32
} //
end class
Compile
& Execute
nd
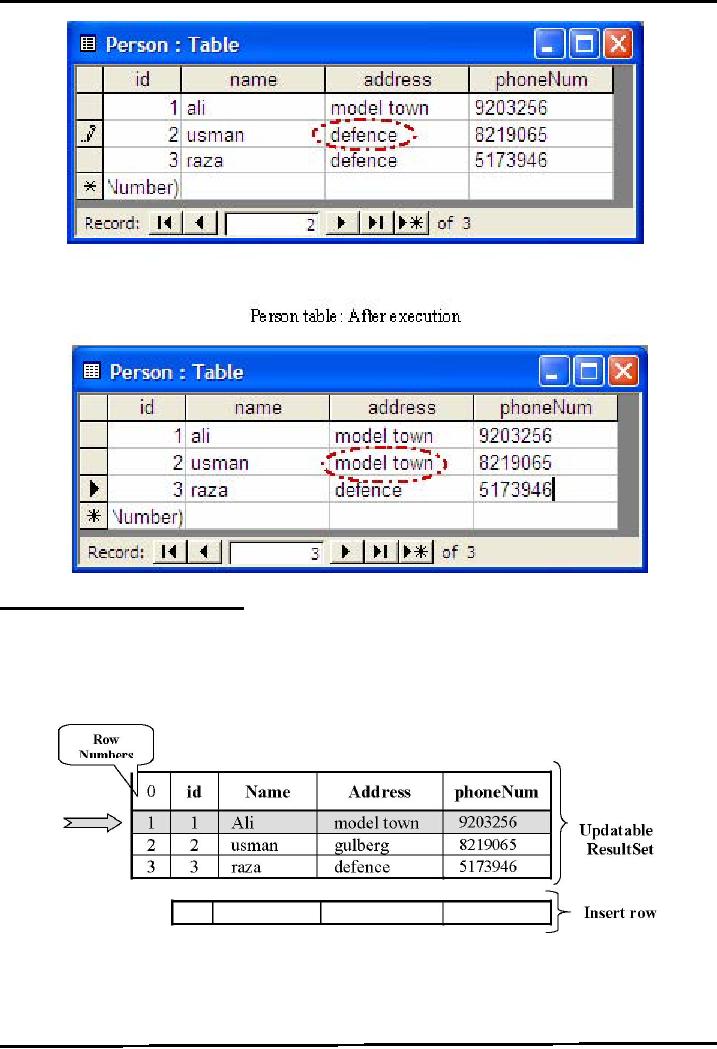
Given
below are two states of
Person table. Notice that
address of 2 row is updated. Person
table:
Before
execution
127
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
Person
table: After
execution
Useful
ResultSet's Methods (cont.)
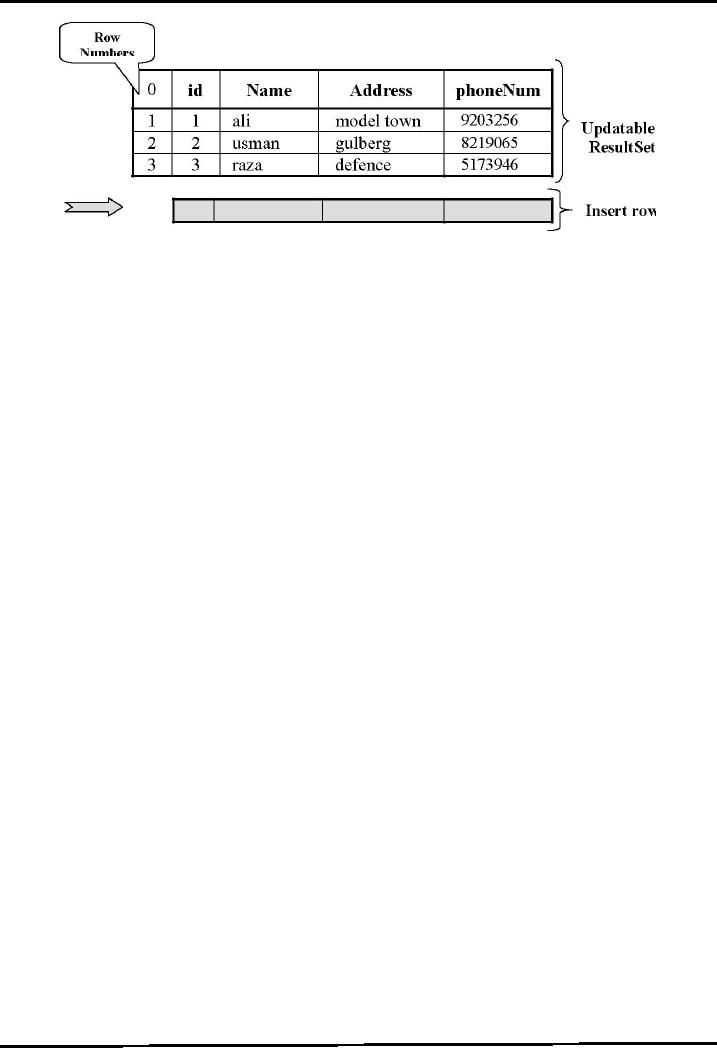
. moveToInsertRow(int)
-An
updatable resultset object
has a special row associate
with it i.e.
insert
row -Insert row a
buffer, where a new row may
be constructed by
calling
updater methods. -Doesn't insert the
row into a result set or
into a
databse.
-For
example, initially cursor is
positioned on the first row as shown in
the diagram.
-By
calling moveToInsertRow( ), the
cursor
128
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
129
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
19
ResultSet
rs = pStmt.executeQuery();
20
//
moving cursor to insert
row
21
rs.moveToInsertRow();
22
//
updating values in insert
row
23
rs.updateString(
"Name" , "imitiaz" );
24
rs.updateString(
"Address" , "cantt" );
25
rs.updateString(
"phoneNum" , "9201211" );
26
//
inserting row in resultset &
into database
27
rs.insertRow(
);
28
//Step
8: close the connection
29
con.close();
30
}catch(Exception
sqlEx){
31
System.out.println(sqlEx);
32
}
33
} // end
main
34
} //
end class
Compile
& Execute
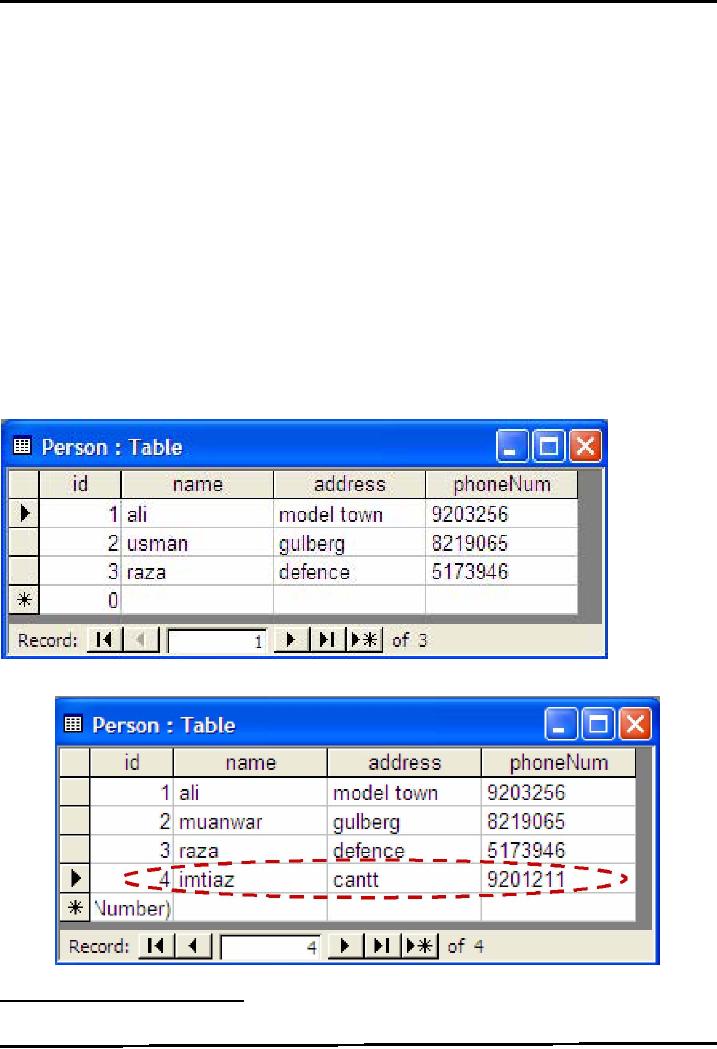
Given
below are two states of
Person table. Note that
after executing program, a
newly added row is
present.
Person
table: Before
execution
Person
table: After
execution
Useful
ResultSet's Methods (cont.)
. last( ) &
first( )
130

Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
the ResultSet is
TYPE_FORWARD_ONLY
. getRow(
)
-Returns the
current row number
-As
mentioned earlier, the first
row has index 1 and so
on.
. deleteRow(
)
-Deletes the
current row from this
ResultSet object and from the underlying
database.
-Throws
exception if the cursor is on the insert
row.
Example
Code 16.4: Deleting existing
row
The
given below example code
shows the usage of last( ),
getRow( ) and deleteRow( )
method.
This
code is also the modification of the last
one. Changes made are shown in
bold face.
1
//
File ResultSetEx.java
2
import
java.sql.*;
3
public
class ResultSetEx {
4
public
static void main (String args[ ])
{
5
try
{
6
//Step
2: load driver
7
Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
8
//Step
3: define the connection
URL
9
String
url = "jdbc:odbc:personDSN";
10
//Step
4: establish the connection
11
Connection
con =
DriverManager.getConnection(url);
12
//Step
5: create PrepareStatement by passing
sql and
13
// ResultSet
appropriate fields
14
String
sql = "SELECT * FROM
Person";
15
PreparedStatement
pStmt = con.prepateStatement(sql,
16
ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE,
17
ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE);
18
//Step
6: execute the query
19
ResultSet
rs = pStmt.executeQuery();
20
//
moves to last row of the
resultset
21
rs.last();
22
//
retrieving the current row
number
23
int
rNo = rs.getRow();
24
System.out.println("current
row number" +
rNo);
25
// delete
current row from rs & db
i.e. 4 because
26
//
previously we have called last()
method
27
rs.deleteRow(
);
28
//Step
8: close the connection
29
con.close();
30
}catch(Exception
sqlEx){
31
System.out.println(sqlEx);
32
}
33
} // end
main
34
} //
end class
Compile
& Execute
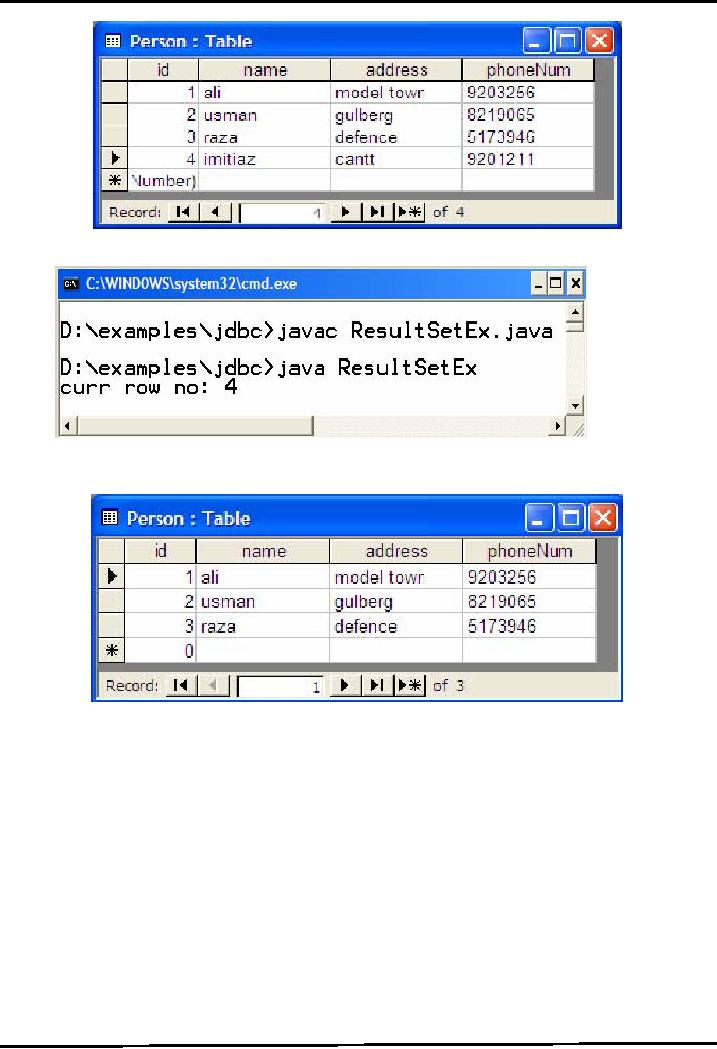
The
first diagram shows the
Person table before
execution. Person table:
Before execution
131
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
Execution
program from command prompt
will result in displaying
current row number on console.
This
can
be
confirmed
from
following
diagram.
After
execution, the last row (4) is
deleted from ResultSet as well as
from database. The Person
table is
shown
after execution
Person
table: After
execution
References:
Entire
material for this handout is
taken from the book JAVA A
Lab Course by Umair
Javed.
This
material
is available just for the
use of VU students of the course Web
Design and Development and not
for
any
other commercial purpose without the
consent of author.
132
Table of Contents:
- JAVA FEATURES
- Java Virtual Machine & Runtime Environment
- Learning Basics of JAVA
- JAVA: Object Oriented Programming
- JAVA: Inheritance
- JAVA: Collections
- JAVA: Intro to Exceptions
- JAVA: Streams
- JAVA: Modification of Address Book Code
- JAVA: Graphical User Interfaces
- JAVA: Event Handling
- JAVA: More Examples of Handling Events
- JAVA: Problem in Last Code Example
- Java Database Connectivity
- JAVA: More on JDBC
- JAVA: Result Set
- JAVA: Meta Data
- Java Graphics
- JAVA: How to Animate
- JAVA Applets
- JAVA: Socket Programming
- JAVA: Serialization
- JAVA: Multithreading 1
- JAVA: Multithreading 2
- JAVA Web Application Development
- Java Servlets
- JAVA: Creating a Simple Web Application in Tomcat
- JAVA: Servlets Lifecycle
- JAVA: More on Servlets
- JAVA: Dispatching Requests
- JAVA: Session Tracking 1
- JAVA: Session Tracking 2
- JAVA: AddressBook Case Study Using Sevlets
- Java Server Pages 1
- JavaServer Pages 2
- Java Server Pages 3
- JAVA: JSP Action Elements and Scope
- JAVA: JSP Custom Tags
- JAVA: MVC + Case Study
- JAVA: MVC Model 2 Architecture
- JAVA: Layers and Tiers
- JAVA: Expression Language
- JAVA: JavaServer Pages Standard Tag Library (JSTL)
- JAVA: Client Side Validation & JavaServer Faces (JSF)
- JAVA: JavaServer Faces