 |
VU
Information
System (CS507)
LESSON
4
Unique
Attributes of Organization
Organizations
can be distinguished on the basis of
various criteria. These are as
follows.
�
Organizational
structure
�
Culture of the
Organizations
�
Management
Style
�
Decision
Making Style
4.1
Organizational Structure
Pyramid/Tall/Hierarchical
4.1.1
Hierarchical organization
A hierarchical
organization is organization
structured in a way such
that every entity in
the
organization,
except one, is subordinate to a single
other entity. This is the dominant
mode of
organization
among large organizations;
most corporations and governments
are hierarchical
organizations
�
Low
number of subordinates per
supervisor
�
Long
chain of command
�
Greater number of
levels
4.1.2
Organizational Structure
Flat
Flat
organization refers to an organizational structure
with few or no levels of
intervening management
between
staff and managers. The idea
is that well-trained workers will be
more productive when they
are
more
directly involved in the decision making
process, rather than closely supervised
by many layers of
management.
This
structure is generally possible
only in smaller organizations or
individual units within
larger
organizations.
When they reach a critical size,
organizations can retain a streamlined
structure but cannot
keep a
completely flat manager-to-staff relationship
without impacting productivity. Certain
financial
responsibilities
may also require a more
traditional structure. Some theorize
that flat
organizations
become
more traditionally hierarchical when they
begin to be geared towards
productivity.
10
VU
Information
System (CS507)
Following
are the characteristics of a flat
organization.
� High
number of subordinates per
supervisor
� Short of
chain of command
� Less
number of levels
� Eliminates
middle level managers
� Decentralizes
authority to low level
managers
4.1.3
Culture of the
Organization
Organizational
culture is the specific collection of
values and norms that
are shared by people and
groups in
an organization
and that control the way
they interact with each other
and with stakeholders
outside the
organization.
Organizational values are beliefs
and ideas about what kinds of
goals members of an
organization should
pursue and ideas about the appropriate
kinds or standards of behavior
organizational
members should use to achieve
these goals. From organizational
values develop
organizational
norms, guidelines or expectations
that prescribe appropriate kinds of
behavior by
employees
in particular situations and control the
behavior of organizational members
towards one
another.
Culture is
set of Fundamental Assumptions
that exist and grow with the
organization. It's not
publicly
announced
but spoken about within the organization.
It is a combination of implicit values
that keep the
organization
together. It is essential that the
employees understand the culture-What
drives the
organization.
4.2
Management Styles
�
Authoritative
�
Participative
�
Mixed
4.2.1
Authoritative
� An
Autocratic or authoritarian manager
makes all the decisions, keeping the
information and
decision
making among the senior management.
Objectives and tasks are set
and the workforce is
expected
to do exactly as required. The communication
involved with this method is
mainly
downward,
from the leader to the sub-ordinate
critics such as Elton Mayo
have argued that this
method
can lead to a decrease in
motivation from the employee's
point of view. The
main
advantage
of this style is that the direction of
the business will remain
constant, and the
decisions
will
all be similar, this in turn
can project an image of a confident,
well managed business. On
the
11
VU
Information
System (CS507)
other
hand, subordinates may
become highly dependent upon
the leaders and supervision
may be
needed.
Decisions are taken centrally by the
senior management themselves
and are enforced at
all
levels.
4.2.2
Participative
In a
Democratic
style,
the manager allows the employees to
take part in decision-making:
therefore
everything is
agreed by the majority. The communication
is extensive in both directions (from
subordinates
to
leaders and vice-versa).
This style can be particularly
useful when complex decisions
need to be made
that
require a range of specialist skills:
for example, when a new
computerized system needs to be
put in
place
and the upper management of the business
is computer-illiterate. From the overall
business's point of
view,
job satisfaction and quality
of work will improve.
However, the decision-making process is
severely
slowed
down, and the need of a
consensus may avoid taking
the 'best' decision for the
business.
4.2.3
Mixed
The
approach is a combination of both
authoritative and participative style.
Input from employees is
taken
and
respected, final decision is
taken by the senior management keeping in
view the views given by the
employees.
4.3
Decision Making Approach
�
Structured
Procedures
are predefined for solving routine
repetitive problems
�
Non-structured
When
problems require individual judgment, evaluation
and insight varying on case-to-case
basis
4.4
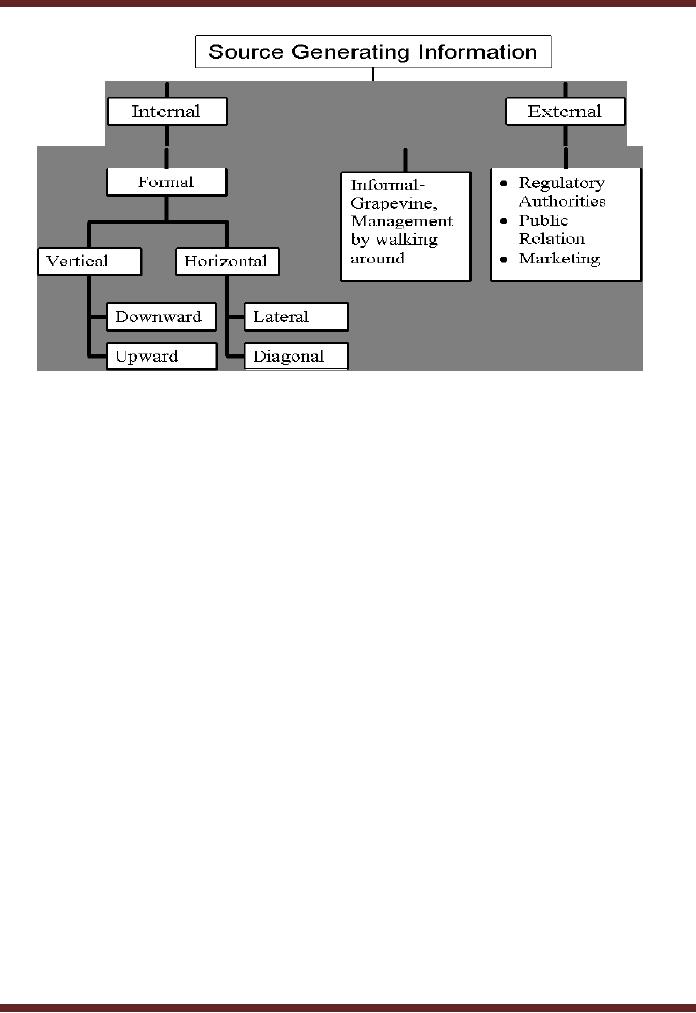
Sources of information in
Organizations
There
can be sources of information
both internal and external to the
organization. Following is a list
of
important
sources.
Internal
External
� Loan
applications
� Staff
meetings
�
�
Purchasing
agreements
Formal
reporting systems
�
�
Advertisement
Project
proposals
�
�
Research
results
Distribution
Contracts
�
Employee
Surveys
�
Persuasive
interviews
Table
4.1
4.5
Direction of Information
Flow
12
VU
Information
System (CS507)
Ideal
Information Network in an
Organization
�
Periodically
updated / continuously updated the information
should be updated so that
whenever
accessed,
the user should be fully
informed.
�
Efficient
Processing data should not be
kept unprocessed for long.
Timely processing helps
in
effective
decision making.
�
Value
driven the information kept in a
computerised system should add
value to the user's
knowledge.
�
Audience
Centred every one should
receive that part of
information that is relevant to the
user.
Conclusion
�
Availability
of timely and accurate
information helps in proper
decision making and meeting
the
organizational
goals.
�
Information
should be tailored in accordance with the
organization's culture and
structure.
13
Table of Contents:
- Need for information, Sources of Information: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Sources
- Data vs. Information, Information Quality Checklist
- Size of the Organization and Information Requirements
- Hierarchical organization, Organizational Structure, Culture of the Organization
- Elements of Environment: Legal, Economic, Social, Technological, Corporate social responsibility, Ethics
- Manual Vs Computerised Information Systems, Emerging Digital Firms
- Open-Loop System, Closed Loop System, Open Systems, Closed Systems, Level of Planning
- Components of a system, Types of Systems, Attributes of an IS/CBIS
- Infrastructure: Transaction Processing System, Management Information System
- Support Systems: Office Automation Systems, Decision Support Systems, Types of DSS
- Data Mart: Online Analytical Processing (OLAP), Types of Models Used in DSS
- Organizational Information Systems, Marketing Information Systems, Key CRM Tasks
- Manufacturing Information System, Inventory Sub System, Production Sub System, Quality Sub system
- Accounting & Financial Information Systems, Human Resource Information Systems
- Decision Making: Types of Problems, Type of Decisions
- Phases of decision-making: Intelligence Phase, Design Phase, Choice Phase, Implementation Phase
- Planning for System Development: Models Used for and Types of System Development Life-Cycle
- Project lifecycle vs. SDLC, Costs of Proposed System, Classic lifecycle Model
- Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD), Design of the information flow, data base, User Interface
- Incremental Model: Evaluation, Incremental vs. Iterative
- Spiral Model: Determine Objectives, Alternatives and Constraints, Prototyping
- System Analysis: Systems Analyst, System Design, Designing user interface
- System Analysis & Design Methods, Structured Analysis and Design, Flow Chart
- Symbols used for flow charts: Good Practices, Data Flow Diagram
- Rules for DFD’s: Entity Relationship Diagram
- Symbols: Object-Orientation, Object Oriented Analysis
- Object Oriented Analysis and Design: Object, Classes, Inheritance, Encapsulation, Polymorphism
- Critical Success Factors (CSF): CSF vs. Key Performance Indicator, Centralized vs. Distributed Processing
- Security of Information System: Security Issues, Objective, Scope, Policy, Program
- Threat Identification: Types of Threats, Control Analysis, Impact analysis, Occurrence of threat
- Control Adjustment: cost effective Security, Roles & Responsibility, Report Preparation
- Physical vs. Logical access, Viruses, Sources of Transmissions, Technical controls
- Antivirus software: Scanners, Active monitors, Behavior blockers, Logical intrusion, Best Password practices, Firewall
- Types of Controls: Access Controls, Cryptography, Biometrics
- Audit trails and logs: Audit trails and types of errors, IS audit, Parameters of IS audit
- Risk Management: Phases, focal Point, System Characterization, Vulnerability Assessment
- Control Analysis: Likelihood Determination, Impact Analysis, Risk Determination, Results Documentation
- Risk Management: Business Continuity Planning, Components, Phases of BCP, Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
- Web Security: Passive attacks, Active Attacks, Methods to avoid internet attacks
- Internet Security Controls, Firewall Security SystemsIntrusion Detection Systems, Components of IDS, Digital Certificates
- Commerce vs. E-Business, Business to Consumer (B2C), Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), E-Government
- Supply Chain Management: Integrating systems, Methods, Using SCM Software
- Using ERP Software, Evolution of ERP, Business Objectives and IT
- ERP & E-commerce, ERP & CRM, ERP– Ownership and sponsor ship
- Ethics in IS: Threats to Privacy, Electronic Surveillance, Data Profiling, TRIPS, Workplace Monitoring