 |

VU
Information
System (CS507)
LESSON
28
Critical
Success Factors
(CSF)
Critical
Success Factor (CSF) is a business term
for an element which is
necessary for an organization or
project
to achieve its mission. For
example, for an international
package delivery system, CSF's
can be
identified
such as safe transport of customer
consignments, timely delivery of
consignment, online
status
confirmation
system to inform customers
and proper packaging and
handling.
Critical
Success Factors differ from
organization to organization. While approving any
project, the
management
may evaluate the project on the
basis of certain factors critical to the
success or failure of
the
project.
For instance:
� Money
factors: positive cash flow,
revenue growth, and profit
margins.
� Acquiring
new customers and/or
distributors
� Customer
satisfaction No. of complaints,
after sales service
� Quality
Customer feed back on the
product.
� Product /
service development -- what's new
that will increase business
with existing customers
and
attract new ones?
� Intellectual
capital enhancing production
techniques and acquiring knowledge relating
to
advancement
in hardware/machines, equipment,
processes.
� Strategic
relationships -- new sources of business,
products and outside revenue,
sub contracting.
� Employee
development and retention
� Sustainability
� Corporate
social responsibility
� Corporate
Governance
27.1
Sources of Critical Success
Factors
Critical
Success Factors have to be
analyzed and established.
CSF's may be developed from
various sources.
Generally
four major sources of identifying
CSF's are
� Industry
CSFs resulting from specific
industry characteristics;
� CSF's
resulting from the chosen competitive
strategy of the business e.g.
quick and timely
delivery
may be
critical to courier service
business
� Environmental
CSFs resulting from economic or
technological changes; and
� Temporal
CSFs resulting from internal
organizational needs and
changes.
27.2
CSF vs. Key Performance
Indicator
A critical
success factor is not a key
performance indicator or KPI. Critical
Success Factors are
elements
that
are vital for a strategy to
be successful. A KPI measures the
achievements.
The
following example will
clarify the difference. A CSF for
improved sales may be
adopting a new sales
strategy
through better and regularly arranged
display of products in the shop windows.
However, the KPI
identified
would be the increased/decreased Average
Revenue Per Customer as a
result of the strategy.
Key
Performance Indicators directly or
indirectly measure the results of
implementation of Critical Success
Factors.
KPI's are measures that
quantify objectives and
enable the measurement of strategic
performance.
Computing
Environments
Availability
of information to various users
also depends on how the
information is processed, at what
location
the information is processed and
where and to whom it is
available after being processed.
This
leads
us to the issues like processing
information at one location or
different locations. Organizations
work
with
various computing environments for proper
use of information
system
125

VU
Information
System (CS507)
�
Stand
Alone Processing
�
Centralised
Environment
�
Distributed
Environment
�
Web
Based Environment
Stand
Alone Processing
Stand-alone,
self-contained computer is usually a microcomputer
that is not connected to a
network of
computers
and can be used in isolation
from any other device.
The processing activities undertaken
on
such a
computer are usually termed as
stand-alone processing.
Stand
alone environment may exist
in some organization, but is not the
generally followed practice
in
today's
business environment. Therefore we
will not be discussing this
environment.
27.3
Centralized vs. Distributed
Processing
Centralized
Processing is performed in one computer
or in a cluster of coupled computers in a
single
location.
Centralized processing was the
architecture that evolved
from the very first computers;
however,
user
access was via dumb
terminals that performed none of the
primary processing. Today,
centralized
computers
are still widely used,
but the terminals are mostly
full-featured desktop computers.
Distributed
processing refers to any of a variety of
computer systems that use
more than one computer, or
processor,
to run an application. More often,
however, distributed processing refers to
local-area networks
(LANs)
designed so that a single program
can run simultaneously at
various sites. Most
distributed
processing
systems contain sophisticated software
that detects idle CPUs on
the network and parcels
out
programs
to utilize them. Another
form of distributed processing involves
distributed databases,
databases
in
which the data is stored
across two or more computer
systems. The database system
keeps track of where
the
data is so that the distributed
nature of the database is not
apparent to users.
Distributed
processing is a programming paradigm
focusing on designing distributed, open,
scalable,
transparent,
fault tolerant systems. This
paradigm is a natural result of the use
of computers to form
networks.
Distributed computing is decentralized
and parallel computing, using two or
more computers
communicating
over a network to accomplish a common
objective or task. The types of
hardware,
programming
languages, operating systems and
other resources may vary
drastically. It is similar to
computer
clustering with the main difference being
a wide geographic dispersion of the
resources.
As the
terms can explain, processing
can be done at one location in
case on centralized or at
different
locations
in case of distributed processing.
The question arises is how
both types of processing are
different
from
each other.
126
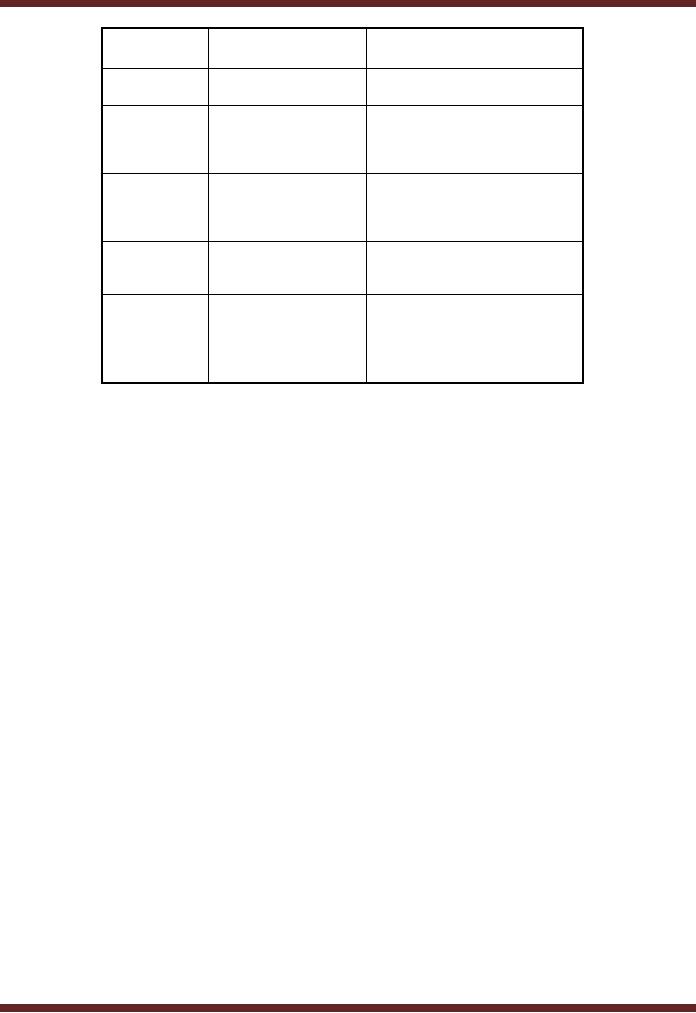
VU
Information
System (CS507)
Aspect
Centralized
Distributed
Processing
Processing
managed
On multiple
machines
at one
server
Computing
Low
(since processing High
(since more than
one
Power
managed at
one
machines
are involved)
machine)
Data
Limited
(Depends
Flexible
(can be increased by
processing
upon
the central
distributing
the task on
multiple
machine)
machines)
capability
System
Controls
Integrated
Controls
integrated but
Management
but
limited to central
distributed to
the various
server
servers
Security
High
(Physical and
High
(Physical and
Logical
Logical
Controls)
controls
distributed to all
servers,
therefore requiring
high
level of security
management)
27.4
Web based
Environment
The
typically refers to the use of
web, internet and browser
based applications for transactions
execution. In
Web
based environment, clients
connect to the application through Broad-band or
base band/dial up
connection.
Application is located on the enterprise
server which is accessed by the
client through the
internet
connection. Access may be given to single
application software or the entire operating
system. Web
based
environment can be combined with
and applied to both centralized or
decentralized to optimize the
performance.
Web
based architecture can be
used, either to give access to the
company employees to the
information
system
e.g Virtual Private Networks
(VPN) in case of banks or to give
access to any body and
every body to
company's
information system.
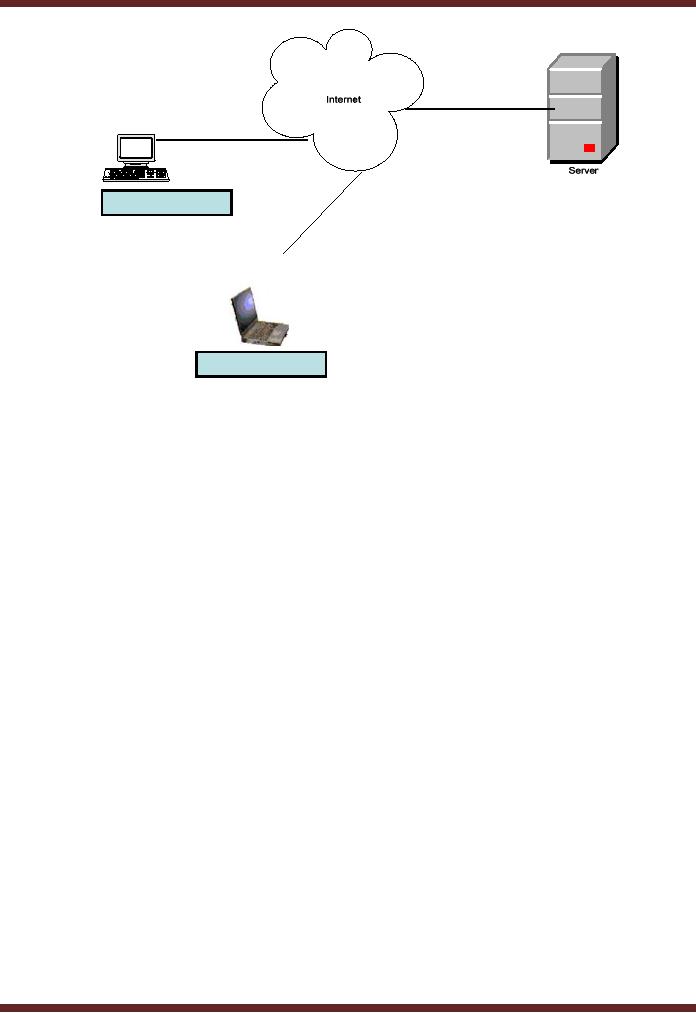
Following
example can explain the concept in a
better fashion. Two users A & B
present at remote
locations
or we can say outside the organization
may want to access the server
located within the
organization. They
may get connected with the
internet and access the
server located in the
organization.
The
server needs to be online as
well so as to be accessed by A & B
through any of the means (broad
band,
base
band, wi-fi, or satellite).
Hence data can be transmitted
and retrieved using the internet.
Availability of
connection of
proper bandwidth allowing appropriate
internet connection speed is critical to
both
transmission
and retrieval. Due to this reason,
companies have taken
dedicated lines to enjoy
uninterrupted
service.
127
VU
Information
System (CS507)
Remote
User A
Remote
User B
27.5
Internet
An interconnected
system of networks that connects
computers around the world via the TCP/IP
protocol.
Companies
contact Internet service providers
for availability of connection which
allows them to be a part
of
internet. An intranet is a private
enterprise owned communication network
that uses Internet
Protocols,
network
connectivity, and public
telecommunication system to share
organization's information or
operations
with its employees, and to
enable the employees to communicate
with each other.
The
Internet`s technological success depends on
its principal communication tools, the
Transmission
Control
Protocol (TCP) and the
Internet Protocol (IP). They
are referred to frequently as TCP/IP.
A
protocol
is an agreed-upon set of conventions that
defines the rules of communication. TCP
breaks down
and
reassembles packets, whereas IP is
responsible for ensuring
that the packets are sent to
the right
destination.
Data
travels across the Internet
through several levels of networks
until it reaches its destination.
E-mail
messages
arrive at the mail server (similar to the local post
office) from a remote
personal computer
connected
by a modem, or a node on a local-area
network. From the server, the
messages pass through
a
router,
a special-purpose computer ensuring that
each message is sent to its
correct destination. A message
may
pass through several networks to
reach its destination. Each
network has its own
router that
determines
how best to move the message
closer to its destination, taking
into account the traffic on
the
network.
A message passes from one
network to the next, until it arrives at
the destination network, from
where
it can be sent to the recipient, who
has a mailbox on that
network.
128
Table of Contents:
- Need for information, Sources of Information: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Sources
- Data vs. Information, Information Quality Checklist
- Size of the Organization and Information Requirements
- Hierarchical organization, Organizational Structure, Culture of the Organization
- Elements of Environment: Legal, Economic, Social, Technological, Corporate social responsibility, Ethics
- Manual Vs Computerised Information Systems, Emerging Digital Firms
- Open-Loop System, Closed Loop System, Open Systems, Closed Systems, Level of Planning
- Components of a system, Types of Systems, Attributes of an IS/CBIS
- Infrastructure: Transaction Processing System, Management Information System
- Support Systems: Office Automation Systems, Decision Support Systems, Types of DSS
- Data Mart: Online Analytical Processing (OLAP), Types of Models Used in DSS
- Organizational Information Systems, Marketing Information Systems, Key CRM Tasks
- Manufacturing Information System, Inventory Sub System, Production Sub System, Quality Sub system
- Accounting & Financial Information Systems, Human Resource Information Systems
- Decision Making: Types of Problems, Type of Decisions
- Phases of decision-making: Intelligence Phase, Design Phase, Choice Phase, Implementation Phase
- Planning for System Development: Models Used for and Types of System Development Life-Cycle
- Project lifecycle vs. SDLC, Costs of Proposed System, Classic lifecycle Model
- Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD), Design of the information flow, data base, User Interface
- Incremental Model: Evaluation, Incremental vs. Iterative
- Spiral Model: Determine Objectives, Alternatives and Constraints, Prototyping
- System Analysis: Systems Analyst, System Design, Designing user interface
- System Analysis & Design Methods, Structured Analysis and Design, Flow Chart
- Symbols used for flow charts: Good Practices, Data Flow Diagram
- Rules for DFD’s: Entity Relationship Diagram
- Symbols: Object-Orientation, Object Oriented Analysis
- Object Oriented Analysis and Design: Object, Classes, Inheritance, Encapsulation, Polymorphism
- Critical Success Factors (CSF): CSF vs. Key Performance Indicator, Centralized vs. Distributed Processing
- Security of Information System: Security Issues, Objective, Scope, Policy, Program
- Threat Identification: Types of Threats, Control Analysis, Impact analysis, Occurrence of threat
- Control Adjustment: cost effective Security, Roles & Responsibility, Report Preparation
- Physical vs. Logical access, Viruses, Sources of Transmissions, Technical controls
- Antivirus software: Scanners, Active monitors, Behavior blockers, Logical intrusion, Best Password practices, Firewall
- Types of Controls: Access Controls, Cryptography, Biometrics
- Audit trails and logs: Audit trails and types of errors, IS audit, Parameters of IS audit
- Risk Management: Phases, focal Point, System Characterization, Vulnerability Assessment
- Control Analysis: Likelihood Determination, Impact Analysis, Risk Determination, Results Documentation
- Risk Management: Business Continuity Planning, Components, Phases of BCP, Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
- Web Security: Passive attacks, Active Attacks, Methods to avoid internet attacks
- Internet Security Controls, Firewall Security SystemsIntrusion Detection Systems, Components of IDS, Digital Certificates
- Commerce vs. E-Business, Business to Consumer (B2C), Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), E-Government
- Supply Chain Management: Integrating systems, Methods, Using SCM Software
- Using ERP Software, Evolution of ERP, Business Objectives and IT
- ERP & E-commerce, ERP & CRM, ERP– Ownership and sponsor ship
- Ethics in IS: Threats to Privacy, Electronic Surveillance, Data Profiling, TRIPS, Workplace Monitoring