 |
VU
Information
System (CS507)
LESSON
14
Marketing
No
information system can exist
in an organization without being linked
with other functional
information
systems.
This linkage is important for the over
all smooth functionality of the
information system since
it
allows
easy transformation and
usage of information.
�
Marketing
Production
subsystem needs to be linked
with the marketing system so as to
produce right amount of
product.
�
Human
resource system
Most
of the human resource is involved in the
manufacturing process. Since factory
premises has to be
working
continuously, availability of relevant labour is
critical.
�
Accounts and
Finance
Accounts should
have a control over various
recording points in the entire process
from procurement
to
finished good store room.
This would help both in recording
transactions for financial
statements
and
approving and arranging for
cash payments.
Accounting
information system (AIS) is
linked to all the information
systems in an organization. This is
important
because the data required for
proper book keeping and
generation of transactional reports is
extracted
from all over the organization.
For instance sales
information can be sought
only from marketing
information
system and stock information
is available in manufacturing information
system.
Here
we would consider an example to see
how AIS records internal
data describing manufacturing
operations
this requires use of data
collection terminals at the manufacturing
facility. It also
records
external
data describing firms transactions
with its suppliers.
55

VU
Information
System (CS507)
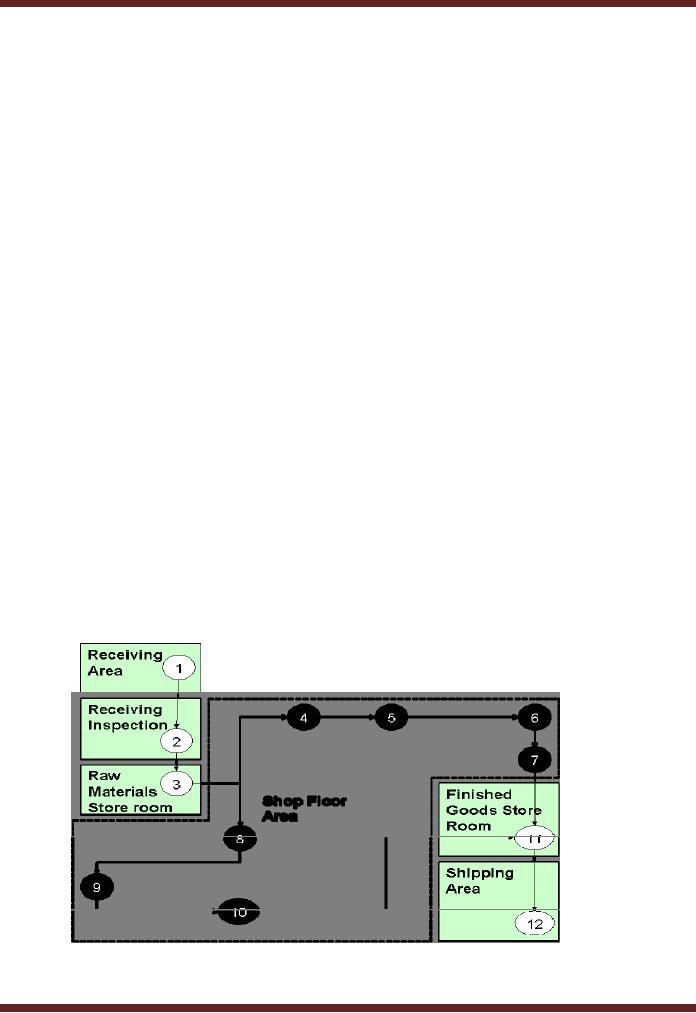
The
figure shows twelve data
collection terminals located at the
factory area. Raw materials
are received
from
suppliers, and receipt data
is entered into the terminal. Quality
control inspection is conducted
and
results
are recorded at terminal two.
Acceptance into and release
from the raw materials room
is logged in
to the terminal
three. Terminals four to ten
are used by production
employees to record start
and
completion
of each step of production.
Terminal eleven records the
entry into the finished
goods store
room.
Shipping to customers is recorded at terminal
12.
14.1
Accounting & Financial Information
Systems
Accounting
and financial information systems
cater for the needs of Accounts &
Finance Department.
These
are responsible for managing
financial assets in order to maximise
return, like
Cash
o
Stocks
o
Bonds
o
Other
investments
o
Financial
liabilities
o
Capitalization of
the firm through acquisition of new
financial assets
o
It
also produces the periodic
and annual financial
statements.
Importance
of Accounting & financial Information
Systems
Every
transaction that an organization
undertakes has a financial impact, to be
recorded and reported by the
accounts
& finance department. Hence there is
a share of interest for
every department in reports and
information
produced by this system. Financial Information
Systems like other
information systems should
cater
for information requirements at
each level, for
instance.
Strategic
level
1.
Investment goals
2.
long range forecasts for
firm's financial performance
3.
Acquisition of financial resources and
goals
Knowledge
Level
1.
Analytical tools to design the
right mix for
investment
2.
Portfolio updates
3.
Market information
analysis
Management
level
1.
Control over firm's financial
resources
2.
Investment management
3. Budget
management
4. Tax
management
5.
Profitability & Performance
Evaluation
Operational
Level
1.
Cash flow statements through
various transactions
2.
Inventory and debtors
management
3. Creditors
Management
14.2
Human Resource Information
Systems
56
VU
Information
System (CS507)
It is an
information system that
combines many human
resources functions, including
benefits
administration,
payroll, recruiting and
training, and performance
analysis and review into one
package. It
helps
in
o Building
database of employees
o Keeping
track for new positions or
vacancies
o Keeping
master records for each
employees
o Performance
evaluations and training
assessments
14.3
IT Department
Information
by itself is proving to be the most
critical resource for organizations.
Such is the criticality
that
other
resources of the organization cannot be managed
without it. This has lead to
the evolution of
information
systems to efficiently manage the
information resource of the organization. This
system is
usually
employed by the Information Services
department which is the major functional
area of the
organization.
14.3.1
Evolution of the IT Department
IS department
function has been evolving
based on the needs of user
departments
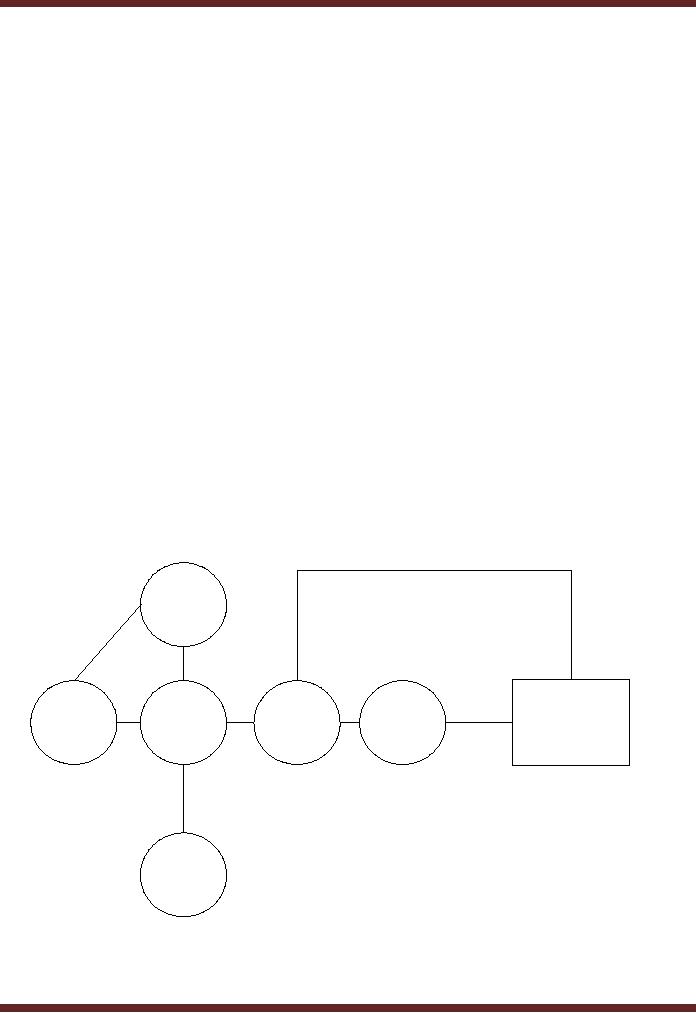
�
Traditional
Computing -- Initially User
was not directly linked with
using the computing facilities
and
the IT
workforce was involved in
assisting user to achieve
his computer related
goals.
Database
administrator
Systems
User
Programmer
Operator
Computer
Analyst
Network
Specialist
57
VU
Information
System (CS507)
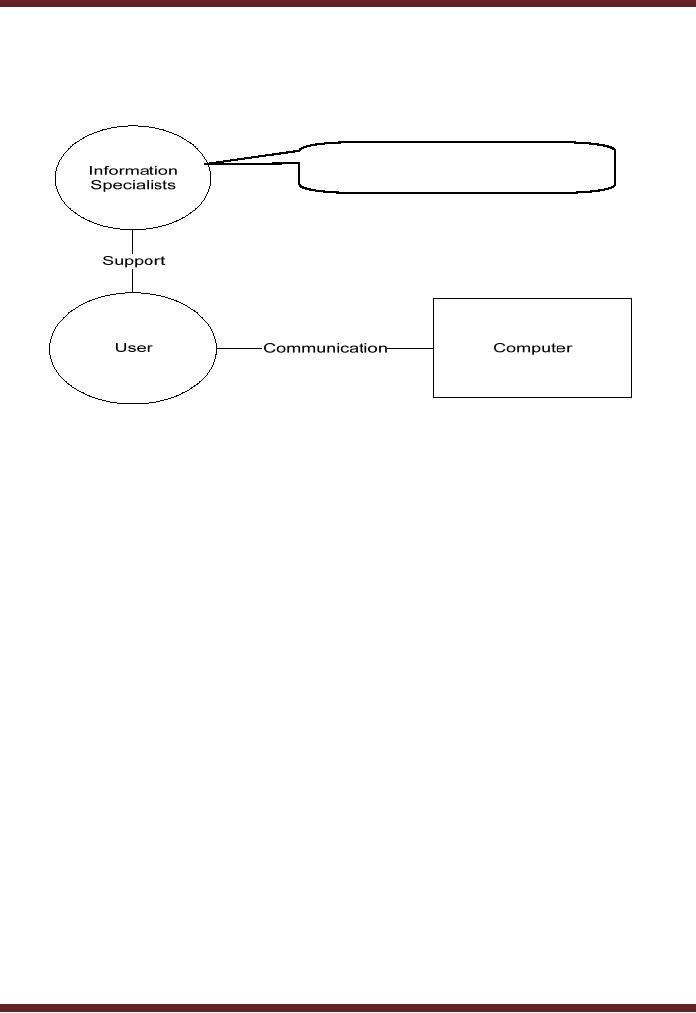
�
End
User Computing As the computer
users become more literate,
much of the work was done
by
users
themselves and IT department took
over as a support
function.
All information specialists
collectively
support the user in using
computing
facilities.
58
Table of Contents:
- Need for information, Sources of Information: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Sources
- Data vs. Information, Information Quality Checklist
- Size of the Organization and Information Requirements
- Hierarchical organization, Organizational Structure, Culture of the Organization
- Elements of Environment: Legal, Economic, Social, Technological, Corporate social responsibility, Ethics
- Manual Vs Computerised Information Systems, Emerging Digital Firms
- Open-Loop System, Closed Loop System, Open Systems, Closed Systems, Level of Planning
- Components of a system, Types of Systems, Attributes of an IS/CBIS
- Infrastructure: Transaction Processing System, Management Information System
- Support Systems: Office Automation Systems, Decision Support Systems, Types of DSS
- Data Mart: Online Analytical Processing (OLAP), Types of Models Used in DSS
- Organizational Information Systems, Marketing Information Systems, Key CRM Tasks
- Manufacturing Information System, Inventory Sub System, Production Sub System, Quality Sub system
- Accounting & Financial Information Systems, Human Resource Information Systems
- Decision Making: Types of Problems, Type of Decisions
- Phases of decision-making: Intelligence Phase, Design Phase, Choice Phase, Implementation Phase
- Planning for System Development: Models Used for and Types of System Development Life-Cycle
- Project lifecycle vs. SDLC, Costs of Proposed System, Classic lifecycle Model
- Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD), Design of the information flow, data base, User Interface
- Incremental Model: Evaluation, Incremental vs. Iterative
- Spiral Model: Determine Objectives, Alternatives and Constraints, Prototyping
- System Analysis: Systems Analyst, System Design, Designing user interface
- System Analysis & Design Methods, Structured Analysis and Design, Flow Chart
- Symbols used for flow charts: Good Practices, Data Flow Diagram
- Rules for DFD’s: Entity Relationship Diagram
- Symbols: Object-Orientation, Object Oriented Analysis
- Object Oriented Analysis and Design: Object, Classes, Inheritance, Encapsulation, Polymorphism
- Critical Success Factors (CSF): CSF vs. Key Performance Indicator, Centralized vs. Distributed Processing
- Security of Information System: Security Issues, Objective, Scope, Policy, Program
- Threat Identification: Types of Threats, Control Analysis, Impact analysis, Occurrence of threat
- Control Adjustment: cost effective Security, Roles & Responsibility, Report Preparation
- Physical vs. Logical access, Viruses, Sources of Transmissions, Technical controls
- Antivirus software: Scanners, Active monitors, Behavior blockers, Logical intrusion, Best Password practices, Firewall
- Types of Controls: Access Controls, Cryptography, Biometrics
- Audit trails and logs: Audit trails and types of errors, IS audit, Parameters of IS audit
- Risk Management: Phases, focal Point, System Characterization, Vulnerability Assessment
- Control Analysis: Likelihood Determination, Impact Analysis, Risk Determination, Results Documentation
- Risk Management: Business Continuity Planning, Components, Phases of BCP, Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
- Web Security: Passive attacks, Active Attacks, Methods to avoid internet attacks
- Internet Security Controls, Firewall Security SystemsIntrusion Detection Systems, Components of IDS, Digital Certificates
- Commerce vs. E-Business, Business to Consumer (B2C), Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), E-Government
- Supply Chain Management: Integrating systems, Methods, Using SCM Software
- Using ERP Software, Evolution of ERP, Business Objectives and IT
- ERP & E-commerce, ERP & CRM, ERP– Ownership and sponsor ship
- Ethics in IS: Threats to Privacy, Electronic Surveillance, Data Profiling, TRIPS, Workplace Monitoring