 |
TEXT BOXES, CHECK BOXES, RADIO BUTTONS |
| << BASICS OF HTML 2 |
| FRAMES AND IMAGES IN HTML >> |
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Lesson
07
TEXT
BOXES, CHECK BOXES, RADIO
BUTTONS
-<input
type=text Name="URL" Value=http://> -
here `value' attribute would
pre-fix the information in
the
text box which is given as
its value (e.g,
http://)
-<Input
type=text Name="address" size="40">
-`size' is used to set size
of the box.
-<input
type=text Name="age" maxlength="3">
-`maxlength' limits the length of the
text in the text box.
Check
boxes are normally used to
get yes/no or true/false
information from a reader.
Syntax is to keep
value
of `type' attribute as `checkbox' in the
input tag. Using `checked'
attribute certain values can
be
displayed
pre-checked in the checkbox. Moreover,
`Name' attribute indicates the unique
field name for a
checkbox.
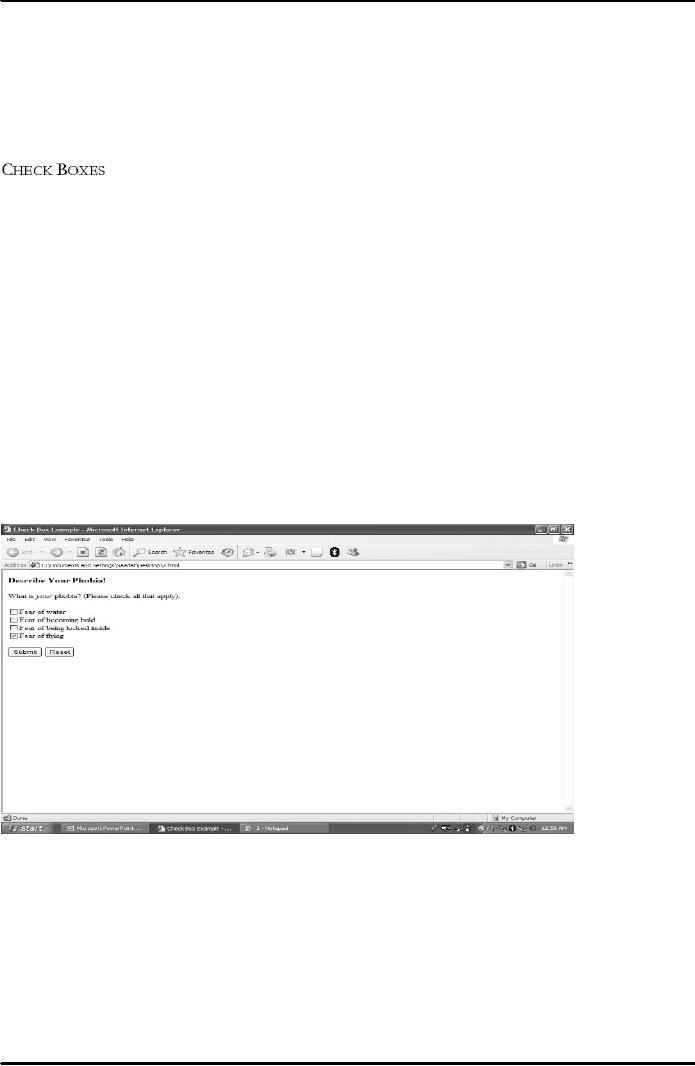
Example
Check box
<HTML>
<HEAD><TITLE>Check Box
Example</TITLE> </HEAD> <BODY>
<H3>Describe
Your
Phobia!</H3> <FORM
ACTION=http://www.sad.com/scripts/formtest.asp
METHOD="POST">
What is <I>your</I> phobia?
(Please check all that
apply):
<P>
<INPUT
TYPE="CHECKBOX" NAME="Water">Fear of
water<BR> <INPUT
TYPE="CHECKBOX"
NAME="Bald">Fear of becoming
bald<BR> <INPUT
TYPE="CHECKBOX"
NAME="Lock">Fear
of being locked inside<BR> <INPUT
TYPE="CHECKBOX" NAME="Flying"
Checked
>Fear of flying<BR>
<P>
<INPUT
TYPE="SUBMIT" VALUE="Submit">
<INPUT TYPE="RESET"> </FORM>
</BODY>
</HTML>
Result
is shown in Fig. 1 below.
Fig.
1
Radio
buttons
Instead of
yes/no choices, you might
want your readers to have
one choice out of many
options. For that
Radio
buttons can be used. General
format <input type="radio"
Name="field name" value="value">
You
supply
the same field name to all
the radio buttons that you
want to group together. `Value' is the unique
text
string that specifies the value of the
option when it is selected.
Example
Radio button
<HTML>
<HEAD><TITLE>Radio Button
Example</TITLE> </HEAD>
<BODY>
<H3>Survey</H3>
<FORM
ACTION="http://www.sad.com/scripts/formtest.asp"
METHOD="POST">
Which of the following best describes
your current income
28

E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
level:<BR><BR><INPUT
TYPE="RADIO" NAME="Income"
VALUE="Poverty">living below
the
poverty
line<BR> <INPUT TYPE="RADIO"
NAME="Income" VALUE="Middle"
Checked>living at
the level of
middle class<BR> <INPUT
TYPE="RADIO" NAME="Income"
VALUE="Upper">living
at the level
ofupper class<BR><BR>
Which of the
following best describes
your political inclination
:<BR><BR><INPUT
TYPE="RADIO"
NAME="Politics"
VALUE="Nationalist" CHECKED>Worker of
Nationalist Party<BR>
<INPUT
TYPE="RADIO"
NAME="Politics" VALUE="Socialist">Member of
Socialist Party<BR>
<INPUT
TYPE="RADIO" NAME="Politics"
VALUE="Republican">Supporter ofRepublican
Party<BR>
<INPUT TYPE="RADIO" NAME="Politics"
VALUE="None">None of the
above<BR>
<P>
<INPUT
TYPE="SUBMIT" VALUE="Submit">
<INPUT TYPE="RESET"> </FORM>
</BODY>
</HTML>
Result
is shown in Fig. 2 below.
Fig.
2
Selection
lists
General
format <select name="field name"
size="no. of items"> Between the
<select> and </select>
tags
are the <option> and
</option> tags whichdefine the list
items. If you omit "size"
the list becomes a
drop-down
list. If size is two or more, the
list becomes a rectangle
with scroll bars for navigating
the
choices.
Using `Selected' attribute an item is
selected by default. Multiple attribute
allows the reader to
select
multiple
items from the list.
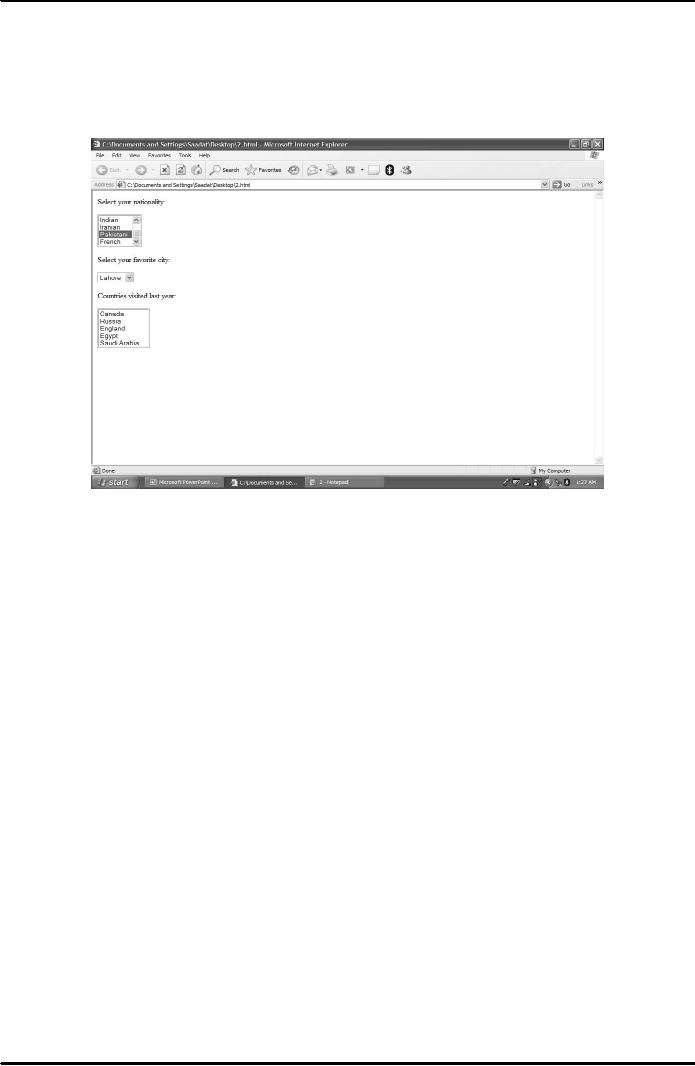
Example -
lists
<HTML><BODY>
<FORM
ACTION="http://www.sad.com/scripts/formtest.asp"
METHOD="POST">
Select your nationality
:<P> <SELECT NAME="Nationality"
SIZE="4">
<OPTION>American</OPTION>
<OPTION>Australian</OPTION>
<OPTION>Hungarian</OPTION>
<OPTION>Indian</OPTION>
<OPTION>Iranian</OPTION>
<OPTION
SELECTED>Pakistani</OPTION>
<OPTION>French</OPTION>
</SELECT><P> Select
your
favorite
city:<P> <SELECT NAME="City">
<OPTION>Sydney</OPTION>
<OPTION>London</OPTION>
<OPTION SELECTED>Lahore</OPTION>
</SELECT><P>
Countries visited
last year:<P> <SELECT
NAME="Countries" SIZE="5"
MULTIPLE>
29
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
<OPTION>Canada</OPTION>
<OPTION>Russia</OPTION>
<OPTION>England</OPTION>
<OPTION>Egypt</OPTION>
<OPTION>Saudi Arabia</OPTION>
</SELECT>
</BODY></HTML>
Result
is shown in Fig. 3 below.
Fig.
3
30
Table of Contents:
- E-COMMERCE
- WHAT IS A NETWORK
- HOW MANY CLASS A, B, C NETWORKS AND HOSTS ARE POSSIBLE
- NETWORKING DEVICES
- BASICS OF HTML 1
- BASICS OF HTML 2
- TEXT BOXES, CHECK BOXES, RADIO BUTTONS
- FRAMES AND IMAGES IN HTML
- TAG ATTRIBUTES, SOUNDS FILES, ANIMATIONS
- STYLE SHEETS 1
- STYLE SHEETS 2
- SOME USEFUL STYLE SHEETS PROPERTIES
- JAVA SCRIPTING 1
- JAVA SCRIPTING 2
- JAVA SCRIPTING 3
- JAVA SCRIPTING AND XML
- CLIENT AND SERVER SIDE PROCESSING OF DATA
- APPLETS, CGI SCRIPTS
- MAINTAINING STATE IN A STATELESS SYSTEM
- INTEGRATION WITH ERP SYSTEMS
- FIREWALLS
- CRYPTOGRAPHY
- HASH FUNCTION AND MESSAGE DIGEST
- SYMMETRIC KEY ALGORITHMS
- VIRTUAL PIN PAYMENT SYSTEM
- E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 1
- E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 2
- SECURE SOCKET LAYER (SSL)
- E-BUSINESS: DISADVANTAGES OF E-BUSINESS
- E-BUSINESS REVENUE MODELS
- E-MAIL MARKETING
- CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM)
- META INFORMATION
- DATA MINING
- CONFIDENCE AND SUPPORT
- ELECTRONIC DATA INTERCHANGE (EDI)
- PERSONAL FINANCE ONLINE
- SUPPLY CHAIN
- PORTER’S MODEL OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY
- BARRIERS TO INTERNATIONAL E-COMMERCE
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 1
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 2
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 3
- GLOBAL LEGAL ISSUES OF E-COMMERCE - 1
- GLOBAL LEGAL ISSUES OF E-COMMERCE - 2