 |
REVIEW & WRAP-UP of Introduction to Computing |
| << PROGRAMMING METHODOLOGY |
Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
LESSON
45
REVIEW &
WRAP-UP
During
the last Lesson we discussed
Programming Methodology
·
We
looked at a few effective
programming practices that
result in the development of
correct
programs
with minimum effort
·
We
also became familiar with
testing & debugging
readable
program?
A program
that is easy to read
&
understand,
and therefore, easy
to
maintain &
enhance
Design
Guidelines
·
Break
your code down into short
and simple functions (e.g. take the 3
swap statements out from
the
last
example and put them into a
function of their
own)
·
Do
not use global
variables
Coding
Guidelines
·
Indent
blocks of code (2 to 5
spaces)
·
Always
use semicolons to end
statements
·
Identifiers:
Use
the camelBack scheme
Make
them descriptive but
concise
Variables:
nouns
Functions:
verbs
·
Comment
liberally
Guidelines
for Developing Short
Programs
·
Read,
understand the
·
problem
Write the
code on a piece of
·
paper
Do you have
all the
·
required
data?
Hand-check
it
No: Get
it
·
Type it
in
Else
assume it. State it
·
Run & check it on
test cases
explicitly
·
Errors?
fix & redo 9
·
Do the
design
·
Done!
·
Write test
cases
Design
& Code Reviews
·
Probably
the most efficient way of
improving the a program
·
Being
humans, at time we see what
is supposed to be there instead of what is
actually there
·
Another
pair of eyeballs may not
have the same problem, especially if
they are were not
involved
in
building the design or code
307
Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
Testing
& Debugging
·
Testing:
The
tasks performed to determine the
existence of defects
·
Debugging:
The
tasks performed to detect the exact
location of defects
·
Defects
are also called bugs or
errors
·
Let
us now look at one of their
classifications
Types
of Errors
·
Syntax
errors
·
Semantic
errors
·
Run-time
errors
Today's
Goal:
(Review
& Wrap-Up)
·
To
review some of the interesting
ideas that we discussed over
the last 44 lectures
·
Please
note that this lectures is
not a comprehensive review, just a
sampler!
Course
Objectives
1.
To build an
appreciation
for
the fundamental concepts
in
computing
To achieve a
beginners
proficiency in Web
page development
2.
To become
familiar
with
popular PC productivity
software
3.
Progression
of Computer Technology
1.
Mechanical
computing
2.
Electro-mechanical
3.
Vacuum
tube
4.
Transistor
(the
current state-of the-art)
5.
Quantum
computing
Quantum
Computers
·
Quantum
computers may one day be
millions of times more efficient
than the current
state-of-the-
art
computers ...
·
as
their quantum mechanical nature will
allow them to examine all possible
answers to a question,
simultaneously
The
World Wide Web
·
A huge
resource of info
·
Logically
unified, but physically
distributed
308

Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
·
It is
unlike any previous human
invention:
It is a
world-wide resource, important to
all and shared by all of the
people in the world
The
Semantic Web
Whereas,
today's Web's content is designed for
humans to read; the Semantic Web's
content will be
designed
for computers to understand
meaningfully
Internet:
Network of Networks
·
A
large number of networks, interconnected
physically
·
Capable of
communicating and sharing data with
each other
·
From
the user's point view,
Internet a collection of interconnected
networks looks like a
single,
unified
network
Language of
the Internet:
TCP/IP
Transmission
Control Protocol/Internet
Protocol
·
TCP
breaks down the message to be
sent over the Internet into
packets
·
IP
routes these packets through
the Internet to get them to their
destination
·
When
the packets reach the destination
computer, TCP reassembles them into the
original message
Instant
Messaging
·
eMail:
Slow response times
·
eMail:
No way of knowing if the person we
are sending eMail to is there to read
it
·
eMail:
The process of having a
conversation through eMail by
exchanging several short messages
is
too cumbersome
·
Instant
messaging (IM) solves these
problems
On-Chip
Cache Memory
·
That
small amount of memory located on the
same chip as the uP
·
The
uP stores a copy of frequently
used data and instructions
in its cache memory
·
When
the uP desires to look at a piece of
data, it checks in the cache
first. If it is not there,
only
then
the uP gets it from the main
memory
·
Its
proximity to the uP makes access times
short
Ways
of Enhancing A uP
·
Increase
the clock frequency
·
Increase
the word-width
·
Add
more functional units (e.g. ALU's,
FPU's, Vector/SIMD units,
etc.)
309
Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
Hardware
Operating
System
Device
Driver
Utilit
Language
Scientific
Business
Productivit
Entertainment
y
Translator
Apps.
Apps.
y
Apps.
Apps.
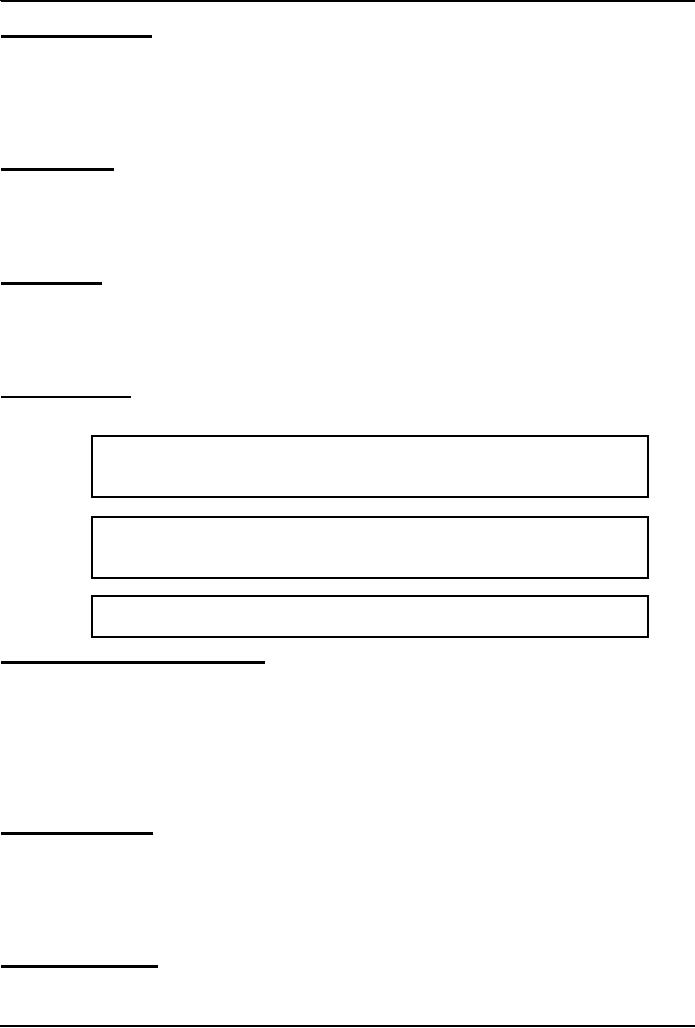
System
software
Application
software
The
Role of An OS
·
Manages the HW
and SW resources of the computer
system, often invisibly.
These include the
processor,
memory, disk drives,
etc.
·
Provides
a simple, consistent way for
applications to interact with the HW
without having to
know
all
the details of the HW
Who
Owns Software?
·
Generally,
although a piece of SW that is being
used by millions, it is not
owned by any of them!
·
When
we buy a SW package, we do not
really buy it we just
buy a license that allows us to
use it,
the
ownership stays with the
maker
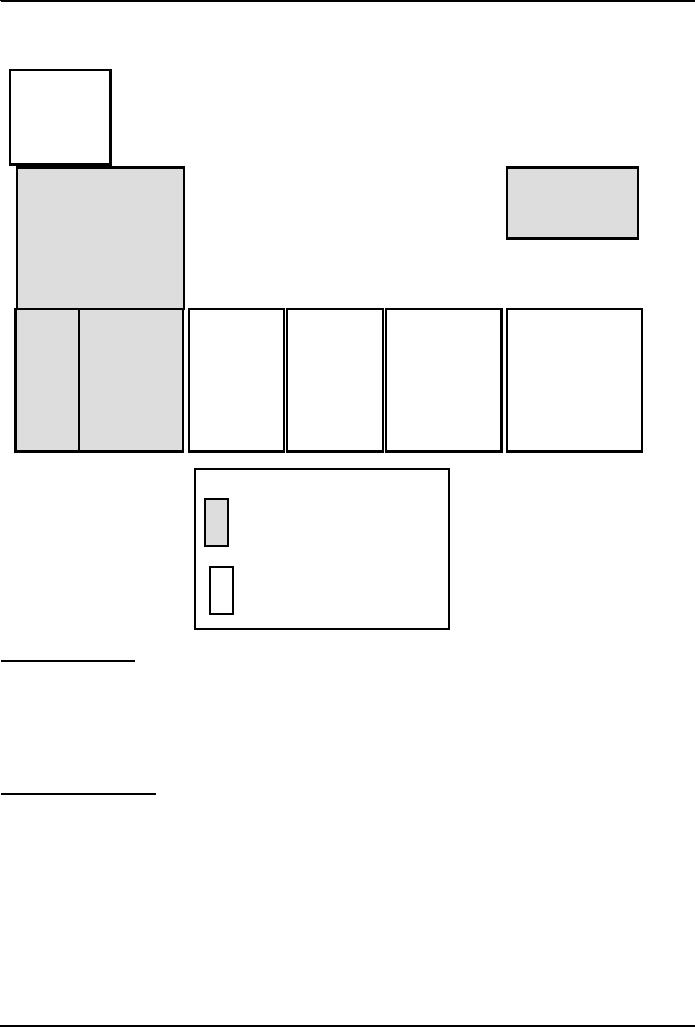
4th-generation
languages
310
Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
Machine
languages
Interpreters:
Immediate
response, but execute code
slowly
Compilers:
Compiling
takes time, but super-fast
execution
High-level
languages
Assembly
languages
311
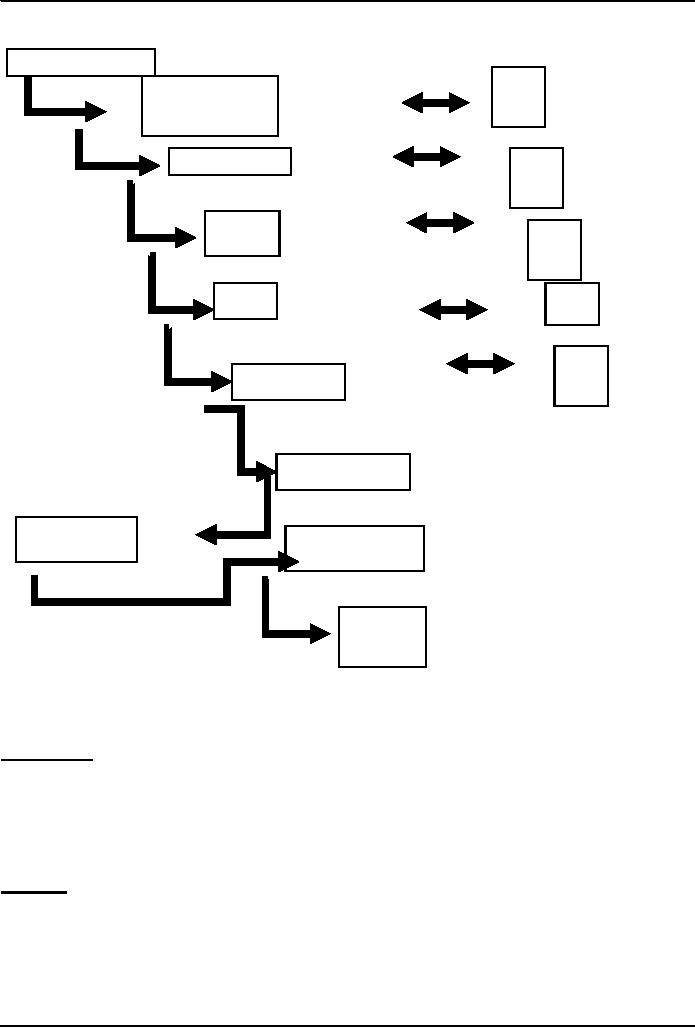
Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
Concept
&
Feasibility
Test
User
Requirements
Developer
Specs
Test
Planning
Test
Design
Test
Test
Implementatio
n
Integration
Testing
Acceptance
Opr.
&
Test
Maintenance
Retirement
Algorithm
1st
Definition:
Sequence
of steps that
is taken
to
solve a problem
Better
Definition:
A precise
sequence of a
limited
number
of unambiguous,
executable
steps
that
terminates
in
the
form of a solution
Pseudo
Code
·
Quite
suitable for SW development as it is
closer in form to real
code
·
One
can write the pseudo code,
then use it as a starting
point or outline for writing
real code
·
Many
developers write the pseudo code
first and then incrementally
convert each line into
real
code
Heuristic
Common
sense Lesson drawn from
experience
(Artificial)
Intelligent Systems
SW
programs or SW/HW systems designed to
perform complex
tasks
employing strategies that
mimic
some
aspect of human thought
312

Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
Not
a Suitable Hammer for All
Nails!
if
the nature of
computations required in a task is not
well understood
or
there
are too many exceptions to
the
rules
or
known
algorithms are too complex
or inefficient
then
artificial
intelligent systems have the potential of
offering an acceptable
solution
Database
·
A
collection of data organized in
such a fashion that the computer
can quickly search for a
desired
data
item
·
All
data items in it are generally
related to each other and
share a single domain
Relational
Databases
·
Databases
consisting of two or more related
tables are called relational
databases
·
A
relational database stores
all its data inside tables,
and nowhere else
·
All operations on
data are done on those
tables or those that are
generated by table operations
Future
Trends:
On-Demand
Computing Power
·
Almost
infinite "computing power"
supply
·
Reliable,
maintenance-free, just like the
electricity, telephone, or water-supply
service
·
No
capital expenditure; you pay
for only what you
use!
·
Same
will be true for
storage
Future
Trends: Immortal
Minds
·
Some
day it will be possible to load
all the lectures, papers, books and SW produced by an
expert
into
an intelligent system
·
After
that system processes, indexes and
restructures the info in
those artifacts, it will be
possible
to have a
conversation in plain English
(or some other language)
with that system
Distances
Are Contracting!
Distances
Are Increasing!
·
Because
of the ever-decreasing costs of verbal,
text, video communications, it is
becoming easier to
stay
in touch of anyone, regardless of
their physical
location
·
Solitude
is the order of the day as many
children & adults spend their
free time surfing,
chatting,
playing
computer games, instead of spending it on interacting
with friends or
family
Computers
may Become too
Powerful!
·
Computers keep on
becoming more and more powerful, gaining
more and more autonomy
·
They
are being equipped with
fail-safe and self-healing
technologies
·
Are
we heading towards a future where the
role of the masters and the
slaves will be
reversed?
Why
JavaScript?
·
HTML is great
for static Web pages; however,
supports only rudimentary
interactivity through
forms
and hyperlinks
·
JavaScript
can be used (along with
HTML) to develop interactive content for
the Web
313
Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
Some
of things that JavaScript cannot
do!
·
The
following file ops. on the
client computer:
Read
--
Modify
Rename
--
Delete
Create
·
Create
graphics (although, it does have the
ability to format pages
through HTML - including the
placement of
graphics)
·
Any
network programming bar one function: the
ability to download a file to the browser
specified
through
an arbitrary URL
Advantages of
Client-Side Scripting
·
Reduced
server load as it does not
have to send messages to the user's
browser about missing or
incorrect
data
·
Reduced
network traffic as the form's
data is sent only once
instead of many to's and
fro's
A collection
of
properties
&
methods
All
objects have the
"name"
property: it holds
the name
of the object
(collection)
prop
1
method
2
prop
2
prop
5
prop
3
method
1
method
3
prop 4
Object: A
named
collection
of properties (data, state) & methods
(instructions, behavior)
Functions
·
A
named group of statements
that is put together once
and then used (by reference)
repeatedly on a
Web
page
·
Code
becomes easier to read, understand
and maintain
314

Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
Local
and Global
Variables
Local
or Function-level Variable
Effective
only in the function in which
they are declared
Global
Variables
Visible
everywhere on the Web page
Image
Preloading
·
The
Image object can be used to
download an image into the cache
before it is actually needed
for
display
·
This
technique can be used to
create smooth animations or to display
one of several images based
on the
requirement
Productivity
SW
·
The
lectures and assignments were designed to
give a brief introduction,
and no more
·
All we desired
was for you to become
able to open the package and
perform some trivial
tasks
·
With
time, you will find more and
more use for these packages,
and gradually develop an expertise
that
later will become very
useful in your career
Course
Objectives
1.
To
build an appreciation
for
the fundamental concepts in
computing
2.
To achieve a
beginners
proficiency in Web
page development
3.
To
become familiar
with
popular PC productivity
software
·
How
successful were we in helping you achieve
those objectives?
·
Please
do let us know so that we
can modify the future
offerings of this course
accordingly. I will
be
most grateful
·
I have
enjoyed doing this course
with you very
much
·
Hope
it was enjoyable & useful
for you as well
·
I
thank you for your
attention and especially for
your eMail & discussion
board messages
·
A
good number of those messages were
quite informative and I thank
you for sharing that
info with
me
·
Until
the next time when we meet
...
********************THE
END*******************
315
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION
- EVOLUTION OF COMPUTING
- World Wide Web, Web’s structure, genesis, its evolution
- Types of Computers, Components, Parts of Computers
- List of Parts of Computers
- Develop your Personal Web Page: HTML
- Microprocessor, Bus interface unit, Data & instruction cache memory, ALU
- Number systems, binary numbers, NOT, AND, OR and XOR logic operations
- structure of HTML tags, types of lists in web development
- COMPUTER SOFTWARE: Operating Systems, Device Drivers, Trialware
- Operating System: functions, components, types of operating systems
- Forms on Web pages, Components of Forms, building interactive Forms
- APPLICATION SOFTWARE: Scientific, engineering, graphics, Business, Productivity, Entertainment, Educational Software
- WORD PROCESSING: Common functions of word processors, desktop publishing
- Interactivity to Forms, JavaScript, server-side scripts
- ALGORITHMS
- ALGORITHMS: Pseudo code, Flowcharts
- JavaScript and client-side scripting, objects in JavaScript
- Low, High-Level, interpreted, compiled, structured & object-oriented programming languages
- Software Design and Development Methodologies
- DATA TYPES & OPERATORS
- SPREADSHEETS
- FLOW CONTROL & LOOPS
- DESIGN HEURISTICS. Rule of thumb learned through trial & error
- WEB DESIGN FOR USABILITY
- ARRAYS
- COMPUTER NETWORKS: types of networks, networking topologies and protocols
- THE INTERNET
- Variables: Local and Global Variables
- Internet Services: FTP, Telnet, Web, eMail, Instant messaging, VoIP
- DEVELOPING PRESENTATIONS: Effective Multimedia Presentations
- Event Handlers
- GRAPHICS & ANIMATION
- INTELLIGENT SYSTEMS: techniques for designing Artificial Intelligent Systems
- Mathematical Functions in JavaScript
- DATA MANAGEMENT
- DATABASE SOFTWARE: Data Security, Data Integrity, Integrity, Accessibility, DBMS
- String Manipulations:
- CYBER CRIME
- Social Implications of Computing
- IMAGES & ANIMATION
- THE COMPUTING PROFESSION
- THE FUTURE OF COMPUTING
- PROGRAMMING METHODOLOGY
- REVIEW & WRAP-UP of Introduction to Computing