 |
ELECTRONIC DATA INTERCHANGE (EDI) |
| << CONFIDENCE AND SUPPORT |
| PERSONAL FINANCE ONLINE >> |

E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Lesson
36
ELECTRONIC
DATA INTERCHANGE (EDI)
EDI is
used by organizations for
transactions that occur on a
regular basis according to a
pre-determined
format.
It involves exchange of electronic
business documents, i.e.,
purchase orders, invoices
etc. EDI
transactions
are carried through special
EDI software. This technology was
popularly used before
the
introduction
of e-commerce by different trading
partners on private electronic networks.
Key features of
EDI
include:
No
paper work
No
human intervention
Exchange
of information takes place in
seconds
EDI
documents are formatted
using published standards. Two
popular EDI standards are -
ANSI
(American
National Standards Institute)
X12 standard and EDIFACT
(United Nations Standard
of
Electronic
Data Interchange for Administration,
Commerce and Transport).
EDI
Example
Assume
E-Pens (a manufacturing company of pens
and ballpoints) reviews
sales and orders on
monthly
basis
to make forecast of its
sales for the coming month.
Sales forecast is compared
with the stocks of
raw
material
and other components and a
production plan is devised. This
monthly plan needs to be
flexible so
that
materials could be ordered at short notice if these
are not available in the
store. For instance,
packaging
material
should only be ordered for just in time
(JIT) delivery, so that E-Pens
can cut down on its
stock of
packaging
and reduce the inventory
cost. On the other hand,
packaging supplier also wants to
improve its
processing
of orders, particularly urgent orders. Before
using EDI technology, the order used to
be
generated
in the following format:
From:
E-Pens
---------
To:
ABC & C0.
--------------------
Order
Ref:AC8484
Order
Date:15.3.2006
Qty
Description
Product
Code
1500
Superior
Red
PC-1075-R
1300
Superior
Silver
PC-1075-S
-End
of Order-
After
both E-Pens and its supplier
start using EDI system, any
amendment of the schedule on
the
production
control system reviews the
materials requirements and the
order is automatically generated.
In
case
the above paper order is to be
generated using EDI software, the
order data is coded and
structured
into a
common and generally accepted
format. The order would be
written as follows in
EDIFACT
(See
Fig. 1 - not for
exam):
147

E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
UNB+UNOA:2+8484:xx+1149:xx+
Interchange
Header
BEN0273
UNH+000001+ORDERS:2:932:UN
Message
1
Header
BGM+220+AC8484
DTM+4:20060315:102
Data
Segments
NAD+BY+8484326::91
NAD+SU+1149646:91
UNS+D
LIN+1++PC-1075-R:VP
Qty+21:1500
LIN+2++PC-1075-S:VP
Qty+21:1300
UNT+11+000001
Trailer
UNH
Message
2
......
UNT
UNZ+1+BEN0273
Trailer
Fig.
1
In the
above, `UNB' refers to the
start of interchange or envelop header,
`UNOA:2' to the United
Nations
Control
Agency (level A) version 2, `8484' to sender
code, `1149' to recipient code,
`BEN0273' to control
reference,
`UNH' to message header,
`000001' to message no., `ORDERS' to the
message type, `2:932'
to
version 2
and release 932, `UN' to
control agency. `BGM' refers
to beginning of message, `220' to
message
name
code (i.e, order), `AC8484' to order no.,
`DTM' to date and time of
message, `4' to a
qualifier,
`20060315'
to date, `102' to format
qualifier (century date),
`NAD' to name and address,
`BY' to buyer, `SU'
to supplier,
`8484326' to buyer address code,
`91' to code list agency,
`1149646' to supplier address
code.
`UNS'
represents section control
(that is, start of a
section), `D' is for section
identification. `LIN'
indicates
line
item (e.g, line item number 1 and
2), `PT-1075-R' and
`PT-1075-S' indicate item number, and
`VP' stand
for
item number type (that is, vendor part).
`QTY' represents quantity,
`21' is quantity qualifier
(indicating
ordered
quantity), `1500' and `1300'
is the number of ordered quantity. `UNT' is
message trailer/end, `11'
is
control
count (indicating no. of line
segments in the message), `000001' is
message no. `UNZ'
represents
interchange
trailer. Note that an interchange
can have more than
one message, as shown in Fig. 1
above.
Value
Added Network (VAN)
Value
added networks are third party networks
that provide services to
execute authorized transactions
with
valid
trading partners using EDI.
Each VAN has a centralized computer
system that maintains two
files for
each
user, that is,
Postbox:
where outgoing messages are
placed, and
Mailbox:
where incoming messages can
be picked up
148
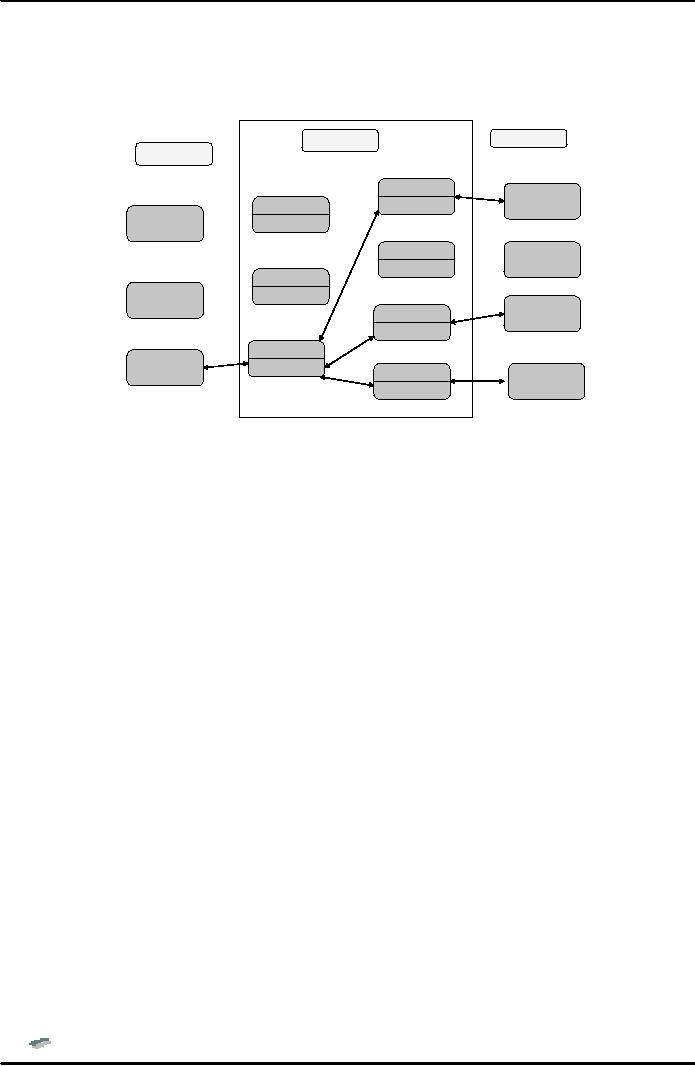
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
VAN
Example
Value
Added Network (VAN)
Supplier
VAN
Customer
Postbox
Bread
shop
Mailbox
Postbox
Super
Mailbox
Food
Postbox
Fruit
shop
Mailbox
Postbox
Best
Mailbox
Vegetables
Food
Postbox
Shop
Mailbox
Postbox
Nice
Mailbox
Postbox
Food
Meat
Shop
Mailbox
Fig.
2
Note
that in Fig. 2 above, Nice
Store needs to place orders
for bread, meat and
vegetables. It
establishes
a link to VAN through the dial up
line, and sends EDI-based
order messages for the
three
suppliers
which are temporarily stored
in its postbox. VAN computer system
inspects postbox, unpacks
interchanges
(electronic envelopes), repackages them
as new interchanges and
moves them to the
mailbox
of the intended recipients. The three
recipients check their
mailboxes for new
interchanges,
pick
them up and cause them to be transmitted to
their respective processing
systems. They can
also
send
acknowledgment messages and
cause them to be stored in their
respective postboxes. VAN
checks
them and put them in the mailbox of
Nice Food.
Advantages
of VAN
Two
big advantages of using a VAN in EDI
are time independence and
protocol independence.
Time
independence
means that the sending and
receipt of the interchange or messages
can be carried out at
the
convenience of the users involved.
Thus, they are not required to be
connected with each other
at
the
same time. Protocol independence
means that interchanges are
re-enveloped with the transmission
protocol
appropriate to the recipient when they are retrieved
from the postbox by the VAN. Thus,
a
VAN
can provide protocol
compatibility between the sender
and the recipient, wherever that
is
missing.
Internet-Based
EDI
Internet
can support EDI in a variety of ways.
Internet e-mail can be used
as EDI message transport
mechanism
in place of having a VAN. An extranet can be
created with the trading partner
allowing a
partner to
enter information in the fields of web
forms which correspond to the fields of EDI
message.
Also,
web-based EDI hosting service can be
utilized through web-based EDI
software. However, a
lot
of
work is still required to be done to make
use of and popularize internet-based
EDI.
Benefits
of EDI
Some
of the benefits of EDI are listed as
under:
Shortened
ordering time
149

E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Since
an order is generated automatically
according to a pre-defined format, thus,
the ordering time is
very
short.
Cost
cutting
An EDI
transaction is more cost-effective in the
sense that paper/stationary
cost as well as cost
of
hiring
staff to complete a transaction is eliminated in
case of EDI. The only major
cost is the expensive
EDI
software itself. However, once an EDI
system is in place, it can
save many expenses
otherwise
associated
with a normal
transaction.
Elimination
of errors
Messages
are generated automatically, so the
chances of any typing errors
caused by human
intervention
are
negligible.
Fast
response
An EDI
message can be read and
processed on the receiver side
electronically with the help of
EDI
software.
So, if the receiver is a supplier of raw
material, it can quickly
fulfill/implement the order as
compared
to a paper order.
Accurate
invoicing
Invoices
or payment requests by the
merchant/supplier can also be
generated using EDI
standard
format,
which are more accurate than
paper invoices.
EDI
payment
EDI
standard documents can be
used to electronically provide financial
information for
payment
purposes.
Enterprise
Resource Planning
(ERP)
ERP is
an approach that attempts to
integrate all departments
and functions across a
company onto a single
computer
system that can serve
all those different
departments' particular needs. For
example, finance,
manufacturing
and the warehouse department of a company
may have their own
software to perform
tasks
specific
to each one of them.
However, each software can
be linked together so that a customer
service
representative
can see the credit rating of a customer
from finance module, warehouse
information from
warehouse
module, and shipment information from the
shipment module. SAP is an example of
ERP
software.
ERP is complex. It is not
intended for public consumption as
proper integration of ERP
with e-
commerce
applications is still a major problem.
Electronic
Banking
Electronic
banking, also known as cyberbanking,
virtual banking, home banking
and online banking,
includes
various banking activities conducted
from home, business, or on the
road, instead of at a
physical
bank
location.
Advantages
of e-banking
Get
current account balances at any
time
Obtain
credit card statements
Pay
utility bills
Download
account information
Transfer
money between
accounts
150

E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Send
e-mail to your bank
Manage
your own schedule
Handle
your finances from any
location
Apply
for loans online
For
banks, e-banking represents an
inexpensive alternative to branch banking
and a chance to enlist
remote
customers.
151
Table of Contents:
- E-COMMERCE
- WHAT IS A NETWORK
- HOW MANY CLASS A, B, C NETWORKS AND HOSTS ARE POSSIBLE
- NETWORKING DEVICES
- BASICS OF HTML 1
- BASICS OF HTML 2
- TEXT BOXES, CHECK BOXES, RADIO BUTTONS
- FRAMES AND IMAGES IN HTML
- TAG ATTRIBUTES, SOUNDS FILES, ANIMATIONS
- STYLE SHEETS 1
- STYLE SHEETS 2
- SOME USEFUL STYLE SHEETS PROPERTIES
- JAVA SCRIPTING 1
- JAVA SCRIPTING 2
- JAVA SCRIPTING 3
- JAVA SCRIPTING AND XML
- CLIENT AND SERVER SIDE PROCESSING OF DATA
- APPLETS, CGI SCRIPTS
- MAINTAINING STATE IN A STATELESS SYSTEM
- INTEGRATION WITH ERP SYSTEMS
- FIREWALLS
- CRYPTOGRAPHY
- HASH FUNCTION AND MESSAGE DIGEST
- SYMMETRIC KEY ALGORITHMS
- VIRTUAL PIN PAYMENT SYSTEM
- E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 1
- E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 2
- SECURE SOCKET LAYER (SSL)
- E-BUSINESS: DISADVANTAGES OF E-BUSINESS
- E-BUSINESS REVENUE MODELS
- E-MAIL MARKETING
- CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM)
- META INFORMATION
- DATA MINING
- CONFIDENCE AND SUPPORT
- ELECTRONIC DATA INTERCHANGE (EDI)
- PERSONAL FINANCE ONLINE
- SUPPLY CHAIN
- PORTER’S MODEL OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY
- BARRIERS TO INTERNATIONAL E-COMMERCE
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 1
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 2
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 3
- GLOBAL LEGAL ISSUES OF E-COMMERCE - 1
- GLOBAL LEGAL ISSUES OF E-COMMERCE - 2