 |

VU
Information
System (CS507)
LESSON
34
Types of
Controls
Implementation
of controls is a critical security feature of
information systems. They
block and
detect
various forms of intrusion and
protect various components of the
entire information
systems,
are these telecommunication
lines or computer software's and
hard wares.
1. Access
Controls
Controlling who can access
the system.
2. Input
Controls
Controls over how the
data is input to the
system.
3. Communication
Controls
Controls over the transfer
of data between LAN, WAN
or
internet.
4. Processing
Controls
controlling the processing of
data
5. Database
Controls
Securing the most important
asset of the
organization
6. Output
controls
controlling the privacy of
the data.
Access
Controls
34.1
These
controls establish the interface
between the would-be user of
the computer system and
the
computer
itself. These controls
monitor the initial handshaking procedure
of the user with
the
operating
system. For example when a
customer enter the card and
the pin code in an
automatic
teller
machine (ATM), the access
controls are exercised by
the system to block unwanted
or
illegitimate
access.
The
identity of the user needs
to be established before granting access.
The user should be
given
access
to the nature and kind of
resources he is entitled to access.
Actions taken by users to
have
access
beyond the limits defined
should be blocked and
recorded.
Why
Access Controls?
Access
controls have gained
critical importance in the
modern computing age for
two significant
reasons.
� Widespread
deployment of distributed systems
has resulted in many users
being
disbursed
physically. e.g. through Web
based systems, local Area
Networks, wide
Area
Networks
� The
rapid growth of E-Commerce systems
has resulted in substantial work
being
undertaken
to identify and authenticate the
parties.
Cryptography
34.2
In
literal terms, cryptography means
science of coded writing. It is a
security safeguard to render
information
unintelligible if unauthorized
individuals intercept the transmission.
When the
information
is to be used, it can be decoded.
"The conversion of data into
a secret code for
the
secure
transmission over a public network is
called cryptography."
Encryption
& Decryption
Cryptography
primarily consists of two
basic processes. These
processes are explained
through
a
diagram.
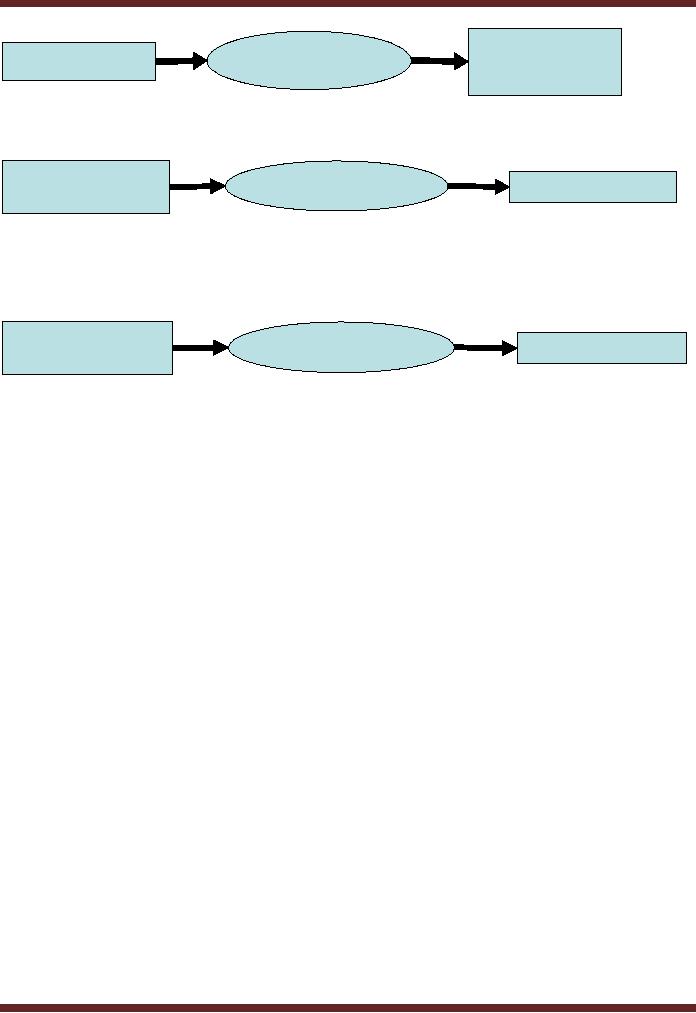
� Encryption
the process of converting
data into codes
(cryptograms)
146
VU
Information
System (CS507)
Ciphertext
/
Encryption
Original
Data
Encrypted
data
�
Decryption
the process of decoding
the code arrived at data
actually encrypted
Ciphertext
/
Decryption
Original
Data
Encrypted
data
The
above processes give rise to
two forms of data
� Clear
text it is the data to be
encrypted.
� Cipher
text it is the code
created out of data after
encryption
Ciphertext
/
Decryption
Original
Data
Encrypted
data
As
shown in the above diagram,
the original text, or
"plaintext," is converted into a
coded
equivalent
called "ciphertext" via an encryption
process.
Identification
& Authentication
Access
controls focus on the
correct identification of the
user seeking permission to access
the
system.
There can be various sources of
identifying and authenticating
the user.
� What
a user remembers name,
birthdate, password
� What
a user possesses badge,
plastic card
� What
a user is personal
characterictics
Biometrics
34.3
Identification
of an individual through unique physical
characteristics is proving to be quite
safe
and
secure for allowing access.
The study of personal
characteristics has been extensively
used
for
identification purposes. Biometrics can
be defined as study of automated methods
for
uniquely
recognizing humans based upon one or
more intrinsic physical or behavioral
traits.
Scope
of Biometrics
Most
commonly, following personal physical
characteristics are
covered,
� Finger
print
� Hand
print
� Voice
Print
� Facial
profiling measuring distance
between various points on
face
� Iris/retinal
recognition eye patterns
In
addition to the aforesaid
access controls, there may
be
1.
Input controls controls
over correct data
entry
2.
Communications controls controls
over transporting data
safely through local
area
networks
(LAN's) or wide area
networks (WAN's).
147

VU
Information
System (CS507)
3.
Processing controls Controls
over the integrity of
processing instructions being
executed
by the
operating system and application
software's.
4.
Database controls implemented to
maintain the integrity of
the database.
5.
Output controls controls
over providing right content
to the users.
The
construction of effective security system
should take into account
the design and
implementation
of all the above
controls.
Processing
instructions carried out by
the operating system and application
software should be
monitored
by implementation of controls. If the
processing controls are not
effectively
implemented, we
could have undesirable situations
arising. For example, in
case of an operating
system,
while connecting to a website, a
concealed link may be
activated at the same time
to
transfer
specified or all information. In
case of an application software designed to
compute
interest at
month end may contain
unauthorized instruction to transfer
pennies or cents or
paisas
to a particular account. Hence care needs
to be taken that calculations are
accurate and
any
rounding up or down is adequately
explained and carried out,
data is processed correctly
as
expected,
control totals reconcile and
processing errors are logged,
researched and corrected
timely
and sufficient audit trail
to trace from source to
output and vice
versa.
LESSON
35
148
Table of Contents:
- Need for information, Sources of Information: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Sources
- Data vs. Information, Information Quality Checklist
- Size of the Organization and Information Requirements
- Hierarchical organization, Organizational Structure, Culture of the Organization
- Elements of Environment: Legal, Economic, Social, Technological, Corporate social responsibility, Ethics
- Manual Vs Computerised Information Systems, Emerging Digital Firms
- Open-Loop System, Closed Loop System, Open Systems, Closed Systems, Level of Planning
- Components of a system, Types of Systems, Attributes of an IS/CBIS
- Infrastructure: Transaction Processing System, Management Information System
- Support Systems: Office Automation Systems, Decision Support Systems, Types of DSS
- Data Mart: Online Analytical Processing (OLAP), Types of Models Used in DSS
- Organizational Information Systems, Marketing Information Systems, Key CRM Tasks
- Manufacturing Information System, Inventory Sub System, Production Sub System, Quality Sub system
- Accounting & Financial Information Systems, Human Resource Information Systems
- Decision Making: Types of Problems, Type of Decisions
- Phases of decision-making: Intelligence Phase, Design Phase, Choice Phase, Implementation Phase
- Planning for System Development: Models Used for and Types of System Development Life-Cycle
- Project lifecycle vs. SDLC, Costs of Proposed System, Classic lifecycle Model
- Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD), Design of the information flow, data base, User Interface
- Incremental Model: Evaluation, Incremental vs. Iterative
- Spiral Model: Determine Objectives, Alternatives and Constraints, Prototyping
- System Analysis: Systems Analyst, System Design, Designing user interface
- System Analysis & Design Methods, Structured Analysis and Design, Flow Chart
- Symbols used for flow charts: Good Practices, Data Flow Diagram
- Rules for DFD’s: Entity Relationship Diagram
- Symbols: Object-Orientation, Object Oriented Analysis
- Object Oriented Analysis and Design: Object, Classes, Inheritance, Encapsulation, Polymorphism
- Critical Success Factors (CSF): CSF vs. Key Performance Indicator, Centralized vs. Distributed Processing
- Security of Information System: Security Issues, Objective, Scope, Policy, Program
- Threat Identification: Types of Threats, Control Analysis, Impact analysis, Occurrence of threat
- Control Adjustment: cost effective Security, Roles & Responsibility, Report Preparation
- Physical vs. Logical access, Viruses, Sources of Transmissions, Technical controls
- Antivirus software: Scanners, Active monitors, Behavior blockers, Logical intrusion, Best Password practices, Firewall
- Types of Controls: Access Controls, Cryptography, Biometrics
- Audit trails and logs: Audit trails and types of errors, IS audit, Parameters of IS audit
- Risk Management: Phases, focal Point, System Characterization, Vulnerability Assessment
- Control Analysis: Likelihood Determination, Impact Analysis, Risk Determination, Results Documentation
- Risk Management: Business Continuity Planning, Components, Phases of BCP, Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
- Web Security: Passive attacks, Active Attacks, Methods to avoid internet attacks
- Internet Security Controls, Firewall Security SystemsIntrusion Detection Systems, Components of IDS, Digital Certificates
- Commerce vs. E-Business, Business to Consumer (B2C), Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), E-Government
- Supply Chain Management: Integrating systems, Methods, Using SCM Software
- Using ERP Software, Evolution of ERP, Business Objectives and IT
- ERP & E-commerce, ERP & CRM, ERP– Ownership and sponsor ship
- Ethics in IS: Threats to Privacy, Electronic Surveillance, Data Profiling, TRIPS, Workplace Monitoring