 |
Characteristics of a High-Quality WBS |
| << WBS- A Mandatory Management Tool |
| Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) >> |

Software
Project Management
(CS615)
LECTURE
# 34
7.
Work Breakdown Structure
7.4
WBS-
A Mandatory Management
Tool
h)
Characteristics of a High-Quality
WBS
a) Review
and signoff from top to
bottom
b)
Includes logical flow and is
hierarchical in nature
c) Clear
and concise
d)
Provides ability to roll-up
information to higher
levels
e) Receives
100% team buy-in
f) Should
have at least 2 levels: Level 1
defines 100% of the
service/product/result;
Level 2
defines the deliverables in
terms of work
(groupings)
g)
Project Management (and
sub-contract management) at Level
2.
h) The
deliverables in the WBS must
match the scope or contract
(WBS should not
contain
work that is not defined in
the scope Scope should
not describe work
not
contained in the WBS)
i) All
deliverables should be accounted
for regardless of
responsibility
j) Every
WBS element should be
clearly defined or should be
clarified in the WBS
Dictionary
k)
Features
The
WBS should contains 100% of
the work defined by the
scope or contract
Development
of WBS should involve the
entire project team
Should be
deliverable-oriented
Should
captures all deliverables (Internal,
External, Interim) in terms of
work to
be
completed
l)
Usefulness
248

Software
Project Management
(CS615)
Should
define the context of the
project and clarifies the
work
Should
communicates project scope to
all stakeholders in terms of
the
work to
be completed
Is "in
sync" with the scope
statement and project
schedule
Implies
and allows for continual
improvement/update of the WBS
to
maintain
current-ness and "vitality" within
the project
m) WBS Is
Not
A single
document that substitutes
for the project schedule or
project plan
The
project schedule
A listing
of tasks or activities
i) Types
of WBS
The
two types of Work Breakdown
Structures are:
a)
Program Work Breakdown
Structures
b)
Contract Work Breakdown
Structures
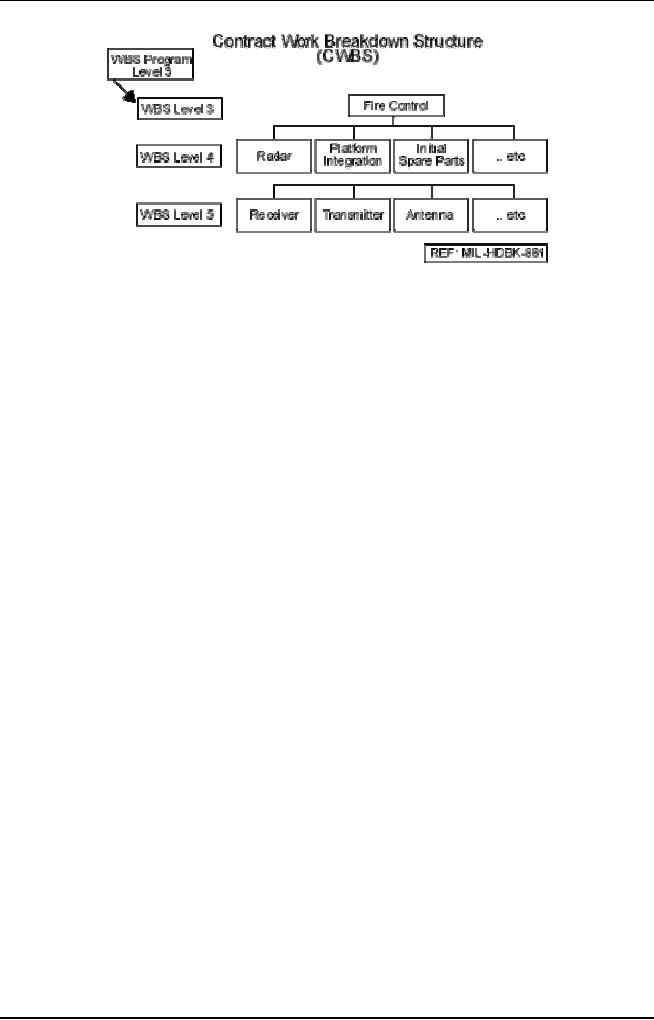
a) Contract
WBS
A
Contract WBS extends the
Program WBS to a lower level
in order to provide
management and cost
information to the Government. It
includes all the
elements
for
products (e.g., hardware,
software, data, or services)
that are the
responsibility
of the
contractor. It must be consistent
with the Program
WBS.
249
Software
Project Management
(CS615)
Contract
WBS: Contractor's
Responsibility
Contractors
may extend the work
breakdown structure to whatever
level they feel
is
necessary to manage the
program. Contractors also use
the Contract WBS to
define
work packages. Work packages
are:
Discrete
portions of the project that
can be charged to a single
organization.
Building
blocks for program management and cost
reporting.
Remember
that a Contract WBS:
�
Is
prepared and maintained by each
contractor working on different
portions
of the
program.
�
Includes
the number of levels thought
sufficient by the contractor to
manage
the
program.
�
Must be
updated if changes are made to
the Program WBS.
b) Program
WBS
A Program
WBS is defined as "the work
breakdown that covers the
acquisition of
a
specific defense materiel
item and is related to contractual
effort."
A Program
WBS is:
�
Tailored
to each specific
program.
�
Prepared
and maintained by the
Government.
�
Provides
a basis for developing the
Contract WBS.
Program
WBS Levels
250
Software
Project Management
(CS615)
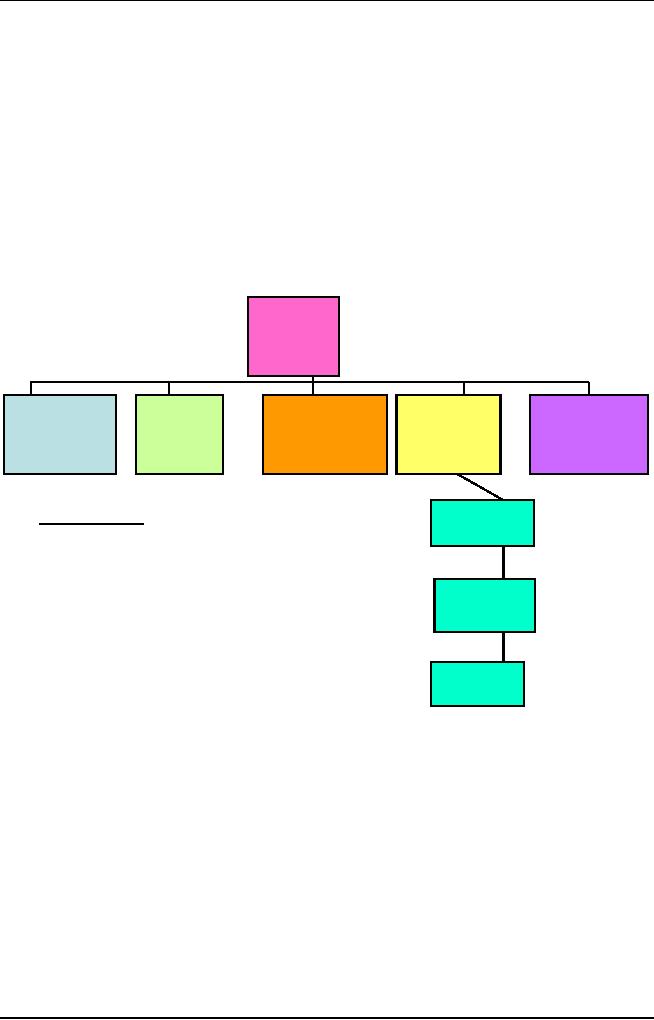
Typically,
a Program WBS consists of the
upper three levels.
WBS
Level 1:
The
entire defense materiel
item.
WBS
Level 2:
Major
elements of the defense
materiel item, which are
subordinate
to Level
1.
WBS
Level 3:
Elements
subordinate to Level 2
elements.
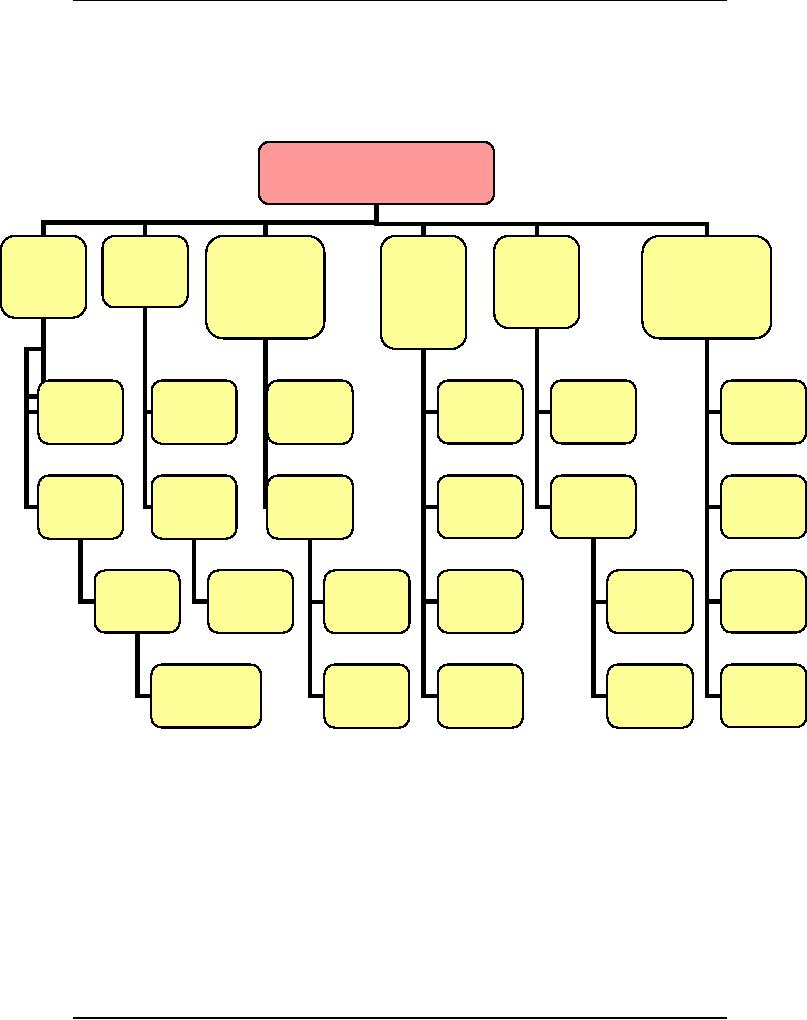
j) Sample
WBS
Sample 1: A
Product WBS
Software
Project
Documentation
Design
Software
Training
&
Project
&
System
BPR
Management
Engineering
What
About?
Web
based
Requirements
Prototyping
Classroom
Testing
User
Acceptance
Life-cycle
Management
Hands-on
Warranty
251
Software
Project Management
(CS615)
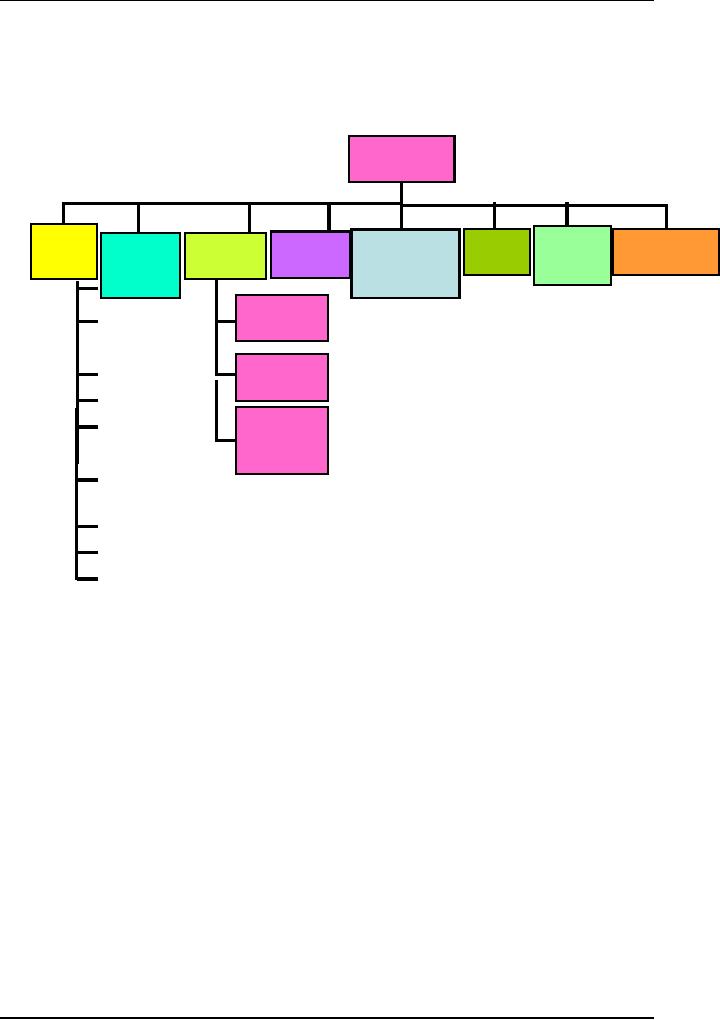
WBS
Sample 2: System
Development Projects
Level
1
Project
Level
2
Software
Hardware
Project
System
System
Data
1.2
Mgt
Test
1.1
Engr
Mgt
1.4
1.5
1.3
1.6
Level
3
1.1.2
1.2.2
1.1.2.1
Level
4
1.1.2.1.1
Level
5
252
Software
Project Management
(CS615)
WBS
Sample 3: Software/Hardware
System Development
Project
A
Level
1
1.7
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.6
1.8
1.5
Project
Support
System
Installation
Deliverables
Hardware
Software
Systems
Mgt.
Services
Test
Mgt.
Engr.
Level
2
Software
Build
1.3.1
Unit
1.3.2
Level
3
Testing
Software
1.3.3
Design
READING
REFERENCE:
For
detailed reading refer
to:
(i)
Chapter
No. 6 entitled "How to handle
large projects: Divide and
Conquer"
of "Software Project management A
Practitioner
Approach
by E. M. BENNATAN.
(ii)
Chapter
5 entitled Software Project
Planning" of: SEA
Practitioner
Approach by Roger S. Pressman.
(iii)
Chapter 7 entitled "Software
Project Estimation: Tools
and
Techniques
by NIIT
253
Table of Contents:
- Introduction & Fundamentals
- Goals of Project management
- Project Dimensions, Software Development Lifecycle
- Cost Management, Project vs. Program Management, Project Success
- Project Management’s nine Knowledge Areas
- Team leader, Project Organization, Organizational structure
- Project Execution Fundamentals Tracking
- Organizational Issues and Project Management
- Managing Processes: Project Plan, Managing Quality, Project Execution, Project Initiation
- Project Execution: Product Implementation, Project Closedown
- Problems in Software Projects, Process- related Problems
- Product-related Problems, Technology-related problems
- Requirements Management, Requirements analysis
- Requirements Elicitation for Software
- The Software Requirements Specification
- Attributes of Software Design, Key Features of Design
- Software Configuration Management Vs Software Maintenance
- Quality Assurance Management, Quality Factors
- Software Quality Assurance Activities
- Software Process, PM Process Groups, Links, PM Phase interactions
- Initiating Process: Inputs, Outputs, Tools and Techniques
- Planning Process Tasks, Executing Process Tasks, Controlling Process Tasks
- Project Planning Objectives, Primary Planning Steps
- Tools and Techniques for SDP, Outputs from SDP, SDP Execution
- PLANNING: Elements of SDP
- Life cycle Models: Spiral Model, Statement of Requirement, Data Item Descriptions
- Organizational Systems
- ORGANIZATIONAL PLANNING, Organizational Management Tools
- Estimation - Concepts
- Decomposition Techniques, Estimation – Tools
- Estimation – Tools
- Work Breakdown Structure
- WBS- A Mandatory Management Tool
- Characteristics of a High-Quality WBS
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- WBS- Major Steps, WBS Implementation, high level WBS tasks
- Schedule: Scheduling Fundamentals
- Scheduling Tools: GANTT CHARTS, PERT, CPM
- Risk and Change Management: Risk Management Concepts
- Risk & Change Management Concepts
- Risk Management Process
- Quality Concept, Producing quality software, Quality Control
- Managing Tasks in Microsoft Project 2000
- Commissioning & Migration