 |
PORTER’S MODEL OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY |
| << SUPPLY CHAIN |
| BARRIERS TO INTERNATIONAL E-COMMERCE >> |
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Lesson
39
PORTER'S
MODEL OF COMPETITIVE
RIVALRY
Porter's
Model helps a firm to
identify threats to its
competitive position and to
devise plans including
the
use of
IT and e-commerce to protect or
enhance that position. Porter
identified five forces of
competitive
rivalry
described as under:
Threat of
potential/new entrants to the
sector
Threat of
substitute product or service in the
existing trade
Bargaining power of
the buyers
Bargaining power of
the suppliers
Competition
between existing players
These
five forces are also
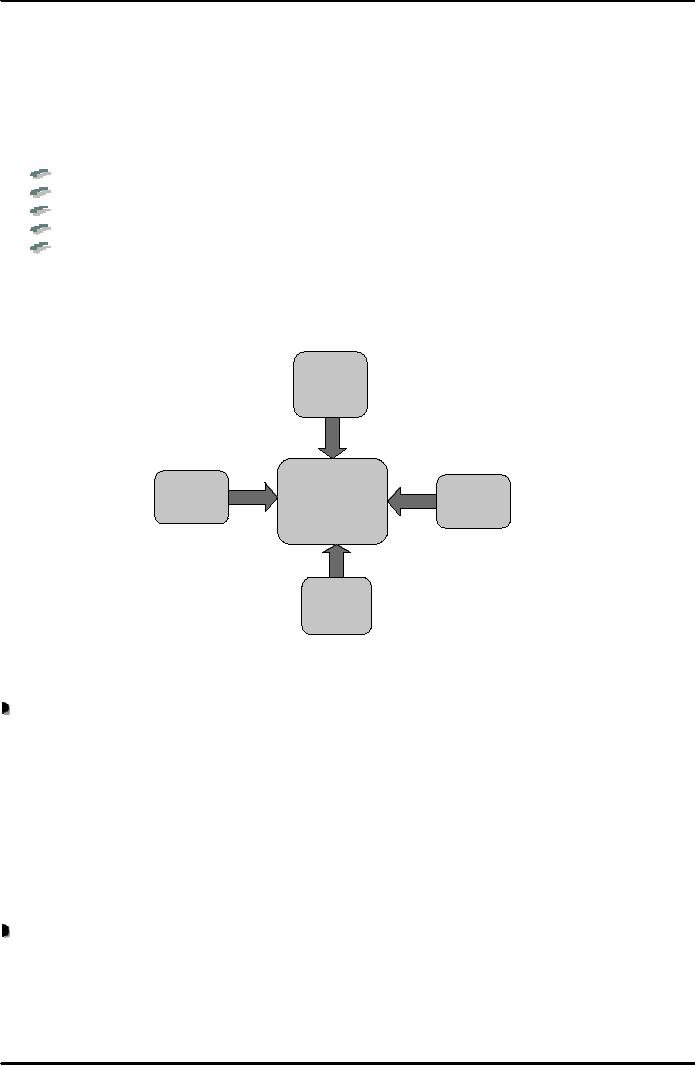
shown in Fig. 1 below:
Threat
of
potential
entrants
Bargaining
Competitive
Bargaining
power
of
rivalry
among
power
of
suppliers
existing
players
buyers
Threat
Of
substitution
Fig.
1
Threat of
new entrants
This threat
relates to the ease with
which a new company or a
company in different product
area can enter a
given
trade sector. Typically, barriers to
entry are capital, knowledge or
skill. IT/EC can be a barrier for
new
entrants,
for instance, where competing
businesses have heavily invested in EDI
and are using the
same,
their
investment would act as a barrier for
new businesses to enter that
trade sector.
Conversely,
advancements
in technology have given rise to new
ideas providing opportunity to
new entrants without
any
need to build the IT infrastructure or
make heavy investment to compete existing
players. For example,
to
start online banking a
company does not require
heavy investment in constructing buildings
(branch
offices),
hiring staff etc. as required in
traditional banking. Rather, making use
of internet technology
coupled
with a sound marketing plan, unique
online banking services can
be initiated.
Threat of
substitution
This threat
arises when a new product is
available that provides the same
function as existing
product/service.
For example, cotton fiber
was, in the past, replaced by
synthetic fiber, and glass
bottles
were
substituted by plastic ones. This threat
got materialized in case of
music shops in physical
world when
due to
the advent of e-commerce; music became
available in downloadable format through
the artist's
158
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
website.
The site, in fact, had
provided a substitute distribution
channel. Another example is
that of online
banking
which substituted traditional
banking in physical
world.
Bargaining
power of buyers
The
cost of producing and
distributing a product should be less
than the price it can bring
in the market in
order
to be profitable. Number of competitors
and the supply of a product are the
two major factors
that
determine
bargaining power of the buyers. A buyer is in a strong
position to bargain for low
price if there
are
many competitors and/or the supply of the
product in the market is in surplus.
Note that with the
help
of
e-commerce, low production
cost, more inventory control
and quick response time can
be achieved.
Besides,
direct sale to the customers is also
possible that cuts the cost
of involving intermediaries.
Therefore, a
business using IT/EC can
reduce the overall production
cost and afford to keep the
price of
the
product relatively low.
Bargaining
power of suppliers
Businesses
try to find more favorable
terms from their own
suppliers. If supply of raw material is
plentiful
and/or
there are many suppliers,
the supply can be procured at a low
price. Otherwise, position is
more
favorable to the
supplier having more bargaining power. Ability to
trade electronically is a factor in
the
quality
of service and may be a requirement of
the buying organization. Accordingly, bargaining power
of a
supplier is
reduced if it is not electronically
enabled.
Competition
between existing players
Competition
among businesses is to get
more buyers and trade at a
price that produces an
acceptable profit.
If
there are many players of
the same size, capacity and
strategy having little difference between
their
product/service,
then there is fierce
competition among them as regards the
price of the product/service.
Even a
small change in the price of the
product/service can be crucial
for the business. Again, the
use of
EC can
cause a significant difference by reducing
administration/transaction cost,
increasing efficiency of
supply
chain, improving product
quality and customer
service.
The
five force analysis determines
attractiveness of the industry whether to
enter that industry as a
business
or
not.
Strategic
Planning Cycle
E-business
competitive strategy is normally
formed and implemented according to a
planning cycle which
is
called
strategic planning
cycle.
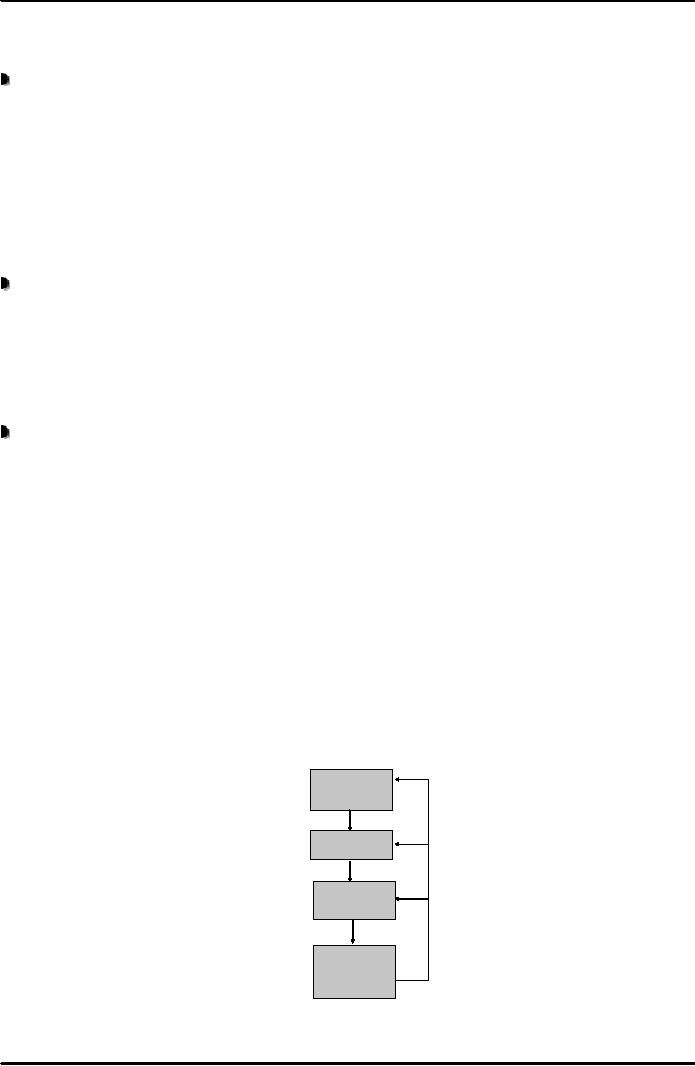
There
are four stages in this
planning cycle as shown in
Fig. 2 below:
Strategic
Planning Cycle
Industry
and
Competitive
Analysis
Strategy
Formulation
Implementation
Performance
Assessment
or
Strategy
Reassessment
Fig.
2
159
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Industry
and competitive analysis
It
aims at identifying those
factors on which the success of an EC
project or business would
depend. One
way of
doing that is to carry out
SWOT analysis and study
your business as well as the
business of your
competitors.
Analysis of online competitor
businesses is relatively easy since they
are just a few clicks
away
on the
web.
Strategy
formulation
Based
upon this study of internal
and external business environment
and in light of a company's
strengths
and
weaknesses, a competitive business
strategy is formed. It may be a
strategy of cost leadership,
product
differentiation
or focus. One can also
identify ways how
information technology can be used
to
implement/enforce
such strategy.
Implementation
In the
implementation stage, you
build a plan to identify
steps needed to put the
strategy into action
and
practically
take those steps. For
example, where your strategy
is to pursue differentiation in terms of
quality
of
service by using/arranging a web-based
call centre through which
the customers can immediately
register
their
complaints; then you will
have to select appropriate individuals
who are suitable for the
job in the
implementation
stage. Creating a web team
and defining the role/ responsibility of
each member of the
team
is a critical component of implementation stage.
For example, you define
that this person would
be
the
team leader; this would be in the
technical staff (web master
etc.) or the management staff. Note
that
involvement
of key persons from marketing,
accounting, finance, human
resource, IT, customer
relations
etc.
will be important in decision marking as
to how a particular implementation plan
can be executed. A
strategic
plan can be at times
initially implemented in terms of a pilot
project before launching it to a
full
scale.
For example, an automobile
manufacturer in America had implemented a plan/scheme
which allowed
the
potential customers to have
scheduled test drives before
buying a particular car. Initially, this
scheme
was
introduced to four American states
but later it was implemented all
over the country. Another point
is
to
consider whether you should build
your own infrastructure for execution or
outsource the task of
execution of a
strategic plan. For example,
where a strategic plan requires a
particular web design, you
can
either
mange your own team of
web designers or outsource this
task to an outside firm having
expertise in
this
area.
Strategy
assessment
Results
of implementation plan are
monitored and assessed so
that any corrective measures or
expansion
plan
can take place. Basically,
you want to assess whether your
strategy has delivered what it was
supposed
to deliver; whether
your strategy is still
viable/workable in the ever changing
environment. In strategy
assessment
phase, you can learn
from your mistakes and do
your future planning. In
case your EC project
has
been a failure, you can
identity the problems and
try to remove them. Some of
the corrective measures
can be
to property train your web
team, establish or review your
security or privacy policy, review
or
reassess
your web design content,
reconsider your marketing plan etc.
For the strategy assessment,
you can
conduct
surveys, collect information and
receive feedback from
different groups of people so that
you have
solid
input from people coming from a variety
of background. Sometimes, you have to
entirety give up a
particular
strategy you followed and
formulate a new strategy or
set of strategies in light of the
company's
main
objective or its mission.
160
Table of Contents:
- E-COMMERCE
- WHAT IS A NETWORK
- HOW MANY CLASS A, B, C NETWORKS AND HOSTS ARE POSSIBLE
- NETWORKING DEVICES
- BASICS OF HTML 1
- BASICS OF HTML 2
- TEXT BOXES, CHECK BOXES, RADIO BUTTONS
- FRAMES AND IMAGES IN HTML
- TAG ATTRIBUTES, SOUNDS FILES, ANIMATIONS
- STYLE SHEETS 1
- STYLE SHEETS 2
- SOME USEFUL STYLE SHEETS PROPERTIES
- JAVA SCRIPTING 1
- JAVA SCRIPTING 2
- JAVA SCRIPTING 3
- JAVA SCRIPTING AND XML
- CLIENT AND SERVER SIDE PROCESSING OF DATA
- APPLETS, CGI SCRIPTS
- MAINTAINING STATE IN A STATELESS SYSTEM
- INTEGRATION WITH ERP SYSTEMS
- FIREWALLS
- CRYPTOGRAPHY
- HASH FUNCTION AND MESSAGE DIGEST
- SYMMETRIC KEY ALGORITHMS
- VIRTUAL PIN PAYMENT SYSTEM
- E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 1
- E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 2
- SECURE SOCKET LAYER (SSL)
- E-BUSINESS: DISADVANTAGES OF E-BUSINESS
- E-BUSINESS REVENUE MODELS
- E-MAIL MARKETING
- CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM)
- META INFORMATION
- DATA MINING
- CONFIDENCE AND SUPPORT
- ELECTRONIC DATA INTERCHANGE (EDI)
- PERSONAL FINANCE ONLINE
- SUPPLY CHAIN
- PORTER’S MODEL OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY
- BARRIERS TO INTERNATIONAL E-COMMERCE
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 1
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 2
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 3
- GLOBAL LEGAL ISSUES OF E-COMMERCE - 1
- GLOBAL LEGAL ISSUES OF E-COMMERCE - 2