 |
Quality Assurance Management, Quality Factors |
| << Software Configuration Management Vs Software Maintenance |
| Software Quality Assurance Activities >> |

Software
Project Management
(CS615)
LECTURE
# 18
2.
Software Development
Fundamentals
Technical
Fundamentals
2.15
Quality
Assurance Management
⇒ Definition
According
to American Heritage Dictionary,
quality is defined as "an inherent
or
distinguishing
characteristic or a property".
The
distinguishing characteristics of a
software product are the
cyclomatic
complexity,
cohesion, function points, and
lines of code. These
characteristics of
a
software product define the
quality of the
product.
·
The US
DOD (1988) defines software
quality rather simply
as:
The
ability of a software product to
satisfy its specified
requirements.
·
The
British Standards Institution
(1986) has stated
that:
"Quality
is in the eye of the beholder, a
matter, of the client's
judgment."
⇒ Quality
Standards and Procedures
The
quality of software is said to be
high if it meets the
standards and procedures,
defined
for the product. Standards
are criteria to which the
products are compared.
For
example, there may be
standards that govern the
quality review
process.
Documentation
standard design standard and code standard are
the three types of
standards
that software projects
usually follow.
Documentation
standard specifies the form and content
for planning, control,
and
product
documentation. Design standards
provide rules and methods
for
translating
the software requirements
into software design. The design
standards
are
specified in the form and
content of the product
design.
Unlike
documentation standard, code standard
defines the language in
which code
should be
written. The standard clearly
mentions the structures,
style conventions,
and rules
for data structures and
interfaces that will be implemented in
the project.
118

Software
Project Management
(CS615)
Procedures
are criteria to which the
development and control processes
are
compared.
Procedures are explicit
steps followed in a process.
Procedures need to
be
properly documented because
they are needed for
configuration management,
nonconformance
reporting, corrective action,
testing, and formal
inspections.
Proper
documentation of procedures is necessary
because SQA activities rely
on
them
for project compliance.
Organizations normally enforce
quality standards
with
the help of checklists,
common error lists, and
standards and guidelines.
⇒ Concepts
Product
quality depends on its
conformance to software
requirements,
development
standards, and implicit
requirements.
During
software development, the
quality of a product depends on
the quality of
the
design.
The
quality of product design, in turn,
depends on how effectively
the product
designer captures
the client requirements and
specifications. At times, the
client
has
some implicit requirements
that are not captured in
the requirements
document.
There are three things
that guide requirements:
want, desire, and wish.
Usually,
wants are captured
explicitly in the requirements
documents. However, if
you
manage to capture desires and
wishes, the product becomes
a great success.
The
product designer needs to state
these implicit requirements
clearly during
analysis.
The adherence to these
implicit requirements is the
key attribute that
sets
one
product apart from
another.
The
product quality also depends on
how strictly, and to what
degree the
developer
adheres to design specifications. This is
what the concept quality
is
meeting
or exceeding our client's
needs and requirements'
means.
The
product quality is said to be
high if the product is
manufactured according to
design
specifications.
⇒ Quality
Control
Quality
control is a series of review
activities, such as:
·
Inspections
·
Reviews
and
·
Tests,
used throughout the SDLC of
the software product
The
objective of quality control is to
find problems as early as possible and
fix
them.
Quality
control ensures that the
software product meets the
requirements defined
at every
stage in its
development.
119

Software
Project Management
(CS615)
There is
provision for feedback mechanism
during quality control. Any
slippage
in
meeting the requirements
during the development
process is communicated to
the
development team immediately.
Feedback
ensures that errors or
misses found during quality
control are rectified
as soon as
they are detected.
During
software development, quality
control plays a valuable
role by evaluating
products
against standards and
specifications.
Quality
control activities can be fully automated
manual, or a combination of
these.
Quality control involves
monitoring specific project
results to determine
if:
They
comply with relevant quality
standards
Identifying
ways to eliminate causes of
unsatisfactory results.
Project
results include both:
Product
results, such as deliverables,
and
Project
management results, such as cost and
schedule performance.
⇒ Quality
Factors
There
are a number of factors that
determine the quality of a
software product.
These
factors can be measured either
directly or indirectly. McCall
(MCC77) and
his
colleagues proposed some
software quality factors
based on three most
important
aspects of a software
product:
1.
Product operation
2.
Product revision and
3.
Product transition
1.
Product Operation Factors
The
product operation factors
determine the quality of
software when a
program
is executed. Good quality
software is not only correct
and reliable
but also
delivers correct performance in
all circumstances. Some of
the factors
of
product operation are correctness,
reliability, efficiency, integrity,
and
usability.
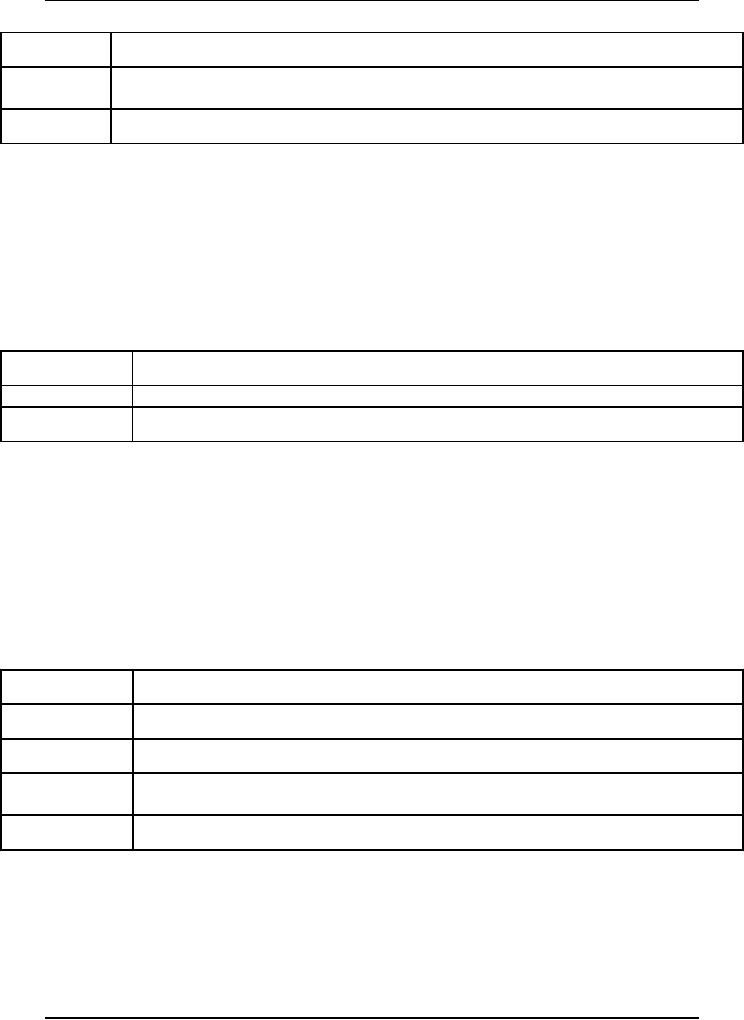
You can look at the factor
description in Table 1.
Table
1:
Product
Operation Factors
Accuracy
of the program and the
extent to which it fulfills design
specifications
Correctness
Extent to
which the program is secure
and its ability to recover
quickly from failure.
Reliability
120
Software
Project Management
(CS615)
Performance
of the program and its
ability to perform tasks
within a time frame
Efficiency
Ability
of the program to take care of
security and the extent to
which it can prevent
Integrity
unauthorized.
Ease
with which a user can learn,
operates, and uses the
program.
Usability
2.
Product Revision Factors
Product
revision factors focus on
the ease of maintenance of
the software
product.
Maintenance tasks could be
either correcting faults in
the original
design or
making improvements to adapt
the functionality to
changing
environments.
Product revision covers the
following factors:
maintainability,
flexibility,
and testability. These factors are
described in Table 2.
Table
2:
Product
Revision Factors
Maintainability
Ease
with which a program is
debugged.
Ease
with which a program is
modified.
Flexibility
Ease
with which a program is
tested.
Testability
3.
Product Transition Factors
The
product transition factors
determine the quality of
programs that are
designed
for open systems. Here the
focus is more on the
portability and
reusability
of a software product. To help a
system run on different
platforms,
certain
parts of a system may be reused. The
product transition factors
are
portability,
reusability, interoperability,
configurability, and
expandability.
These
factors are described in
Table 3.
Table
3:
Product
Transition Factors
Efficiency
with which a program runs on
different platforms or operating
systems
Portability
Extent to
which the program can be
used in more than one
program or system
Reusability
Interoperability
Effort
needed to transfer a program to
another system
Ability
of the program to be installed at
more than one location with
different
Configurability
features
at each location
Ability
of the program to support an
increase in data and
users
Expandability
121
Table of Contents:
- Introduction & Fundamentals
- Goals of Project management
- Project Dimensions, Software Development Lifecycle
- Cost Management, Project vs. Program Management, Project Success
- Project Management’s nine Knowledge Areas
- Team leader, Project Organization, Organizational structure
- Project Execution Fundamentals Tracking
- Organizational Issues and Project Management
- Managing Processes: Project Plan, Managing Quality, Project Execution, Project Initiation
- Project Execution: Product Implementation, Project Closedown
- Problems in Software Projects, Process- related Problems
- Product-related Problems, Technology-related problems
- Requirements Management, Requirements analysis
- Requirements Elicitation for Software
- The Software Requirements Specification
- Attributes of Software Design, Key Features of Design
- Software Configuration Management Vs Software Maintenance
- Quality Assurance Management, Quality Factors
- Software Quality Assurance Activities
- Software Process, PM Process Groups, Links, PM Phase interactions
- Initiating Process: Inputs, Outputs, Tools and Techniques
- Planning Process Tasks, Executing Process Tasks, Controlling Process Tasks
- Project Planning Objectives, Primary Planning Steps
- Tools and Techniques for SDP, Outputs from SDP, SDP Execution
- PLANNING: Elements of SDP
- Life cycle Models: Spiral Model, Statement of Requirement, Data Item Descriptions
- Organizational Systems
- ORGANIZATIONAL PLANNING, Organizational Management Tools
- Estimation - Concepts
- Decomposition Techniques, Estimation – Tools
- Estimation – Tools
- Work Breakdown Structure
- WBS- A Mandatory Management Tool
- Characteristics of a High-Quality WBS
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- WBS- Major Steps, WBS Implementation, high level WBS tasks
- Schedule: Scheduling Fundamentals
- Scheduling Tools: GANTT CHARTS, PERT, CPM
- Risk and Change Management: Risk Management Concepts
- Risk & Change Management Concepts
- Risk Management Process
- Quality Concept, Producing quality software, Quality Control
- Managing Tasks in Microsoft Project 2000
- Commissioning & Migration