 |

VU
Information
System (CS507)
LESSON
43
Enterprise
Resource Planning
Following
are various modes of
integration:
1.
Connect Existing
modules/system
2. Use
Supply Chain Management (SCM) Software
3. Use
ERP Software
The
material on first two modes is
available in the handouts of
lecture 42. The third way
of
integrating
is using an ERP software. Before we start of with what
ERP is, I would like to
touch
a
previously discussed linkage
between IT and business
objectives.
43.1
Business Objectives and
IT
The
goals set by the business
strategy are always of
supreme importance. Some of
these goals
are
meeting customer requirements, reaching customer where he is
--- online, scattered
locations,
achieving distinctive competence and
winning brand loyalty. IT
function in an
organization
is set up in order to support
the business goals set at
all levels of the
organization.
IT objectives
should be flexed according to
the business needs of the
organization. This helps
in
efficient
use of IT resources for the
achievement of business objectives.
Text
in above clips related to IT
objectives
Technology
for the sake of it serves no
purpose. It needs to be driven by objectives
and these
need
to be cleared ahead of time if any
organization wants to embark on the
journey of
advancement in
technology. So we were very
clear and we have been
very clear in our
business
objectives
and tools that are required
for advancement e.g.
equipment, technology. So
that
objectives
which are profitable can be
constantly managed. The objective of any
business is to
operate
in a manner to create value, to create
value for itself and for
the company. There are
of
course
other subsidiary objectives like social
responsibility. And I fully
concur that whatever
the
available
technology that must be used
in an economic manner so that it can
create value for the
company
as a whole.
Gist
of the clips
The
corporate objectives define the IT objectives. The IT
objectives should be of help in
achieving
business objectives as IT is tool being
used for the purpose of achieving
the
corporate
objectives. It is not as end by itself.
Technology for the sake of
technology is futile.
43.2
Using ERP
Software
ERP is
an abbreviation for Enterprise
Resource Planning. In
this three word term,
resource and
planning
may seem as least relevant,
but the most relevant
part is "Enterprise" since
the
software
aims to take an enterprise
level view of the entire
organization. ERP can be defined
as
"ERP
(enterprise resource planning) is an
industry term for the broad
set of activities supported
by
multi-module application software that
helps a manufacturer or other
business manage the
important
parts of its business, including
product planning, parts purchasing,
maintaining
inventories,
interacting with suppliers,
providing customer service,
and tracking orders."
There
are some reasons attracting
companies to take up ERP.
1.
Planning the operations
185

VU
Information
System (CS507)
2.
Integrated customer related
information order tracking
with customer database,
inventory
and
shipment at different locations.
3.
Standardized HR information A
company with multiple
business units will require
a
comprehensive
and all-encompassing method of
locating employees and
communicating
with
them.
4.
Integrated financial information
and analysis
5.
Monitoring the operations including those
of sub-vendors and
manufacturers
6. Standardization
analysis of financial and
non financial information
for decision making
control/regulation.
7. We
will now listen to the views
of the State Bank Of Pakistan's CIO on
the subject.
Gist
of the clips
The
CIO, State Bank is talking
about how they came to
the decision of having an
integrated
system
to help the institution
provide a modern environment
for not only conducting
its
business
but also by using the latest
in technology, achieve the corporate
objectives through
better
speedier accumulation of data,
analysis, thereof to assist in
the regulatory function.
The
system
being used by them not
only had to cater for
data relating to the central bank's
own
activities
but also data of all
commercial banks in Pakistan. This
necessitated a system of
data
warehousing.
43.3
ERP Compared to integrated
Software
The
concept of ERP is that of an integrated software. An
integrated software can be defined as
a software
package that combines many
applications in one program. Previously, the
user
needed
various utilities to operate the
program and provide suitable
interfaces. Today
these
utilities
are an integral part of the software.
Thus the receipt of a
confirmed customer order
should
provide the start of a number of
activities that are essential to complete
and deliver the
order.
There is no need to separately
enter data for each of
the other related
activities.
Integrated
packages can move data
among several programs
utilizing common commands
and
file
structures. In effect, there
are multiple applications using the
same data simultaneously.
An
integrated
package is recommended when identical
source information is to be used
for varying
purposes
and activities.
Most
of the software modules can be integrated
to provide a complete picture.
Generally,
customized
integrated software/lays stress on meeting
the needs of an organization
without
causing
change or too much change in
the business processes. ERP's on
the other hand
incorporate
industry best practices.
Thus ERP's are a generic
solution requiring
business
process
chances. The presence of
best industry practices
makes ERP a highly generic
software.
ERP
though can be customized for a
business, but at very high
costs. Hence the benefits
are
better
earned in implementing the ERP as a
generic software and spending
time realigning the
business
processes and synchronize
with it.
Gist
of the clips
Once
the decision to adopt the ERP
route is made and a product
selected, it is imperative to
establish
what is demanded by the software,
what is the requirement the
business and how
the
two
above can be reconciled for
the benefit of organization.
Thus a gap analysis is
conducted
and
the realignment of the existing
procedures with the requirements of
the ERP have to be
undertaken.
There may be some element of
customization of the ERP, but it is
generally
minimal.
Stress is therefore on the
realignment of the business
process.
186

VU
Information
System (CS507)
Text
in the clips (Packages)
When
we compare an ERP with an integrated
software, an ERP offers much
more than just
being
an integrated software. The reason behind
it is that it has been
developed after
studying
hundreds
of different industries and based on
best practices. ERP
standardizes in itself the
best
practices
that are available.-and
practiced the world over. So
a customized integrated software
may be
serving the needs of the
organization very well.
There business information
flows and
efficiencies
adopting good practices of the
best ERP is indeed very
helpful. An ERP gives
you
the
flexibility to add on new
functionalities and modes of
doing business.
Text
in the clips (State Bank)
The
concept of ERP started in Early 90's
when we had MRP-I and
MRP-II which purely
focused
on manufacturing side. Then later
on, the financials were
added to it. Then the
rest of
the
business i.e. sales,
inventory, receivables, payables
all were added as part of
the software.
ERP is
across the enterprise, that
is why they call is Enterprise
Resource Planning System.
The
other
thing is that it has a
central database. What ever
you are dealing with, be it
sales or
manufacturing,
the data base is the
same. So the paradigm of the
way you use the system is
the
same.
The look and feel is the
same, though the training
issues should be taken care
of. The
programming
and parameterization of the system is
quite similar across the board
and those
benefits
don't come in if let us say
we are having integration at a
limited scope. There
are
interfaces
for each module which
help to reconnect with other modules, so
if we don't have a
system
implemented across the board, benefits
don't start coming in as
expected.
Gist
of the clips
Standardization of
processes based on best
practices makes an ERP a more
effective tool. The
generic
characteristic of an ERP with
all-inclusive tools turns it
into an effective means
of
doing
business efficiently.
43.4
Evolution of ERP
The
current form and version of
ERP has evolved over time.
It took nearly four decades
for the
ERP
model to mature. Let's take
a look at the brief history
of ERP development.
187
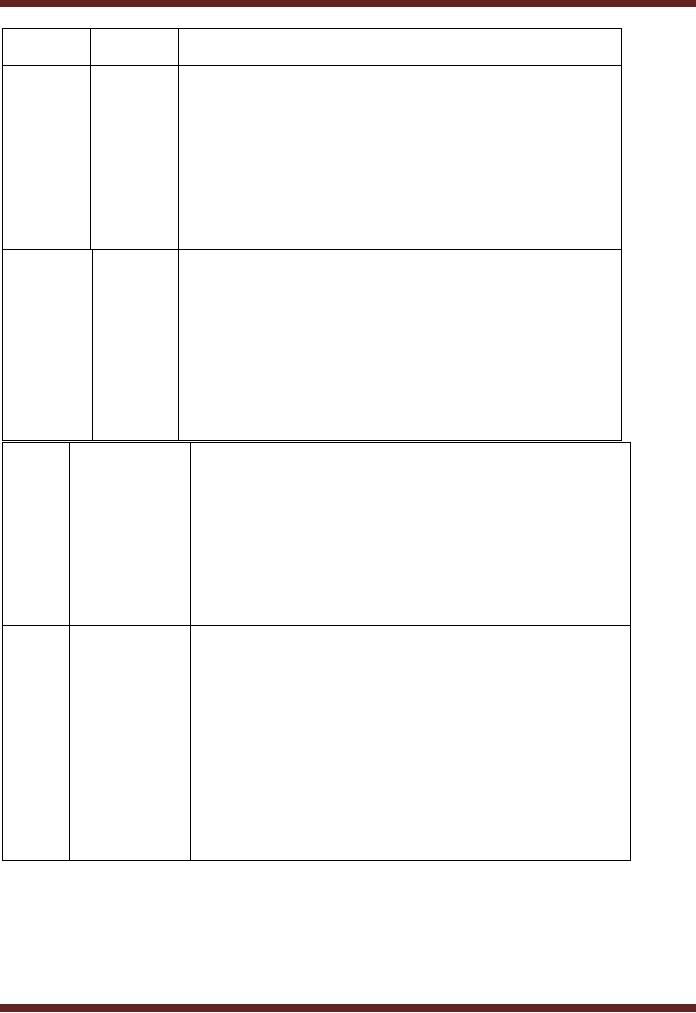
VU
Information
System (CS507)
Timeline
System
Description
1960s
Inventory
Inventory
Management and control is
the combination of
Manageme
information
technology and business
processes of maintaining
the
nt &
Control
appropriate
level of stock in a
warehouse.
The activities of
inventory management
include
o identifying
inventory requirements,
o setting
targets, providing replenishment
techniques and
options,
o monitoring
item usages, reconciling the
inventory balances,
and
reporting inventory
status.
� Materials
Requirement Planning (MRP)
utilizes software
Material
1970s
applications
for scheduling timely
material procurement.
Requirem
� MRP generates
schedules for the operations
and raw
ent
material
purchases based on the
production requirements
Planning
of finished
goods, the structure of the
production system,
(MRP)
the
current inventories levels
and the lot sizing
procedure
for each
operation.
Manufacturing �
Manufacturing Requirements Planning or
MRP utilizes
1980s
software
applications for coordinating
manufacturing
Requirements
processes,
from product planning, parts
purchasing,
Planning
inventory
control to product
distribution.
(MRP
II)
1990s
Enterprise
� Enterprise
Resource Planning or ERP
uses multi-
Resource
module
application software for
improving the
Planning
performance of
the internal business
processes.
(ERP)
� ERP
systems often integrates
business activities
across
functional
departments, from product
planning, parts
purchasing,
inventory control, product
distribution,
fulfillment, to
order tracking.
� ERP
software systems may include
application modules
for
supporting marketing, finance,
accounting and
human
resources.
Attributes
of an ERP software
ERP applications
address the complete business
process. ERP applications are
modular
generally
covering all aspects of the
business as each aspect is
dependant upon the other.
Thus
you
will generally find certain
standard modules as part of ERP software
which are
manufacturing,
supply chain, financials, CRM, human
resources and warehouse
management. It
may
also be stated that
depending upon business size
, phased approach may be opted
to
188

VU
Information
System (CS507)
implement
the ERP. A phased approach
becomes necessary because of
business process
realignment
and implementation issues particulars
relating to change in habits of the
users.
During
the past, the software
laid greater stress on
financial transactions and their
cumulative
result
with information for other
department being provided as a
secondary objective. ERP is
extended
to the enterprise level,
encompassing not only the
organization but also the
entities
external
to organization i.e. suppliers
and customer.
Text
in the clips (Packages)
The
perception was correct in the
past. But as economy is
growing, finance is not the
only
important
field. Supply chain, production, marketing
they all are very
important parts of
industry
whether in form of goods or
services. So for this purpose
information should be
available
as soon as possible through out
the company e.g. about
the stock levels,
processes
used
to produce finished goods till
packing and dispatching it to customers
and recovering.
ERP is a
system that helps in making
information available live
throughout the system at
one
time
and it is available to all. So
now a days it is no longer a
finance driven. It is basically
a
company
driven idea and the
idea is to serve the
customer well.
Gist
of the clips
ERP is
across the enterprise in its
literal sense. ERP is a package
that builds in itself at
facets of
a
business.
43.5
ERP & Customer relationship
management
Integration
involves a broader view of various
soft wares being used by
the organization. Now
CRM is
also being used in
connection with the ERP
for efficient planning and
effective control.
Text
in the clips (Packages)
Some
of the world's good ERP
system, they do have
planning and interpretation
methodology
embedded
in them. When we went under
the procedure of implementing, we were
told that
there
are two modes to do the
same: long procedure and
short procedure. The long
procedure
is
spread over two years.
The short procedure is spanned
over nine month's time.
The short
procedure
can also be termed as the
quick methodology. In short procedure,
the organization
needs
to have a certain time line, certain
procedures and certain things
are to be done. The logic
of
having this short
implementation procedure is that the
human natures if it is too long
people
lose
interest, things change, people
change, processes change, so we
need to do it in a very
quick
implementation
mode. For this we have to
form what we call a project
team. The project
team
is
further headed by the
steering committee in which
members are taken from
various
functions.
We don't need to have all
people present at the same
time but at a time we need
to
have
four or five people to be
present for every function
which is being configured to align
with
the
ERP system and connected by the ERP
consultants.
Gist
of the clips
ERP
should be seen as an independent project.
Like with every other
project, this must
have
an independent
project team. The project
team is made up of generally heads of
departments
of various
functions. This team is led
by a steering committee comprising those
charged with
policy
making to ensure that any decisions
are taken expeditiously.
189
Table of Contents:
- Need for information, Sources of Information: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Sources
- Data vs. Information, Information Quality Checklist
- Size of the Organization and Information Requirements
- Hierarchical organization, Organizational Structure, Culture of the Organization
- Elements of Environment: Legal, Economic, Social, Technological, Corporate social responsibility, Ethics
- Manual Vs Computerised Information Systems, Emerging Digital Firms
- Open-Loop System, Closed Loop System, Open Systems, Closed Systems, Level of Planning
- Components of a system, Types of Systems, Attributes of an IS/CBIS
- Infrastructure: Transaction Processing System, Management Information System
- Support Systems: Office Automation Systems, Decision Support Systems, Types of DSS
- Data Mart: Online Analytical Processing (OLAP), Types of Models Used in DSS
- Organizational Information Systems, Marketing Information Systems, Key CRM Tasks
- Manufacturing Information System, Inventory Sub System, Production Sub System, Quality Sub system
- Accounting & Financial Information Systems, Human Resource Information Systems
- Decision Making: Types of Problems, Type of Decisions
- Phases of decision-making: Intelligence Phase, Design Phase, Choice Phase, Implementation Phase
- Planning for System Development: Models Used for and Types of System Development Life-Cycle
- Project lifecycle vs. SDLC, Costs of Proposed System, Classic lifecycle Model
- Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD), Design of the information flow, data base, User Interface
- Incremental Model: Evaluation, Incremental vs. Iterative
- Spiral Model: Determine Objectives, Alternatives and Constraints, Prototyping
- System Analysis: Systems Analyst, System Design, Designing user interface
- System Analysis & Design Methods, Structured Analysis and Design, Flow Chart
- Symbols used for flow charts: Good Practices, Data Flow Diagram
- Rules for DFD’s: Entity Relationship Diagram
- Symbols: Object-Orientation, Object Oriented Analysis
- Object Oriented Analysis and Design: Object, Classes, Inheritance, Encapsulation, Polymorphism
- Critical Success Factors (CSF): CSF vs. Key Performance Indicator, Centralized vs. Distributed Processing
- Security of Information System: Security Issues, Objective, Scope, Policy, Program
- Threat Identification: Types of Threats, Control Analysis, Impact analysis, Occurrence of threat
- Control Adjustment: cost effective Security, Roles & Responsibility, Report Preparation
- Physical vs. Logical access, Viruses, Sources of Transmissions, Technical controls
- Antivirus software: Scanners, Active monitors, Behavior blockers, Logical intrusion, Best Password practices, Firewall
- Types of Controls: Access Controls, Cryptography, Biometrics
- Audit trails and logs: Audit trails and types of errors, IS audit, Parameters of IS audit
- Risk Management: Phases, focal Point, System Characterization, Vulnerability Assessment
- Control Analysis: Likelihood Determination, Impact Analysis, Risk Determination, Results Documentation
- Risk Management: Business Continuity Planning, Components, Phases of BCP, Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
- Web Security: Passive attacks, Active Attacks, Methods to avoid internet attacks
- Internet Security Controls, Firewall Security SystemsIntrusion Detection Systems, Components of IDS, Digital Certificates
- Commerce vs. E-Business, Business to Consumer (B2C), Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), E-Government
- Supply Chain Management: Integrating systems, Methods, Using SCM Software
- Using ERP Software, Evolution of ERP, Business Objectives and IT
- ERP & E-commerce, ERP & CRM, ERP– Ownership and sponsor ship
- Ethics in IS: Threats to Privacy, Electronic Surveillance, Data Profiling, TRIPS, Workplace Monitoring