 |
HOW MANY CLASS A, B, C NETWORKS AND HOSTS ARE POSSIBLE |
| << WHAT IS A NETWORK |
| NETWORKING DEVICES >> |

E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Lesson
03
HOW MANY CLASS
A, B, C NETWORKS AND HOSTS ARE
POSSIBLE?
Note
that 126 class A networks
are possible (0 and 127
are not used for
general purposes). Each
class A
network
can accommodate a maximum of 16
million hosts on it. There
are 16384 class B networks
possible
and
each can host upto
65000 host machines. There
are 2 million class C networks
possible each having the
capacity
to accommodate upto 256 host
machines on it.
Subnet
mask
An IP
address is meaningless for the
computers unless it is accompanied by a
subnet mask. It tells to
the
computer
machines that what part of the
accompanying IP address corresponds to
the network address
and
what
part corresponds to the host machine on
that network. A subnet mask
is also represented by
four
decimal
numbers separated by a period.
Default subnet masks for
class A, B and C types of IP
addresses are
as
under:
Class
A: 255.0.0.0
Class
B: 255.255.0.0
Class
C: 255.255.255.0
IP
version
The
existing IP scheme (version 4) is likely to be
replaced by IP version 6. It would
provide 128 bits IP
38
addresses
in hexadecimal format. According to an
estimate a total of 3.4 x 10
addresses would then
be
available.
Domain
name system
A
Domain Name is a user friendly
name used to locate a web
site on the internet. For
example, vu.edu,
bestcomputers.com
etc. Domain Name System
(DNS) provides the structure and the
strategy that is used
to
refer to
computers on the internet by these
user friendly names. Domain
Names are Unique. They
are
assigned
as one has to pay and
register for them. With the
help of DNS a domain name is
translated into its
corresponding IP
address (see
Fig. 1 below). A
fully qualified domain name is
processed from right to
left
for
its translation into the corresponding IP
address. A fully qualified domain
name can be made up of a
top
level domain
(TLD), second level domain (SLD)
and subdomains, as
shown in Fig. 2 below.
Seven
popular
TLDs are ".com,.edu,.org,.gov,.net,.countryname,.int".
SLDs represent the name of
a
company/institution/entity.
Subdomains represent the geographical or
functional units of a
company/institution
etc.
11

E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Fig.
1
Fig.
2
Name
resolution
The
translation or resolution of a fully
qualified domain name into
its IP address takes place
using the
hierarchy
of special computer machines called
Domain Name Servers. A DNS
server is a server on the
network
that maintains a database/table
that contains the list of domain
names and their corresponding
IP
addresses.
The name servers for
TLDs are also called
Root Name Servers. There is a program
called
`Resolver'
built into the browser,
which sends the request for
resolution of the domain name to the
machine
called
Local Name Server. Local name server
then contacts the root name
server, which looks into
its
database
and where possible provides the IP
address of the name server
below in the Hierarchy. Hence in a
similar
number of steps the fully qualified
domain name is completely translated into
the IP address of the
web
server where the requested
web page is stored. The
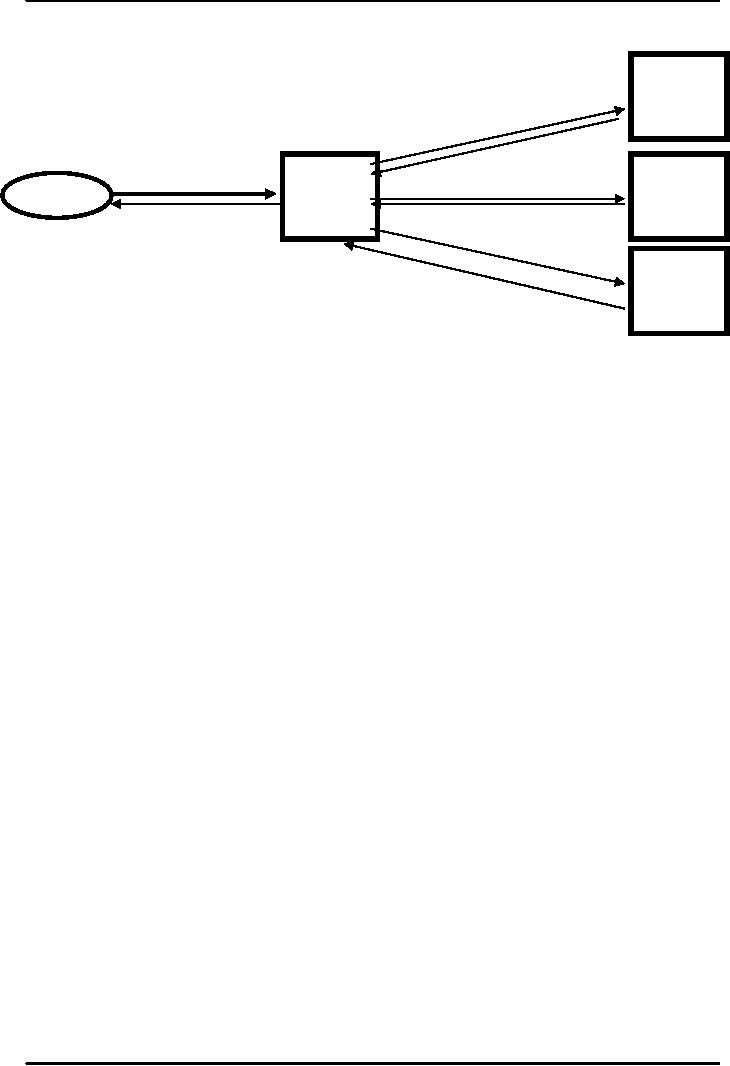
process of name resolution
has been shown in an
example
in Fig.
3 below:
12
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Name
Resolution
Root
2
Name
Server
ecom.cs.vu.edu
3
vu.edu,
128.196.128.233
1
VU
Local
4
ecom.cs.vu.edu
Name
Name
ecom.cs.vu.edu
Client
Server
server
cs.vu.edu,
192.12.69.5
5
192.12.69.60
ecom.cs.vu.edu
6
ecom.cs.vu.edu
8
CS
Name
Server
7
Getting
domain names and IP
addresses
Domain
names are administered in a
hierarchy. At the global level the task
of registration/administration of
domain
names is supervised by the organization
called Internet Corporation
for Assigned Names
and
Numbers
(ICAAN). There are organizations
working under ICAAN in different regions.
For example,
APNIC
is for Asia and Pacific
Rim, ARIN for America and
South Africa, RIPE-NCC for
Europe and
North
Africa etc. Each of the
above are further connected
to Internet Service Providers (ISPs) at
the local
level. One
can register one's domain
name through an ISP also. Similarly,
one can lease IP addresses
from a
local
ISP apart from the direct sources of IP
addresses, that is, APNIC,
ARIN or RIPE-NCC. ISPs can
use
a
server to dynamically supply the IP
addresses to their clients
for a session. Such a server
is called DHCP
(Dynamic
Host Configuration Protocol)
server.
Media
access control (MAC)
address
Data to be
delivered on a network has to be converted
first into serial
transmission. This is done through
a
device
called Network Interface
Card (NIC) that must be
installed in a computer on the network. NIC
has
also
got printed on it a 48 bits unique
address called the MAC or hardware
address of the computer
machine.
In other words, it consists of 12
hexadecimal characters and
can have different format as
shown
below:
090017A9B2EF
09:00:17:A9:B2:EF
09-00-17-A9-B2-EF
Whereas
the IP address of a computer may change
from time to time, its MAC address
would remain the
same
unless the existing NIC is replaced with
another. It can easily be inferred
that there are 248
unique
MAC
addresses possible (which is an unimaginably
high number). An organization called
Institute of
Electrical
and Electronic Engineers
(IEEE) administers the allocation of MAC
addresses, worldwide. It
ensures
that there is no duplication of MAC
addresses by the manufacturers of
NICs.
13
Table of Contents:
- E-COMMERCE
- WHAT IS A NETWORK
- HOW MANY CLASS A, B, C NETWORKS AND HOSTS ARE POSSIBLE
- NETWORKING DEVICES
- BASICS OF HTML 1
- BASICS OF HTML 2
- TEXT BOXES, CHECK BOXES, RADIO BUTTONS
- FRAMES AND IMAGES IN HTML
- TAG ATTRIBUTES, SOUNDS FILES, ANIMATIONS
- STYLE SHEETS 1
- STYLE SHEETS 2
- SOME USEFUL STYLE SHEETS PROPERTIES
- JAVA SCRIPTING 1
- JAVA SCRIPTING 2
- JAVA SCRIPTING 3
- JAVA SCRIPTING AND XML
- CLIENT AND SERVER SIDE PROCESSING OF DATA
- APPLETS, CGI SCRIPTS
- MAINTAINING STATE IN A STATELESS SYSTEM
- INTEGRATION WITH ERP SYSTEMS
- FIREWALLS
- CRYPTOGRAPHY
- HASH FUNCTION AND MESSAGE DIGEST
- SYMMETRIC KEY ALGORITHMS
- VIRTUAL PIN PAYMENT SYSTEM
- E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 1
- E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 2
- SECURE SOCKET LAYER (SSL)
- E-BUSINESS: DISADVANTAGES OF E-BUSINESS
- E-BUSINESS REVENUE MODELS
- E-MAIL MARKETING
- CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM)
- META INFORMATION
- DATA MINING
- CONFIDENCE AND SUPPORT
- ELECTRONIC DATA INTERCHANGE (EDI)
- PERSONAL FINANCE ONLINE
- SUPPLY CHAIN
- PORTER’S MODEL OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY
- BARRIERS TO INTERNATIONAL E-COMMERCE
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 1
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 2
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 3
- GLOBAL LEGAL ISSUES OF E-COMMERCE - 1
- GLOBAL LEGAL ISSUES OF E-COMMERCE - 2