 |
Attributes of Software Design, Key Features of Design |
| << The Software Requirements Specification |
| Software Configuration Management Vs Software Maintenance >> |

Software
Project Management
(CS615)
LECTURE
# 16
2.
Software Development
Fundamentals
Technical
Fundamentals
2.12
Design
⇒ Management
Aspect
Major
design styles
·
Object, structured, data-structured
design
Foundational
design concepts
·
Information hiding, abstraction,
encapsulation, Inheritance,
basic
algorithms
& data structures,
...
⇒ Attributes
of SW Design
Software
design is actually a multi step
process that focuses on
four
distinct
attributes of a program:
Data
structure,
Software
architecture,
Interface
representations, and procedural
(algorithmic) detail.
The
design process translates requirements
into a representation of
the
software
that can be assessed for
quality before coding
begins.
Like
requirements, the design is documented
and becomes part of
the
software
configuration.
Design is
the technical kernel of
software engineering. During
design,
progressive
refinements of data structure,
architecture, interfaces, and
procedural
detail of software components
are developed, reviewed,
and
documented.
Design
results in representations of software
that can be assessed
for
quality.
A number of fundamental software design
principles and concepts
have
been proposed over the
past four decades.
Design
principles guide the
software engineer as the design
process
proceeds.
Design concepts provide basic
criteria for design
quality.
107

Software
Project Management
(CS615)
a.
Code generation
The
design must be translated into a
machine-readable form.
The
code
generation step performs
this task. If design is performed in
a
detailed
manner, code generation
can be accomplished
mechanistically.
b.
Testing
Once
code has been generated,
program testing begins. The
testing
process
focuses on the logical internals of
the software,
ensuring
that
all statements have been
tested and on the functional
externals;
that
is, conducting tests to
uncover errors and ensure that
defined
input
will produce actual results
that agree with required
results.
⇒ Key
Features of Design
A number
of fundamental software design principles
and concepts have
been
proposed over the past
four decades. Design
principles guide the
software
engineer as the design process
proceeds. Design concepts
provide
basic
criteria for design
quality.
Support
Support
Software
will undoubtedly undergo change after it
is delivered to the
customer
(a possible exception is embedded
software). Change will occur
because
errors have been
encountered, because the
software must be
adapted
to accommodate changes in its external
environment (e.g. a
change
required because of a new
operating system or peripheral
device),
or
because the customer
requires functional or performance
enhancements.
Software
support/maintenance reapplies each of the
preceding phases to
an
existing program rather than
a new one.
Modularity
Modularity
(in both program and data) and
the concept of
abstraction
enable
the designer to simplify and reuse
software components.
Refinement
provides a mechanism for
representing successive layers
of
functional
detail. Program and data
structure contribute to an overall
view
of
software architecture, while
procedure provides the
detail necessary for
algorithm
implementation.
108

Software
Project Management
(CS615)
Information
hiding and functional independence
provide heuristics
for
achieving
effective modularity.
We try to
solve the problem by rushing
through the design process so
that
enough
time will be left at the end of
the project to uncover
errors that
were
made because we rushed
through the design
process.
The
moral is this: Don't rush through
it! Design is worth the
effort.
⇒ Standard
design approaches
·
Exception
handling,
·
Localization
·
Portability
·
Reuse
·
Input/output
·
Memory
management,
·
Performance
2.13
Construction
Coding
practices
Naming,
layout, documentation
Data-related
concepts
Scope,
persistence, binding time
Data
usage guidelines
Bytes,
arrays
Use
of construction tools
Programming
environment, group work
support (documents,
code),
code
libraries & generators
2.14
Software
Configuration management
Software
configuration management (SCM) takes
care of changes in a
software
process. SCM identifies
controls, audits, and
reports
modifications
that occur during software
development. SCM
helps
maintain
the integrity of configurable
items produced during
software
development.
SCM is an integral part of
Software Quality
Assurance
(SQA).
SCM involves assessing the
impact of the changes made
during
SQA
activities and making decisions based on
cost and benefit analysis.
SCM is
used to establish and maintain
integrity of software items
and
ensure
that they can be traced easily.
SCM helps define a library
structure
for
storage and retrieval of software
items.
109

Software
Project Management
(CS615)
·
To ensure
that project stays consistent
over time: You need
to:
a)
Evaluate
proposed changes
b)
Track
the changes
c)
Control
the Version
d)
Check
integrity of Source code, documents,
plans, design
e)
Ensure
quality
⇒ Software
Configuration Management
Activities
SCM is
used to establish and maintain
integrity of software items
and
ensure
that they can be traced easily.
Using SCM, you can define a
library
structure
for storage and retrieval of
software items. SCM needs to
be
performed
at all phases in the SDLC of
a software project. The
various
SCM
activities are:
1.
Identifying
Objects
2.
Controlling
Versions
3.
Controlling
Changes
4.
Auditing
5.
Communicating
Changes
1.
Identifying Objects
The
first activity in SCM
involves identifying software
configurable
items
(SCIs). SCI is an aggregation of
software that is designated
for
configuration
management. It is treated as a single
entity in the
configuration
management process. For
example, design documents,
program
code, test case, and custom
requirement document
are
configurable
items.
You can
use the Item Traceability
Matrix to identify SCIs at
the end of
each
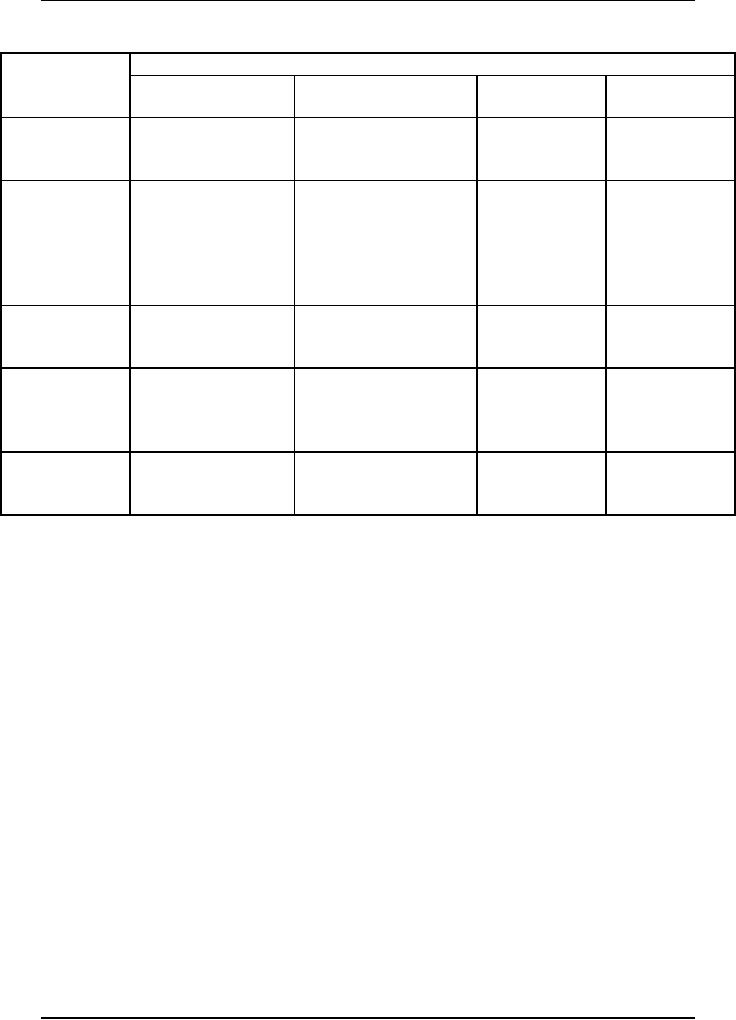
phase. A sample of Item Traceability
Matrix is displayed in
Table
1. In the
table, you can see the
different SCIs in different
phases of the
development
process.
110
Software
Project Management
(CS615)
Table
1:
Item
Traceability Matrix
Phase
Deliverable
Requirement
Name
Design
Construction
Testing
Analysis
Requirement
Requirement
Analysis
Analysis
Document
Document
Functional
Specification
Design
Document
and
Document
Program
Specification
Document
Code
A
Code
Code
B
Code
C
Unit
Test
Cases
Test
Document
System
Test
Cases
Database
Database
Design
Design
Specification
Document
To
identify SCls, you need to
first breakdown the project
deliverable
to the
SCI level. Each phase in the
project has its own
deliverables. To
trace the
deliverables, you need to map
the SCls to the phases in
which
they
are delivered.
2.
Controlling Versions
Version
control combines procedures and tools to
manage different
versions
of configuration objects that
are created during
software
product
development. To control versions,
you can use Version
Control
Register. In Version Control
Register, you enter the
details of
components,
such as component identification
numbers, their
versions,
and dates
of validity. It is advisable to release a
baseline after a version
is
released. Baseline is a specification or
a product that is
formally
reviewed
and agreed upon. This serves
as the basis for
further
development.
Baseline can be changed only through
formal change
control
procedures. A baseline consists of a set of SCIs
that are
logically
related to each other. Baselines
are established when
subsequent
changes to the SCIs need to
be controlled. Version
control
is essential so
that everybody uses only
the latest version. Any kind
of
version
mismatch might result in
rework.
111
Table of Contents:
- Introduction & Fundamentals
- Goals of Project management
- Project Dimensions, Software Development Lifecycle
- Cost Management, Project vs. Program Management, Project Success
- Project Management’s nine Knowledge Areas
- Team leader, Project Organization, Organizational structure
- Project Execution Fundamentals Tracking
- Organizational Issues and Project Management
- Managing Processes: Project Plan, Managing Quality, Project Execution, Project Initiation
- Project Execution: Product Implementation, Project Closedown
- Problems in Software Projects, Process- related Problems
- Product-related Problems, Technology-related problems
- Requirements Management, Requirements analysis
- Requirements Elicitation for Software
- The Software Requirements Specification
- Attributes of Software Design, Key Features of Design
- Software Configuration Management Vs Software Maintenance
- Quality Assurance Management, Quality Factors
- Software Quality Assurance Activities
- Software Process, PM Process Groups, Links, PM Phase interactions
- Initiating Process: Inputs, Outputs, Tools and Techniques
- Planning Process Tasks, Executing Process Tasks, Controlling Process Tasks
- Project Planning Objectives, Primary Planning Steps
- Tools and Techniques for SDP, Outputs from SDP, SDP Execution
- PLANNING: Elements of SDP
- Life cycle Models: Spiral Model, Statement of Requirement, Data Item Descriptions
- Organizational Systems
- ORGANIZATIONAL PLANNING, Organizational Management Tools
- Estimation - Concepts
- Decomposition Techniques, Estimation – Tools
- Estimation – Tools
- Work Breakdown Structure
- WBS- A Mandatory Management Tool
- Characteristics of a High-Quality WBS
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- WBS- Major Steps, WBS Implementation, high level WBS tasks
- Schedule: Scheduling Fundamentals
- Scheduling Tools: GANTT CHARTS, PERT, CPM
- Risk and Change Management: Risk Management Concepts
- Risk & Change Management Concepts
- Risk Management Process
- Quality Concept, Producing quality software, Quality Control
- Managing Tasks in Microsoft Project 2000
- Commissioning & Migration