 |
Java Database Connectivity |
| << JAVA: Problem in Last Code Example |
| JAVA: More on JDBC >> |
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
Lesson
14
Java
Database Connectivity
Introduction
Java
Database Connectivity (JDBC)
provides a standard library
for accessing databases. The
JDBC API
contains number of
interfaces and classes that
are extensively helpful
while communicating with
a
database.
The
java.sql package
The
java.sql package contains basic &
most of the interfaces and classes. You
automatically get this
package
when you download the
J2SETM. You have to import
this package whenever you
want to interact
with
a relational database.
Connecting
With Microsoft
Access
In
this handout, we will learn
how to connect & communicate with
Microsoft Access Database.
We
chooses
Access because most of you
are familiar with it and if
not than it is very easy to
learn.
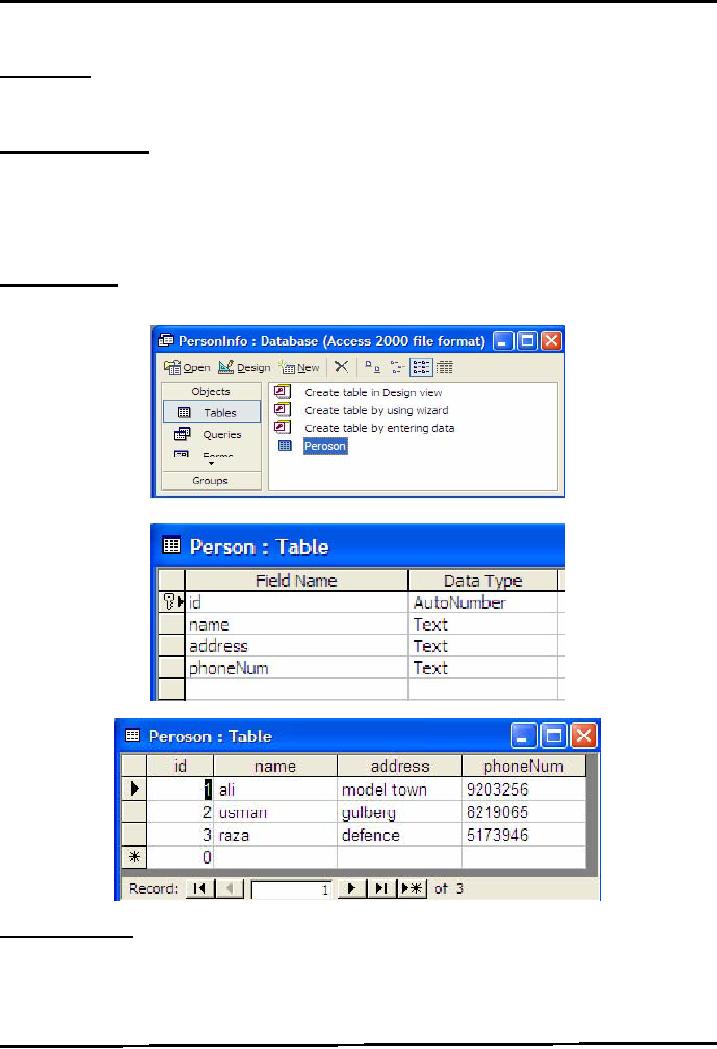
Create
Database
In
start create a database
"PersonInfo" using Microsoft
Access. Create one table
named "Person". The
schema
of the table is shown in the
picture.
Add
the following records into
Person table as shown
below.
Save
the data base in some
folder. (Your database will
be saved as an .mdb file)
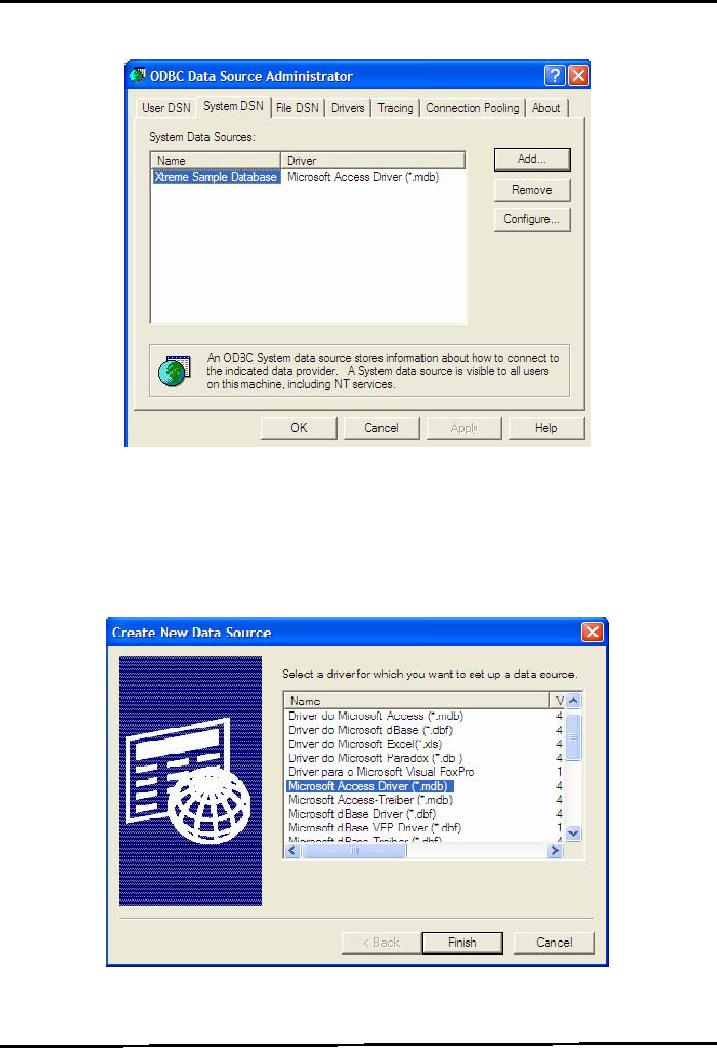
Setup
System DSN
After
creating database, you have to
setup a system Data Source
Name (DSN). DSN is a
name
through
which your system recognizes
the underlying data
source.
Select
Start Settings Control Panel Administrative
Tools Data Sources
(ODBC).
The
ODBC Data Source Administrator
window would be opened as shown below.
Select System
DSN
tab. (If you are unable to
use System DSN tab due to
security restrictions on your
machine,
115
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
you
can use the User DSN
tab)
Press
Add... button and choose
Microsoft Access Driver
(*.mdb) from Create New Data
Source
window
and press Finish button as shown in
diagram.
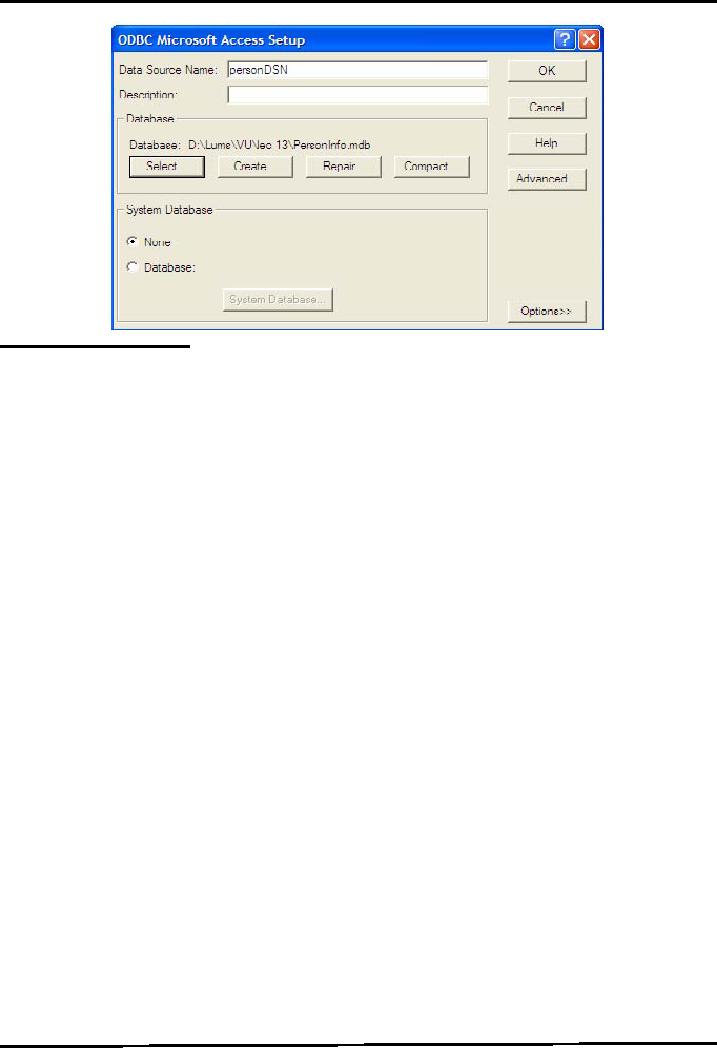
After
that, ODBC Microsoft Access
Setup window would be opened as shown in
following
diagram
Enter
the Data Source Name personDSN
and select the database by
pressing Select button.
The
browsing
window would be opened, select the
desired folder that contains the database
(The
database
.mdb file you have created
in the first step) Press Ok
button.
116
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
Basic
Steps in Using
JDBC
There
are eight (8) basic
steps that must be followed
in order to successfully communicate with a
database.
Let's
take a detail overview of
all these one by one.
1.
Import Required Package
Import
the package java.sql.* that contains
useful classes and interfaces to
access & work
with
database.
import
java.sql.*;
2. Load
Driver
Need
to load suitable driver for
underlying database.
Different
drivers & types for different
databases are
available.
For
MS Access, load following
driver available with
j2se.
Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
For
Oracle, load the following driver.
You have to download it
explicitly.
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
3.
Define Connection
URL
To get a
connection, we need to specify the
URL of a database (Actually we
need to specify
the
address of the database which is in the
form of URL)
As we
are using Microsoft Access
database and we have loaded a
JDBC-ODBC driver.
Using
JDBC-ODBC
driver requires a DSN which we have
created earlier and named it
personDSN.
So the
URL of the database will
be
String
conURL = "jdbc:odbc:personDSN";
4. Establish
Connection With
DataBase
Use
DriverManagerto get the connection
object.
The
URL of the database is passed to the
getConnection method. Connection con
=
DriverManager.getConnection(conURL);
If
DataBase requires username &
password, you can use the
overloaded version of
getConnection
method as shown
below:
String
usr = "umair";
String
pwd = "vu";
Connection
con = null;con =
DriverManager.getConnection(conURL, usr,
pwd);
5. Create
Statement
A
Statement object is obtained
from a Connection
object.
Statement
stmt = con.createStatement( );
117

Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
Once
you have a statement, you
can use it for various
kinds of SQL queries.
6.
Execute a Query
The
next step is to pass the SQL
statements & to execute them.
Two
methods are generally used
for executing SQL queries.
These are:
executeQuery(sql)
method
Used
for SQL SELECT
queries.
Returns
the ResultSET object that contains the
results of the query and can
be used to access the
query
results.
String
sql = "SELECT * from sometable";ResultSet
rs =
stmt.executeQuery(sql);
executeUpdate(sql)method
.
This
method is used for executing an update
statement like INSERT,
UPDATE or
7.
DELETE
Returns
an Integer value representing the number of rows
updated
String
sql = "INSERT INTO tablename " +
"(columnNames) Values (values)"
;
int
count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
Process
Results of the
Query
The
ResultSet provides various getXXX
methods that takes a column
index or name and returns
the
data
The
ResultSet maintains the data in the form
tables (rows & columns)
First
row has index 1, not
0.
The
next method of ResultSet returns true or false
depending upon whether the
next row is
available
(exist) or not and moves the
cursor
Always
remember to call next() method at-least
once
To
retrieve the data of the column of the
current row you need to
use the various getters
provided
by the
ResultSet.
For
example, the following code
snippet will iterate over
the whole ResultSet and illustrates
the
usage
of getters methods
while
( rs.next() ){
//by
using column name
String
name = rs.getString("columnName");
// or by
using column indexString
name = rs.getString(1);
}
8.
Close the
Connection
An
opening connection is expensive, postpone
this step if additional
database operations are
expected
con.close();
Example
Code 14.1: Retrieving Data
from ResultSet
The
JdbcEx.java demonstrates the usage of
all above explained steps. In
this code example, we
connect
with
the PersonInfo database, the one we have
created earlier, and then
execute the simple SQL
SELECT
query
on Person table, and then
process the query
results.
//
File JdbcEx.java
//step 1:
import packageimport
java.sql.*;
public
class JdbcEx {
public
static void main (String args[ ])
{
try
{
//Step 2:
load
driverClass.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
//Step
3: define the connection
URL
String
url = "jdbc:odbc:personDSN";
118
Web
Design & Development CS506
VU
//Step
4: establish the connection
Connection
con =
DriverManager.getConnection(url);
//Step 5:
create Statement
Statement
st = con.createStatement();
//Step 6:
preapare & execute the query
String
sql = "SELECT * FROM
Person";
ResultSet
rs = st.executeQuery(sql);
//Step 7:
process the results
while(rs.next()){
//
The row name is "name" in
database "PersonInfo,//
hence specified in the
getString()
method.
String
name = rs.getString("name");String add =
rs.getString("address");String
pNum
= rs.getString("phoneNum");
System.out.println(name
+ " " + add + " " + pNum);}
//Step
8: close the connection
con.close();
}catch(Exception
sqlEx){
System.out.println(sqlEx);
}
} // end
main} // end class
The
important thing you must
notice that we have put all
code inside try block and
then handle (in the
above
example, only printing the
name of the exception raised) exception
inside catch block.
Why?
Because we are dealing with
an external resource (database). If
you can recall all IO
related
operations
involving external resources in
java throw exceptions. These exceptions
are checked exceptions
and
we must need to handle these
exceptions.
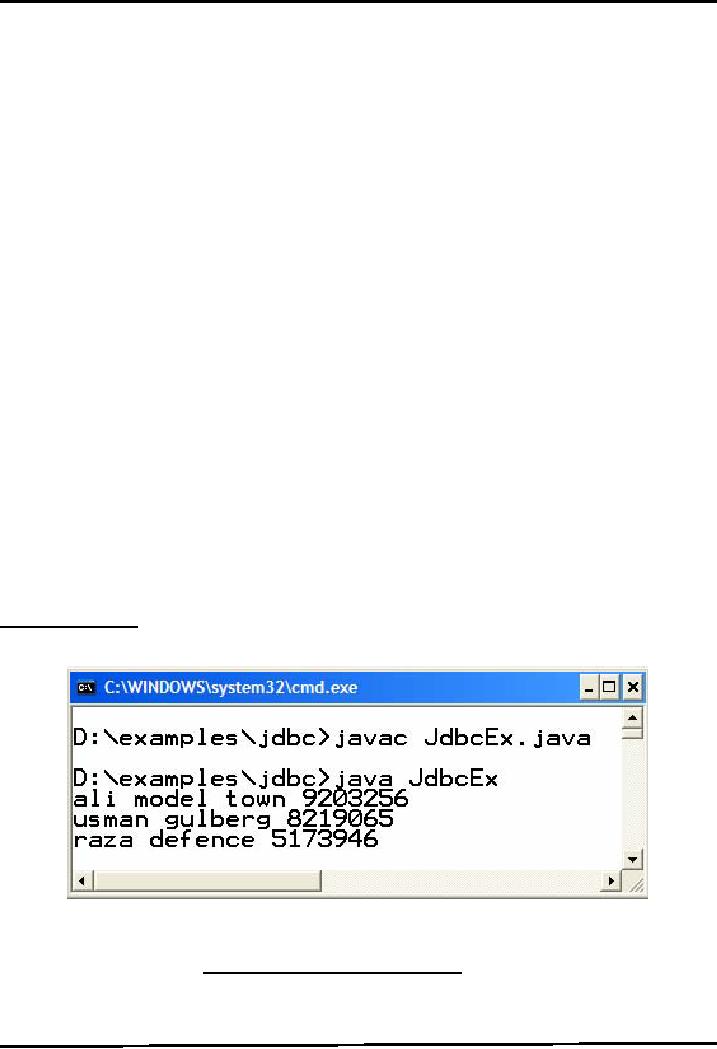
Compile
& Execute
Since the
Person table contains only three
records, so the following output
would be produced on executing
the
above program.
References:
.
Java A Lab Course by
Umair Javed
.
Java tutorial by Sun:
http://java.sun.com/docs/books/turorial
.
Beginning Java2 by Ivor
Hortan
119
Table of Contents:
- JAVA FEATURES
- Java Virtual Machine & Runtime Environment
- Learning Basics of JAVA
- JAVA: Object Oriented Programming
- JAVA: Inheritance
- JAVA: Collections
- JAVA: Intro to Exceptions
- JAVA: Streams
- JAVA: Modification of Address Book Code
- JAVA: Graphical User Interfaces
- JAVA: Event Handling
- JAVA: More Examples of Handling Events
- JAVA: Problem in Last Code Example
- Java Database Connectivity
- JAVA: More on JDBC
- JAVA: Result Set
- JAVA: Meta Data
- Java Graphics
- JAVA: How to Animate
- JAVA Applets
- JAVA: Socket Programming
- JAVA: Serialization
- JAVA: Multithreading 1
- JAVA: Multithreading 2
- JAVA Web Application Development
- Java Servlets
- JAVA: Creating a Simple Web Application in Tomcat
- JAVA: Servlets Lifecycle
- JAVA: More on Servlets
- JAVA: Dispatching Requests
- JAVA: Session Tracking 1
- JAVA: Session Tracking 2
- JAVA: AddressBook Case Study Using Sevlets
- Java Server Pages 1
- JavaServer Pages 2
- Java Server Pages 3
- JAVA: JSP Action Elements and Scope
- JAVA: JSP Custom Tags
- JAVA: MVC + Case Study
- JAVA: MVC Model 2 Architecture
- JAVA: Layers and Tiers
- JAVA: Expression Language
- JAVA: JavaServer Pages Standard Tag Library (JSTL)
- JAVA: Client Side Validation & JavaServer Faces (JSF)
- JAVA: JavaServer Faces