 |
SUPPLY CHAIN |
| << PERSONAL FINANCE ONLINE |
| PORTER’S MODEL OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY >> |
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Lesson
38
SUPPLY
CHAIN
Supply
chain includes all the activities
associated with the flow and
transformation of goods from the
raw
materials
stage all the way to the end
user. Supply chain can be
broken into three parts,
that is, upstream
activities,
internal activities and downstream
activities.
Upstream
activities relate to materials/services or the
input from suppliers
Internal
activities relate to manufacturing and
packaging of goods
Downstream
activities relate to distribution and
sale of goods to
distributors/customers
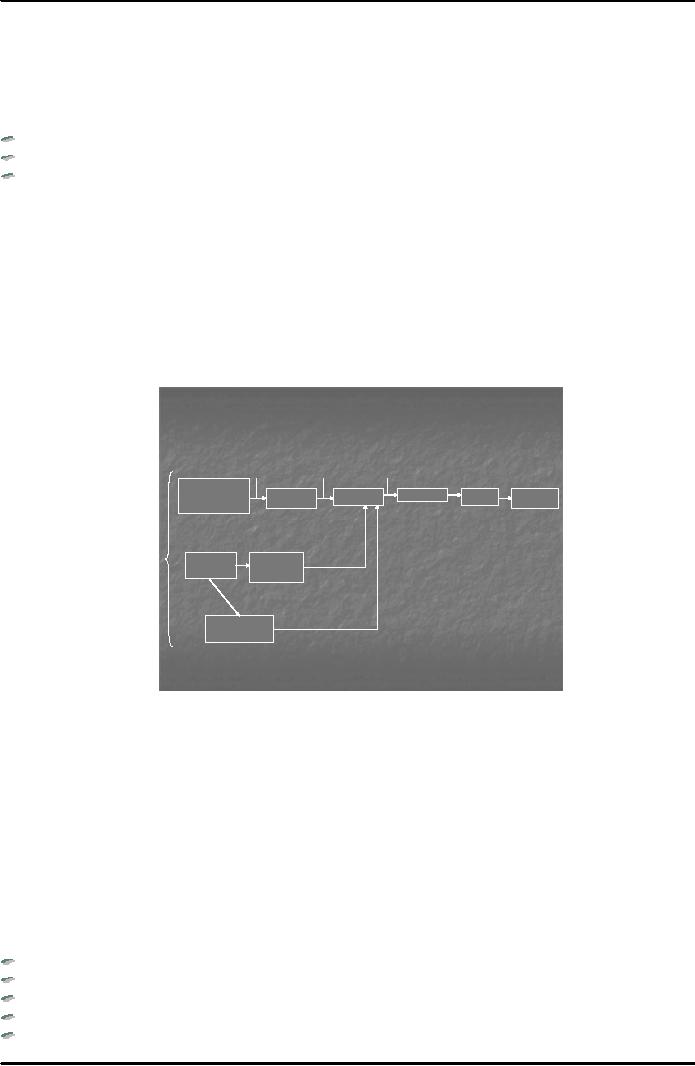
Fig. 1 below
shows a simple example of
supply chain of a milk
processing unit. Note that
milkmen supply
milk
to the processing facility. The
processing business has ordered a
corrugate paper company to
supply
boxes/paperboard
for packaging. The paper
company receives its raw
material from a lumber company
for
manufacturing
boxes. The lumber company
also supplies paper to label
printing business for
making/printing
paper labels. These are
upstream activities. The
boxes and labels should be
available to the
processing
business at the packaging stage.
The milk processing unit
processes the milk, packages it
in
boxes
and attaches labels to them.
These are internal
activities. The packaged
milk is sent to
distributors
who
distribute the same at different
stores from where customers
purchase. These are
downstream
activities.
Supply
The
Milk
Processing
Unit
Chain
Unprocessed
Packaged
Processed
milk
milk
milk
Supplier
of
Processing
Distributors
unprocessed
Packaging
Stores
Customers
Facility
milk
Boxes
Lumber
Corrugate
Company
Paper
Co.
paperboard
Label
manufacturing
Labels
Fig.
1
Supply
chain management
Engaging
and negotiating with suppliers
can be extremely beneficial. The
process of taking active
role in
working
with suppliers to improve products
and processes is called
supply chain management. Today,
firms
are
reaching beyond limits of their
own organizational structure. They are
creating new network form
of
organization
among the members of supply chain.
Supply chain management is
now used to add value
in
the
form of benefits to the ultimate customer at the
end of supply chain. It has
become important for
a
business
to work to establish long term
relationship with at least small number
of capable suppliers.
Internet
technologies and supply chain
Internet
is a very quick and effective tool of
communication. On the other hand, communication is
also a
very critical
element in supply chain
management. Using internet
technology:
suppliers
can share any information
about changes in the customer
demand;
suppliers
can have immediate notice of
any changes in product
design;
drawings/specifications
of a product can be quickly
provided to the suppliers and
vice versa;
processing
speed of a transaction can be
increased;
cost
of handling a transaction can be
reduced;
155

E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
chances
of errors in entering transaction data
are reduced;
Probably, the
only disadvantage of using
internet technology in a supply chain is
that sometimes it may
prove
to be costly. However, in ultimate
analysis, the advantages override the
cost factor.
With
the help of supply chain
management software, one can
not only manage the internal
processes but
also
processes of other members of the
supply chain. Therefore, it can be
predicted that when and
how
much
of certain product would
need to be produced.
Examples
of technology use in supply
chain
A typical
example of the use of technology in supply
chain management is a company
which is well-known
worldwide
as the largest producer of commercial
aircrafts. It makes a big
effort to keep its
production on
schedule.
Most commercial airplanes require
more than 1 million
individual parts and
assemblies and each
airplane
is configured according to specific needs
of the purchasing airline. Timely
availability of these
parts
must
be ensured otherwise entire production
schedule would be disturbed.
In
1997 the company had to stop
its two assembly operations
for several weeks due to
errors in production
and
scheduling system causing it a
huge financial loss. Thereafter, it
decided to invest in information
systems
in every element of its supply
chain. Involving its
suppliers in the process, it began the
use of EDI
and
internet technology, so that the
suppliers could supply the right
part or assembly at right time
to
prevent
production delay. Now, the
suppliers could get engineering
specifications and drawings before
the
start
of manufacturing using a secure internet
connection, and plan their
own business
activities,
accordingly.
Also, members of the supply chain could
have the knowledge of the completion of
milestones
and
any changes in production
schedule. In two years time, this
approach resulted in reducing
half the time
needed
to complete individual assembly
processes. Thus, instead of
waiting for 3 years the
customer airlines
could
now have the ordered airplane
ready for delivery in 10-12
months. Furthermore, the company
launched
a spare parts web site
for ordering replacement
parts. The site allowed
customer airlines to
register
and
order for replacement parts
through browsers. Soon, the
site was processing 5000
transactions per day
at
much lower cost as compared
to orders cost through phone, mail, or
fax. It also improved
customer
service
in the sense that most parts
could now be delivered the same day or
the next day.
Another
example is of a famous computer selling
brand. It realized that by increasing the
amount of
information
about its customers it was
able to reduce amount of inventory it
should hold. It decided to
share
this information with other
members of the supply chain by allowing
its top suppliers to have
access
to a
secure web site which
informed them about its latest
sales forecasts, planned product
changes or any
warranty
claims etc. It also provided
information about its
customers and their buying
pattern. Thus, it
helped
suppliers to plan their own
production in a much better
way.
The
above examples show how
members of supply chain can
work together to reduce inventory,
increase
quality
of product, reduce production
cost and increase process
speed.
Supply
chain and ultimate consumer
orientation
Primary
objective of supply chain is to help each
company to meet needs of the
consumer at the end of
supply
chain. This approach is
called ultimate consumer orientation. In
1995, a company dealing in
the
business
of production of tiers in America adopted a
different approach by shifting
its focus on tire
dealers
from
ultimate customers. It created an extranet
that allowed tire dealers to
access tire
specifications,
inventory
status and promotional
information on the web. Thus, it
gave opportunity to dealers to
access
product
information directly and
immediately. It also saved
money since a web page is
less expensive than
answering
thousands of phone calls daily by the
company. This initiative
provided a better service to
dealers,
so dealers using this extranet were
not likely to recommend to
customers a tire from the
competing
business.
156
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Competitive
Strategy
Ability
of an organization to prosper arises from
its competitive advantage
over other
organizations
operating
within its market sector.
The strategy of a business to
achieve this goal of competitive
advantage
is
known as competitive strategy. Three
basic strategies for
competitive advantage are as
under:
Cost
leadership
Differentiation
Focus
Cost
leadership
It is the
ability to sell the goods or
provide the service at a price
that is lower than that of
competitors, and
thus
attract more
customers.
Differentiation
Differentiation
means that your
product/service has certain
quality that makes it more
attractive than the
one
offered by your competitor,
despite the price of your competitor's
product/service is somewhat lower.
For
instance, you can beat
your competitors for the reason
that the air conditioner produced by
your
company
is unique as it does not produce noise
while in operation, whereas this
feature is missing in the air
conditioners
produced by your competitors.
Focus
Focus
strategy is defined as concentration on a
single aspect of the market.
That single aspect can be
a
particular
market segment or market
area or product type. For
example, if my competitors are focusing
on
different
market areas, I may, on the
other hand, plan that I can
be more profitable by concentrating on
one
particular
area. It may be a particular province or
a city etc. where I may
have a better distribution
channel.
Role
of e-commerce in Competitive Strategy
By
applying EC following major
benefits can be
derived:
Reduced
administration/transaction
cost
Since
things can be done electronically, so infrastructure or
overhead cost (cost of
building, staff, stationary
etc)
is reduced. Similarly, you can
sell directly to your
customers and it eliminates the
cut/revenue payable to
intermediaries
or dealers. Thus, EC helps in
achieving cost
leadership.
Improved
logistics supply chain
Using EC
one can have a quick
response to the order placed. In
other words, just in time
delivery of the
material
is possible. It helps in reducing
inventory and overall
production cost and
achieving cost
leadership/differentiation.
Customization
With
the help of EC, customer data
can be gathered and
analyzing it customers can be
served in a better
manner
according to their needs. One
can, thus, implement differentiation
and focus strategy.
Differentiate
a product in terms of quality of
service
For
example, online business of
sale of music or books etc. In
such cases delivery time and
transaction cost
is
saved as customers can
directly download the product
from the web site, thus, it
helps in achieving
cost
leadership
and differentiation.
157
Table of Contents:
- E-COMMERCE
- WHAT IS A NETWORK
- HOW MANY CLASS A, B, C NETWORKS AND HOSTS ARE POSSIBLE
- NETWORKING DEVICES
- BASICS OF HTML 1
- BASICS OF HTML 2
- TEXT BOXES, CHECK BOXES, RADIO BUTTONS
- FRAMES AND IMAGES IN HTML
- TAG ATTRIBUTES, SOUNDS FILES, ANIMATIONS
- STYLE SHEETS 1
- STYLE SHEETS 2
- SOME USEFUL STYLE SHEETS PROPERTIES
- JAVA SCRIPTING 1
- JAVA SCRIPTING 2
- JAVA SCRIPTING 3
- JAVA SCRIPTING AND XML
- CLIENT AND SERVER SIDE PROCESSING OF DATA
- APPLETS, CGI SCRIPTS
- MAINTAINING STATE IN A STATELESS SYSTEM
- INTEGRATION WITH ERP SYSTEMS
- FIREWALLS
- CRYPTOGRAPHY
- HASH FUNCTION AND MESSAGE DIGEST
- SYMMETRIC KEY ALGORITHMS
- VIRTUAL PIN PAYMENT SYSTEM
- E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 1
- E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 2
- SECURE SOCKET LAYER (SSL)
- E-BUSINESS: DISADVANTAGES OF E-BUSINESS
- E-BUSINESS REVENUE MODELS
- E-MAIL MARKETING
- CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM)
- META INFORMATION
- DATA MINING
- CONFIDENCE AND SUPPORT
- ELECTRONIC DATA INTERCHANGE (EDI)
- PERSONAL FINANCE ONLINE
- SUPPLY CHAIN
- PORTER’S MODEL OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY
- BARRIERS TO INTERNATIONAL E-COMMERCE
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 1
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 2
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 3
- GLOBAL LEGAL ISSUES OF E-COMMERCE - 1
- GLOBAL LEGAL ISSUES OF E-COMMERCE - 2