 |
THE COMPUTING PROFESSION |
| << IMAGES & ANIMATION |
| THE FUTURE OF COMPUTING >> |

Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
LESSON
42
THE
COMPUTING PROFESSION
Focus
of the last Lesson was on
Social Implications of
Computing
We
discussed the impact of
computing on:
Business
Work
Living
Health
Education
Why
should we, as computing
professionals, be interested in studying
the social implications
of
our
creations?
�
Computing
technology has changed our
way of life like no other
technology
�
We
need to study how it has
done it to highlight the mistakes and
success stories of the
past
�
We
need to do it so that we can
learn from them and select
our future direction
accordingly
Dilemma
of Computing
�
Are
we heading towards a future where the
role of the masters and the
slaves will be switched?
�
Should
we slow down or even reverse
some of the technology advances to
avoid that dark
scenario?
Powerful
Global Corporations
�
Internet-based
communication is allowing business
entities to coordinate the activities of
their
globally-spread
units with greater
accuracy
�
All
this has made these
business entities very
powerful, even more powerful than
many nation-
states
The
Network Organization
�
The
network paradigm (all
connected to many others) is becoming the
preferred organizational
structure of more
and more organizations as time goes
by
�
This
new organization is replacing the
old-style layered, tree-structured
organizational model
Working
from Home
�
Computing
has made it possible for
some to avoid going the
office for their
work
�
They
can do their work from home
and communicate their ideas, questions,
answers to their
colleagues
through the Internet
�
This
gives them more time to spend
with their families due to
the time they save on
commuting to
their
place of work
From
Mass- to Personalized-Marketing
�
The
Web has changed marketing
forever, redirecting it from a
mass focus to a single-person focus
The
Political Process
�
Through
computer discussion forums, newsgroups
and mailing-lists, public and politicians
may
engage
285

Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
in a
free, open exchange of ideas
without leaving the comfort of
their not-so-comfortable and
very
comfortable
homes, respectively
Distances
Have Contracted
�
Because
of the ever-decreasing costs of verbal,
text, video communications, it is
becoming easier to
stay
in touch with anyone,
regardless of their physical
location
Distances
Are Increasing
�
Solitude
is the order of the day as many
children & adults spend their
free time surfing,
chatting,
playing
computer games, instead of spending it on interacting
with friends or
family
Virtual
Communities
�
Interest-based,
instead of geography-based
A
Society Under
Surveillance
�
While
surfing, we are being watched,
constantly
The
Changing Face of
Education
�
Distance
learning has received a boost
due to the low-price of
Internet communication and
the
availability
of Web-based interactive
content
The
Changing Face of
Education
�
The
fact, however, remains that
the best mode of education is the
conventional one, which
has
become
more effective with the augmentation of
computer-based learning
aids
Info
Gathering
�
The
time and effort spent on
gathering info can now be
spent on using it
Telemedicine
�
An
audio/video/text connection combined
with a few remote medical instruments and
an on-site
trained
assistant can enable a doctor to
examine and prescribe medicine to a
patient far, far
away
Closure
�
I
command you to "go and
invent the future," it is your
duty and you may
not desist from it,
but,
please,
do think about the social implications
and consequences of what you
are doing before
actually
doing it
Today's
Goals:
(The
Computing Profession)
�
To
discuss several roles and associated
responsibilities of modern computer
professionals
�
To
discuss a few tricky
situations where a knowledge of
professional ethics would
help
286
Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
42.1
IT: Information Technology
The
group of technologies concerned
with the capture, processing and transmission of
information in
the
digital-electronic form
INFORMATION
TECHNOLOGY
Telecom
Engineering
Software
Engineering
Computer
Computer
Engineering
Science
Who
is a computing professional?
�
Professionals
involved in the development and/or
maintenance of SW and/or computer HW
�
Computer
scientists, software engineers, computer engineers,
and some of the telecom engineers
are
generally classified as computing
professionals
Today's
Focus Group
�
Due
to the limitation on time, today we
will be focusing only on a
subset of computing
professionals:
those involved in the development of
SW
�
Let
us further restrict discussion to the
computing professionals belonging to an
organization
focused
solely on custom, SW
development
�
They
work in a 100-person organization
pretty big on a local scale,
but quite insignificant on
an
international
one
42.2
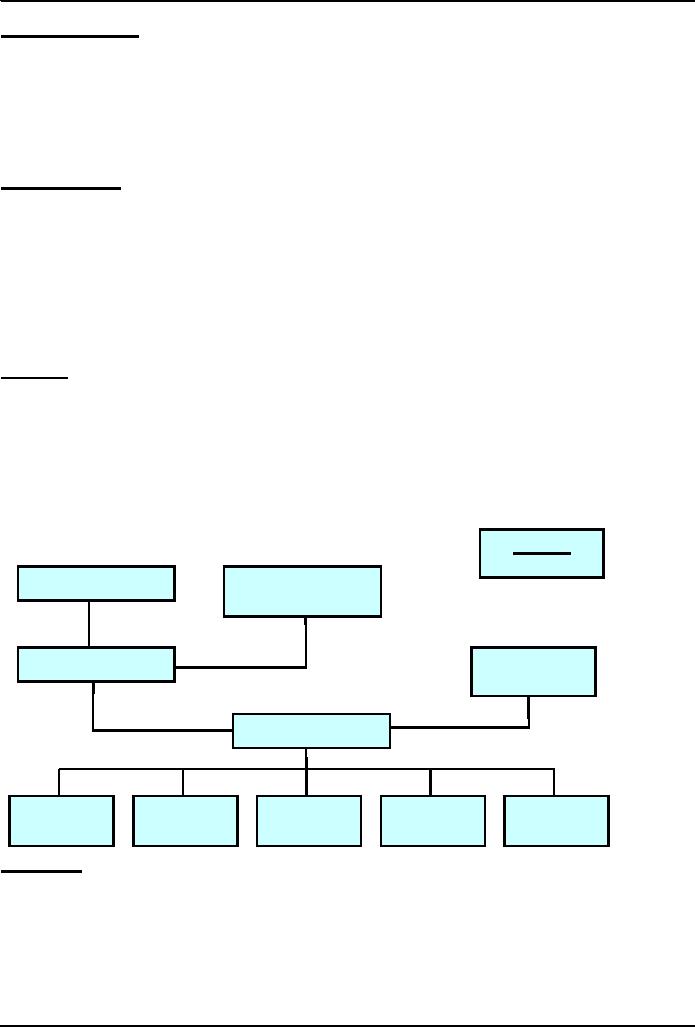
Organization: A Collection of Teams
Executive
Team
CEO, COO,
CMSO
Business
Technology
Architecture
Development
Team
Transfer
Team
Team
Configuration
Proces
Quality
Suppor
Management
Team
s
Assurance
Team
t
Team
Team
Development
Development
Development
Development
Team
A
Team
B
Team
C
Team
D
287
Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
Development
Team
�
The
number of development teams has
varied between 3-7 at this
organization
�
Team-size
has varied between
3-35
�
Large
teams are organized as a
collection of sub-teams
�
Lowest-level
team: No more than 7
members
�
Responsible
for a project from after the
specifications stage till the
very end
Project
Manager
�
Responsibilities:
Planning and tracking of the
project
Arranging of the appropriate
resources
lient relationship
management
�
Profile:
5+
years of team-lead experience
Professional development course(s) in SW
project management
Technical MS and/or Technical BS +
MBA
Architect
�
Responsibilities:
Technology
selection
High-level
design
Makes
certain that the implementation
remains true to the design
�
Profile:
10-15
years of development experience
In-depth
experience in several technologies
MS or
PhD in a technical
discipline
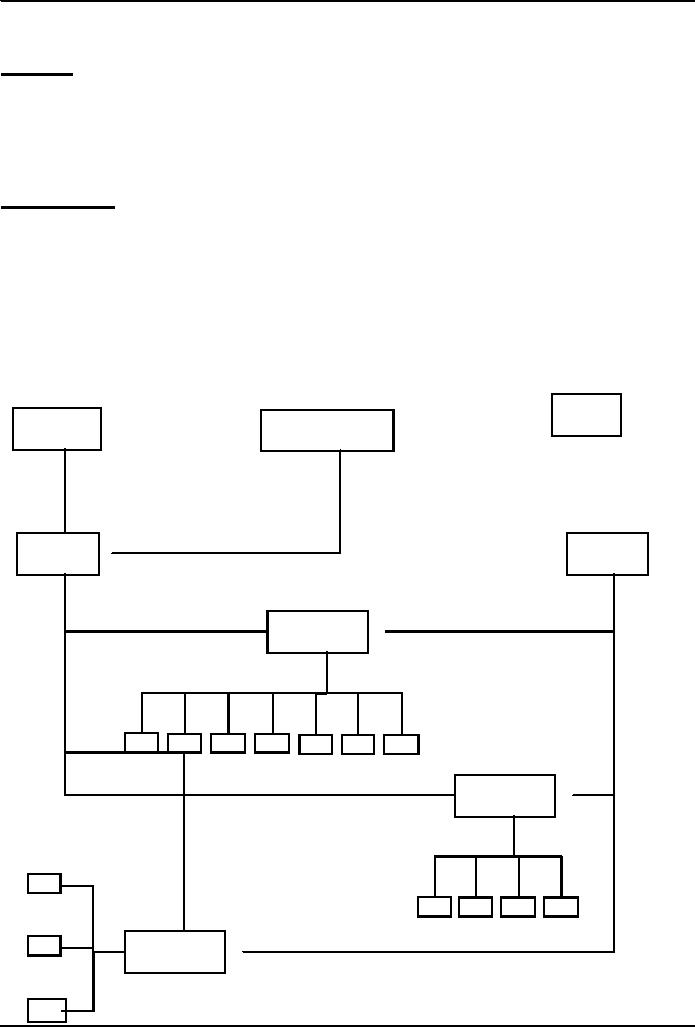
SMALL
PROJECT
Clients's
Project
Executive
Team
Manager
Architect
Team
Leader
(Part-Time)
Team
Leader
Developer
Developer
Developer
Developer
Developer
A
B
C
D
E
Team
Lead
�
Responsibilities:
Planning and tracking of the
project
Detailed design
Professional development of team
members
In
case of small teams,
development activities
�
Profile:
5+
years of development experience
Excellent interpersonal
skills
288
Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
Good planning
skills
Good design skills
Developer
�
Responsibilities:
Module-level design
Coding
Unit-testing
�
Profile:
Technical BS
Executive
Team
�
CEO
Chief Executive
Officer
Developer of the vision of the
organization
Great PR skills
Great knack for
spotting talent
�
COO
Chief Operating
Officer
Responsible for the day-to-day
operations
Great organizational &
interpersonal skills
�
CMSO
Chief Marketing & Sales
Officer
Responsible for bringing in
work
Innovative
Bigger
Executive
Client's
Project
Team
Project
Manager
Project
Project
Manager
Architect
Sub-team
1
Lead
A
B
C
D
F
G
E
Sub-team
2
Lead
A
A
B
C
D
Sub-team
3
B
Lead
C
289

Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
Business
Development Team
�
1-2
members
�
Responsible
for the development of detailed
proposals for projects
�
Profile
of Members:
Combination
of technical and business
expertise
Good
oral & written communication
skills
Combination
of technical & business
degrees
Architecture
Team
�
2-3
members
�
Consists
of the sharpest technical minds in the
company
Configuration
Management Team
�
2-3
members
�
Keeps
a vigilant eye on the process that
keeps an extensive record of all versions
of everything that
is
ever developed for a
particular project: from
proposals to specifications to plans to design to
code
Process
Team
�
1-2
members
�
Team's
goal: To continuously improve the SW
development process to achieve
improvements in
cost,
schedule, and quality
�
Continuously
monitors how SW is developed in the
organization
�
Encourages
and assists all teams
and team-members in improving
their part in the SW
development
process
Quality
Assurance Team
�
Around
20 members
�
Responsible
for assuring the quality of
all SW (i.e. making sure
that it does what it is
supposed to)
that
is produced at the organization
�
Nothing
goes to the customer without the
approval of the QA team
Technology
Transfer Team
�
The
size of this team varies
with the amount of work at the
organization when the times are
good,
this
team is quite small
�
This
team is responsible for:
Evaluating new technologies,
products, processes
Selecting the ones that
are right for the
organization
Developing an expertise in their
use
Introducing them in various
ongoing/future projects
Support
Team
�
2-3
members
�
Members
possess expertise in both HW &
SW
�
Responsible
for the maintenance, expansion,
improvement of the infrastructure
consisting of:
Workstations,
servers, printers
Networking
equipment (router, switch,
hub)
290

Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
SW
(OS, development SW, productivity SW,
etc.)
Network security
That
brings us to the end of our discussion on
various roles and the associated
responsibilities in the
computing
profession. Now we move on to another
topic related to our profession,
Ethics!
Ethics
�
Ethics is a
collection of heuristics that, when
followed, improves our way
of life
�
I
find them wonderful as they
simplify my life
�
For
example, if you believe in the
heuristic always
tell the truth, your
life becomes much
simpler
�
Now,
you don't have to think
before you make every
statement that you make
"Shall
I tell the
truth,
or lie?"
Professional
Ethics
�
Professional
ethics are a category of ethics,
and here we discus the
professional ethics relevant
to
computing
�
Awareness of
professional ethics is gaining
importance with time as the
decision-making process in
the
work place keeps on increasing in
complexity
�
The
professional ethics provide a
way of simplifying that
decision making
process
Let
us now discuss a few
situations where I will request
you for your ethical
opinions
Situation
1: Illegal Use
�
A
person is using a piece of SW without the
author's permission and says: "I'm not
really using it,
I'm
just evaluating it before I
make a firm decision on
buying"
�
That
person is "evaluating" that piece of SW
for 13 months now!
�
Is the conduct of
that person ethical?
Situation
2: Vaporware
�
A
small company announces a new SW
product
�
A
larger, more established competitor hears
about that product, and
starts a whispering campaign
that
she is also working on a
similar product that will be
released soon
�
Potential
customers decide to wait for the
product instead of making the more
riskier purchase from
the smaller
company
�
The
new company's sales become
sluggish, and it fails to
earn back the investment that it
has put
into
developing that new product.
That results in her closure
�
The
larger company never releases the
promised product
�
Is the conduct of
that large company unethical or a
reasonable business tactic?
Situation
3: Whistle Blower
�
SW
bugs, at times, have catastrophic
consequences
�
While
Bhola sahib was working for
a contractor at NASA, he found
such a bug and reported it
to
his
boss, Murphy sahib, who ordered
him to never mention it to
any one, or he will get
fired
�
Bhola
sahib got scared, and did as he
was told
�
Did
Bhola sahib's behave in an ethical
manner? Would you hire
him in your company?
Situation
4: Trade Secrets
�
Bhola
sahib was working at
BholiSoft
�
He
leaves it to work for a
competitor, SuperSoft
291

Introduction
to Computing CS101
VU
�
Even
before starting at SuperSoft, he
already has divulged many of
the trade secrets of BholiSoft
during
his interviews at SuperSoft,
giving them an advantage over
BholiSoft
�
Do
you agree with Bhola
Sahib's ethics? Would you
hire him in your
company?
Today's
Lecture:
(The
Computing Profession)
�
We
discussed several roles and associated
responsibilities of modern computer
professionals
�
We
also discussed a few tricky
situations where a knowledge of
professional ethics would
have
helped
Next
Lecture' Goals:
(The
Future of Computing)
�
To
visualize the advances in computing
that will take place in the
future
�
To
visualize the impact of computing on
our future
292
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION
- EVOLUTION OF COMPUTING
- World Wide Web, Web’s structure, genesis, its evolution
- Types of Computers, Components, Parts of Computers
- List of Parts of Computers
- Develop your Personal Web Page: HTML
- Microprocessor, Bus interface unit, Data & instruction cache memory, ALU
- Number systems, binary numbers, NOT, AND, OR and XOR logic operations
- structure of HTML tags, types of lists in web development
- COMPUTER SOFTWARE: Operating Systems, Device Drivers, Trialware
- Operating System: functions, components, types of operating systems
- Forms on Web pages, Components of Forms, building interactive Forms
- APPLICATION SOFTWARE: Scientific, engineering, graphics, Business, Productivity, Entertainment, Educational Software
- WORD PROCESSING: Common functions of word processors, desktop publishing
- Interactivity to Forms, JavaScript, server-side scripts
- ALGORITHMS
- ALGORITHMS: Pseudo code, Flowcharts
- JavaScript and client-side scripting, objects in JavaScript
- Low, High-Level, interpreted, compiled, structured & object-oriented programming languages
- Software Design and Development Methodologies
- DATA TYPES & OPERATORS
- SPREADSHEETS
- FLOW CONTROL & LOOPS
- DESIGN HEURISTICS. Rule of thumb learned through trial & error
- WEB DESIGN FOR USABILITY
- ARRAYS
- COMPUTER NETWORKS: types of networks, networking topologies and protocols
- THE INTERNET
- Variables: Local and Global Variables
- Internet Services: FTP, Telnet, Web, eMail, Instant messaging, VoIP
- DEVELOPING PRESENTATIONS: Effective Multimedia Presentations
- Event Handlers
- GRAPHICS & ANIMATION
- INTELLIGENT SYSTEMS: techniques for designing Artificial Intelligent Systems
- Mathematical Functions in JavaScript
- DATA MANAGEMENT
- DATABASE SOFTWARE: Data Security, Data Integrity, Integrity, Accessibility, DBMS
- String Manipulations:
- CYBER CRIME
- Social Implications of Computing
- IMAGES & ANIMATION
- THE COMPUTING PROFESSION
- THE FUTURE OF COMPUTING
- PROGRAMMING METHODOLOGY
- REVIEW & WRAP-UP of Introduction to Computing