 |

VU
Information
System (CS507)
LESSON
10
Support
Systems
Seeing
the benefits of MIS for middle level
managers, Computerised systems
have been devised for
other
employees
in the organization to help them complete
their work efficiently and
effectively.
10.1
Support systems can be classified
into two
categories
� Office
automation systems
� Decision
support systems
10.1.1
Office Automation Systems
Office
automation system includes formal
and informal electronic systems
primarily concerned with
the
communication of
information to and from
persons both inside and
outside the firm. It supports
data
workers
in an organization.
For
Instance
� Word
processing
� Desktop
publishing
� Imaging
& Web publishing
� Electronic
calendars manager's appt.
calendars
� Email
� Audio
& video conferencing establishing
communication between geographically
dispersed
persons.
10.1.2
Decision Support Systems
Before
moving forward with the
concept of decision support
system, we would take a look
at the definition
of
MIS
"An integrated
man-machine system for
providing information to support the
operations, management
and
decision
making functions in an
organization."
(Prof.
Gordon Davis University of
Minnesota)
Four
Criteria for designing models
and systems to support
management decisions making were
laid down
by
J.D.C. Little. These
were
�
Robustness
�
Ease
of Control
�
Simplicity
�
Completeness
of relevant detail
Decision Support
Systems was defined by Bill
Inmon, father of data
warehouse, as
"a
system used to support
managerial decisions. Usually DSS
involves the analysis of many units of
data
in a
heuristic fashion. As a rule, DSS
processing does not involve
the update of data"
Heuristic
simply means a particular technique of directing
one's attention in learning, discovery or
problem
solving. It
assists in non-routine decision making
process due to powerful
analytical abilities.
33
VU
Information
System (CS507)
For
Instance
For
any scenario all the related
factors with their ranges of
variability are entered into
DSS, which helps
guide
managers for any new
scenario that emerges. DSS
can stimulate innovation in
decision making by
helping
managers to existing decision making
procedures.
An example of
Decision Support System
An
outfit store maintains ready
made garments and stitched
clothes for various classes
of society. Due to
fluctuating
changes in fashion trends, pre-seasonal
planning becomes critical.
�
A Planning
and forecasting software can
be used by management to
�
Measure
customer reactions to re-pricing
�
When
to initiate clearance sales
for old stock
�
Deciding
about discount percentages
�
When
to order new stock for the
season
10.2
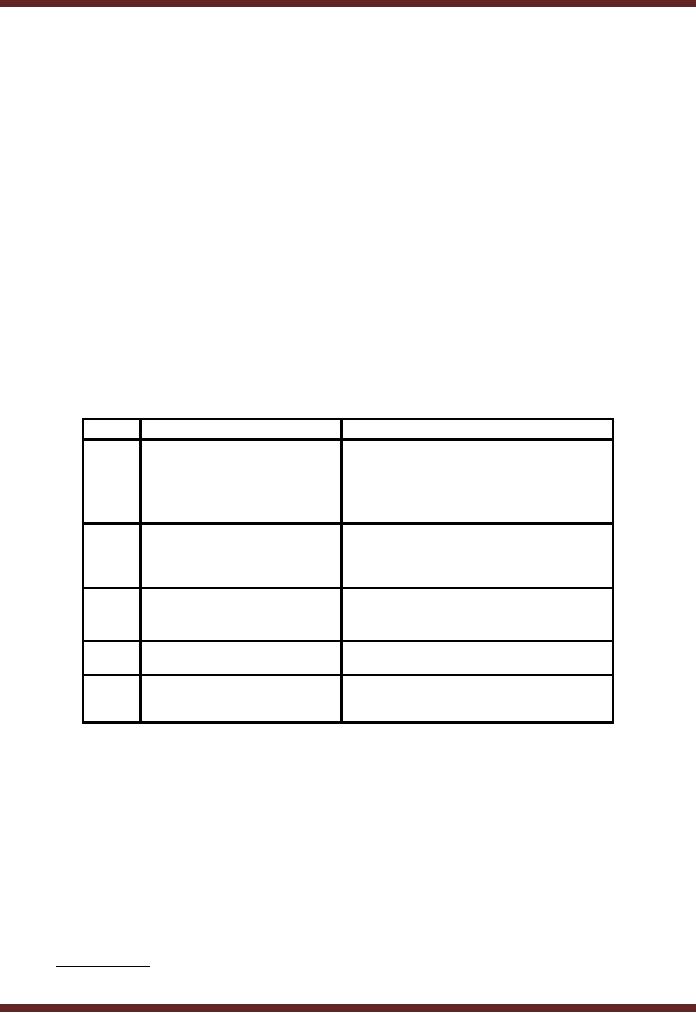
Functionalities of MIS and DSS
Sr.
No. MIS
DSS
1
Provides
information on
Helps
in non routine decision
making.
monitoring
and controlling the
business.
2
Fixed
and regular reports
are
Users
are not linked with the
structured
generated
from data kept in
information
flows.
TPS.
3
Report formats
are predefined. Greater emphasis on
models, display
graphics
& ad hoc queries.
4
User
is part of the system
DSS is
a small part of users'
actions.
5
Controlled
by IT Dept.
Directly
used by middle level
managers
Table
10.1
10.3
Types of DSS
DSS,
may either be
�
Model
Driven DSS
�
Data
Driven DSS
10.3.1
Model Driven DSS
Model
driven DSS uses following
techniques
� What-If
analysis
Attempt
to check the impact of a change in the
assumptions (input
data)
on
the
34

VU
Information
System (CS507)
proposed
solution
e.g.
What will happen to the
market share if the advertising budget
increases by 5 % or
10%?
�
Goal
Seek Analysis
Attempt
to find the value of the inputs
necessary to achieve a desired level of
output. It
uses
"backward" solution
approach
e.g. a
DSS solution yielded a profit of
$2M. What will be the
necessary sales volume
to
generate
a profit of $2.2M?
These
are primarily stand alone
systems isolated from major
organizational information systems
(finance,
manufacturing,
HR, etc). They are developed by
end users and are
not reliant on central
information
systems
control. These systems
combine
�
Use of
a strong model, and
�
Good
user interface to maximise model
utility
They
are not usually data
intensive, hat is very large data bases
are usually not need
for model-driven DSS.
They
use data and parameters
usually provided by decision
makers to aid in analyzing a
situation.
10.3.2
Data Driven DSS
As
opposed to model driven DSS,
these systems use large
pools of data found in major
organizational
systems.
They help to extract information
from the large quantities of data
stored. These systems rely
on
Data
Warehouses created from
Transaction Processing
systems.
�
They
use following techniques for
data analysis
�
Online
analytical processing,
and
�
Data
mining
Components of
DSS
There
are two major
components
�
DSS
data base is a collection of
current and historical data from
internal external sources. It can be
a
massive
data warehouse.
�
Decision Support
Software system is the set of
software tools used for
data analysis. For
instance
� Online
analytical processing (OLAP)
tools
� Data
mining tools
� Models
Data
Warehouse
�
A data
warehouse is a logical collection of
information.
�
It is
gathered from many different
operational databases used to create
business intelligence that
supports
business analysis activities and
decision-making tasks.
�
It is
primarily, a record of an enterprise's
past transactional and operational
information, stored in a
database
designed to favour efficient
data analysis and
reporting.
35

VU
Information
System (CS507)
�
The
term data warehouse generally
refers to the combination of many
different databases across
an
entire
enterprise.
�
Data
warehouses contain a wide variety of data
that present a coherent picture of
business conditions at
a
single point in time.
�
Data
warehouses are generally
batch updated at the end of the
day, week or some period.
Its contents
are
typically historical and static
and may also contain
numerous summaries.
36
Table of Contents:
- Need for information, Sources of Information: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Sources
- Data vs. Information, Information Quality Checklist
- Size of the Organization and Information Requirements
- Hierarchical organization, Organizational Structure, Culture of the Organization
- Elements of Environment: Legal, Economic, Social, Technological, Corporate social responsibility, Ethics
- Manual Vs Computerised Information Systems, Emerging Digital Firms
- Open-Loop System, Closed Loop System, Open Systems, Closed Systems, Level of Planning
- Components of a system, Types of Systems, Attributes of an IS/CBIS
- Infrastructure: Transaction Processing System, Management Information System
- Support Systems: Office Automation Systems, Decision Support Systems, Types of DSS
- Data Mart: Online Analytical Processing (OLAP), Types of Models Used in DSS
- Organizational Information Systems, Marketing Information Systems, Key CRM Tasks
- Manufacturing Information System, Inventory Sub System, Production Sub System, Quality Sub system
- Accounting & Financial Information Systems, Human Resource Information Systems
- Decision Making: Types of Problems, Type of Decisions
- Phases of decision-making: Intelligence Phase, Design Phase, Choice Phase, Implementation Phase
- Planning for System Development: Models Used for and Types of System Development Life-Cycle
- Project lifecycle vs. SDLC, Costs of Proposed System, Classic lifecycle Model
- Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD), Design of the information flow, data base, User Interface
- Incremental Model: Evaluation, Incremental vs. Iterative
- Spiral Model: Determine Objectives, Alternatives and Constraints, Prototyping
- System Analysis: Systems Analyst, System Design, Designing user interface
- System Analysis & Design Methods, Structured Analysis and Design, Flow Chart
- Symbols used for flow charts: Good Practices, Data Flow Diagram
- Rules for DFD’s: Entity Relationship Diagram
- Symbols: Object-Orientation, Object Oriented Analysis
- Object Oriented Analysis and Design: Object, Classes, Inheritance, Encapsulation, Polymorphism
- Critical Success Factors (CSF): CSF vs. Key Performance Indicator, Centralized vs. Distributed Processing
- Security of Information System: Security Issues, Objective, Scope, Policy, Program
- Threat Identification: Types of Threats, Control Analysis, Impact analysis, Occurrence of threat
- Control Adjustment: cost effective Security, Roles & Responsibility, Report Preparation
- Physical vs. Logical access, Viruses, Sources of Transmissions, Technical controls
- Antivirus software: Scanners, Active monitors, Behavior blockers, Logical intrusion, Best Password practices, Firewall
- Types of Controls: Access Controls, Cryptography, Biometrics
- Audit trails and logs: Audit trails and types of errors, IS audit, Parameters of IS audit
- Risk Management: Phases, focal Point, System Characterization, Vulnerability Assessment
- Control Analysis: Likelihood Determination, Impact Analysis, Risk Determination, Results Documentation
- Risk Management: Business Continuity Planning, Components, Phases of BCP, Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
- Web Security: Passive attacks, Active Attacks, Methods to avoid internet attacks
- Internet Security Controls, Firewall Security SystemsIntrusion Detection Systems, Components of IDS, Digital Certificates
- Commerce vs. E-Business, Business to Consumer (B2C), Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), E-Government
- Supply Chain Management: Integrating systems, Methods, Using SCM Software
- Using ERP Software, Evolution of ERP, Business Objectives and IT
- ERP & E-commerce, ERP & CRM, ERP– Ownership and sponsor ship
- Ethics in IS: Threats to Privacy, Electronic Surveillance, Data Profiling, TRIPS, Workplace Monitoring