 |

VU
Information
System (CS507)
LESSON
36
Risk
Management
Risk
Management is the process of measuring,
or assessing risk and then developing
strategies
to
manage the risk. In general,
the strategies employed include
transferring the risk to
another
party,
avoiding the risk, reducing the negative
effect of the risk, and
accepting some or all of
the
consequences
of a particular risk. Risk management is
a general concept which can
encompass
various
aspects or issues to be catered
for. For example risk
management against
natural
disasters,
financial risk management, knowledge risk
management, relationship risk
management.
No matter what aspect of risk is
being covered the general
approach is quite the
same.
Here since we are more
focused on study of information
systems, we would try to
relate
more
to the risks related to
proper working of information
systems.
Managing
the security risks associated
with reliance on information
technology is a continuing
challenge.
Many private organizations, have
struggled to find efficient ways to
ensure that they
fully
understand the information security risks
affecting their operations and
implement
appropriate
controls to mitigate these risks. In
recent years, systems have
become more
susceptible
to virus because computers
have become more
interconnected and, thus,
more
interdependent
and accessible to a larger
number of individuals.
Incorporating
Risk management in SDLC
For
each phase of SDLC, the
process of risk management is no
different. Rather it is iterative
process
which can be performed at
each major phase. Every
step of development has its
own
risks
which need to be handled and
addressed separately. Hence managing risk
in SDLC means
managing
risk of each phase of life
cycle.
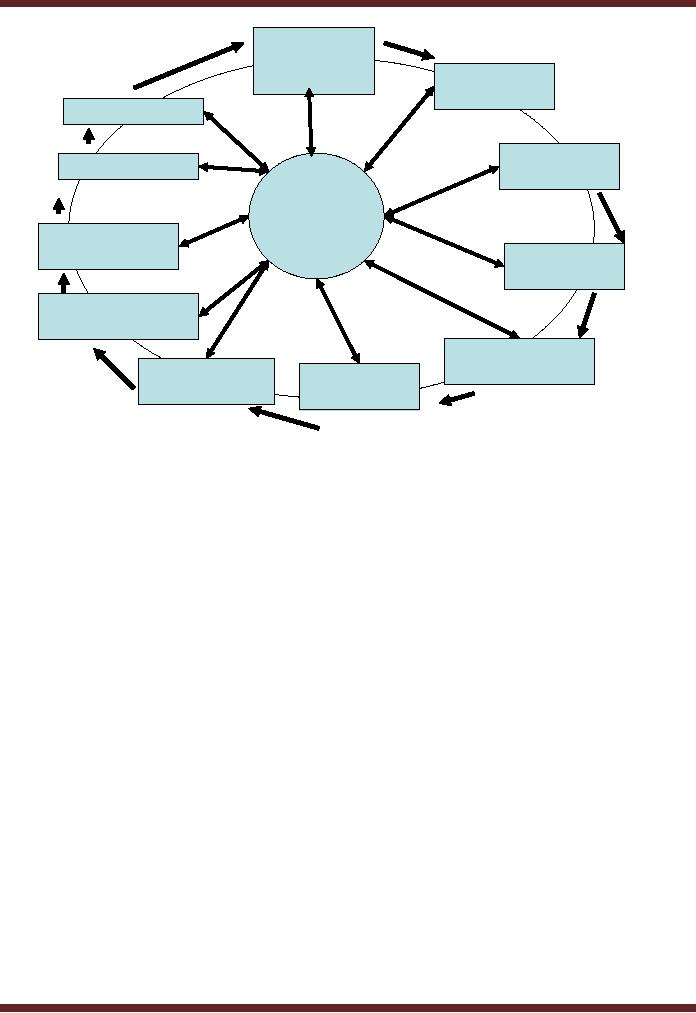
36.1
Phases of Risk
Management
Following
are various phases of SDLC
� System
Characterization
� Threat
Identification
� Vulnerability
Identification
� Control
Analysis
� Likelihood
Determination
� Impact
Analysis
� Risk
Identification
� Control
Recommendation
� Results
Documentation
� Implementation
� Monitoring
This
can also be presented as a
separate diagram.
152
VU
Information
System (CS507)
System
Characterizat
Threat
ion
Identification
Monitoring
Vulnerability
Implementation
Identification
Central
Focal
Results
Point
Control
Documentation
Analysis
Control
Recommendation
Likelihood
Risk
Determination
Impact
Determination
Analysis
36.2
What is focal Point?
A
corporate-level facilitator may
serve as a focal point for
assessments throughout the
company,
including
those pertaining to information security
because of familiarity with
the tools and
the
reporting
requirements. Each business unit in an
organization may have a
designated individual
responsible
for the business unit's risk
assessment activities. The computer
hardware and
software company,
may also create a team
for the purpose of improving
the overall risk
assessment
process and reviewing results of risk
assessments in the hardware and
software
systems
from the perspective of
offering a better, reliable
and risk free product.
36.3
System Characterization
In
assessing risks for an IT
system, the first step is to
define the scope of the
effort. The
resources
and information that
constitute the system are
identified. The system
related
information
is documented which includes.
1.
Hardware
2.
Software
3.
System Interface
4. Data &
Information
5.
People (Who support and
use IT)
6.
Systems Mission (Processes
performed by IT system)
Additional
information that may help in
characterizing the system are:
1.
Functional
requirements of IT system
2.
Users
of system (technical support
and application users)
3.
System
Security Policy
4.
System
Security Architecture
153
VU
Information
System (CS507)
As an output
to this phase we would get:
1.
System Boundary
2.
System function
3.
System and Data criticality
System's value to the
organization
4.
System and data sensitivity
Level of protection required to
maintain system, data
integrity,
confidentiality and availability.
Following
methods can be used to gather
information on the IT system
within its operational
boundary.
1.
Filling up Questionnaire
2.
On-site interviews
3.
Document Review
4. Use
of automated scanning tools
36.4
Steps
in threat identification
Following
steps are followed in this
phase
1.
Threat source identification
sources vary from being
human to natural threats
2.
Motivation and threat
actions Reasons why
someone should instigate a
threat and what
actions
he can take in such instigation
are discovered.
Examples
Threat Source
Motivation
Threat Actions
�Hacking
Challenge
Hacker,
cracker(already
�System
intrusion
Ego
discussed)
�Computer Crime
Rebellion
�System
Blackmail
Terrorist
tampering
Destruction
�Assault on an
Exploitation
employee
Information
is used as an input to determine and
identify what kind of threats
the system is
exposed
to history of system attack,
data from intelligence agencies.
The out put of this
phase is a
threat
statement identifying and defining
threats.
36.5
Vulnerability Assessment
Vulnerability
is a weakness that can be accidentally
triggered or intentionally exploited.
This phase
helps
in building up a list of weaknesses
and flaws that could be
exploited by the potential
threat
sources.
Example
154
VU
Information
System (CS507)
Vulnerability
Threat Source
Terminated
employees'
Terminated
Employees
system ID's are
not
removed from the
system
Organization uses
water
Fire, negligent
persons
sprinklers to suppress
fire
and tarpulins to
protect
hardware
Following
information is used as an
input
1. Reports of
prior risk assessments
2. Any
audit comments
3.
Security requirements
4.
Security test results
The
out put of this phase is a
list of potential
vulnerabilities.
LESSON
37
155
Table of Contents:
- Need for information, Sources of Information: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Sources
- Data vs. Information, Information Quality Checklist
- Size of the Organization and Information Requirements
- Hierarchical organization, Organizational Structure, Culture of the Organization
- Elements of Environment: Legal, Economic, Social, Technological, Corporate social responsibility, Ethics
- Manual Vs Computerised Information Systems, Emerging Digital Firms
- Open-Loop System, Closed Loop System, Open Systems, Closed Systems, Level of Planning
- Components of a system, Types of Systems, Attributes of an IS/CBIS
- Infrastructure: Transaction Processing System, Management Information System
- Support Systems: Office Automation Systems, Decision Support Systems, Types of DSS
- Data Mart: Online Analytical Processing (OLAP), Types of Models Used in DSS
- Organizational Information Systems, Marketing Information Systems, Key CRM Tasks
- Manufacturing Information System, Inventory Sub System, Production Sub System, Quality Sub system
- Accounting & Financial Information Systems, Human Resource Information Systems
- Decision Making: Types of Problems, Type of Decisions
- Phases of decision-making: Intelligence Phase, Design Phase, Choice Phase, Implementation Phase
- Planning for System Development: Models Used for and Types of System Development Life-Cycle
- Project lifecycle vs. SDLC, Costs of Proposed System, Classic lifecycle Model
- Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD), Design of the information flow, data base, User Interface
- Incremental Model: Evaluation, Incremental vs. Iterative
- Spiral Model: Determine Objectives, Alternatives and Constraints, Prototyping
- System Analysis: Systems Analyst, System Design, Designing user interface
- System Analysis & Design Methods, Structured Analysis and Design, Flow Chart
- Symbols used for flow charts: Good Practices, Data Flow Diagram
- Rules for DFD’s: Entity Relationship Diagram
- Symbols: Object-Orientation, Object Oriented Analysis
- Object Oriented Analysis and Design: Object, Classes, Inheritance, Encapsulation, Polymorphism
- Critical Success Factors (CSF): CSF vs. Key Performance Indicator, Centralized vs. Distributed Processing
- Security of Information System: Security Issues, Objective, Scope, Policy, Program
- Threat Identification: Types of Threats, Control Analysis, Impact analysis, Occurrence of threat
- Control Adjustment: cost effective Security, Roles & Responsibility, Report Preparation
- Physical vs. Logical access, Viruses, Sources of Transmissions, Technical controls
- Antivirus software: Scanners, Active monitors, Behavior blockers, Logical intrusion, Best Password practices, Firewall
- Types of Controls: Access Controls, Cryptography, Biometrics
- Audit trails and logs: Audit trails and types of errors, IS audit, Parameters of IS audit
- Risk Management: Phases, focal Point, System Characterization, Vulnerability Assessment
- Control Analysis: Likelihood Determination, Impact Analysis, Risk Determination, Results Documentation
- Risk Management: Business Continuity Planning, Components, Phases of BCP, Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
- Web Security: Passive attacks, Active Attacks, Methods to avoid internet attacks
- Internet Security Controls, Firewall Security SystemsIntrusion Detection Systems, Components of IDS, Digital Certificates
- Commerce vs. E-Business, Business to Consumer (B2C), Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), E-Government
- Supply Chain Management: Integrating systems, Methods, Using SCM Software
- Using ERP Software, Evolution of ERP, Business Objectives and IT
- ERP & E-commerce, ERP & CRM, ERP– Ownership and sponsor ship
- Ethics in IS: Threats to Privacy, Electronic Surveillance, Data Profiling, TRIPS, Workplace Monitoring