 |
SECURE SOCKET LAYER (SSL) |
| << E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 2 |
| E-BUSINESS: DISADVANTAGES OF E-BUSINESS >> |

E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Lesson
28
SECURE
SOCKET LAYER (SSL)
SSL is
a protocol developed by Netscape
Communications. SSL is built
into many browsers. It
operates at
the
TCP/IP layer of the OSI model,
and uses a combination of
symmetric and asymmetric cryptography.
If
there
appears the word "https" in a
URL, (e.g, https://www.microsoft.com) it
indicates that the web
server
hosting this
web site is SSL enabled.
So, if a client machine is configured
for SSL then any
exchange of
information
between such a client and the
web server would be in the
encrypted form.
To configure a
client machine for SSL
following steps are
required:
Internet
Explorer:Tools menu->Internet
options->Advanced tab-> Security
(use SSL option can
be
checked)
SSL
Handshake
SSL
supports a variety of encryption
algorithm and authentication methods.
The combination of algorithms
and
methods is called a cipher suite.
When a client connects to an
SSL server, the SSL
handshake begins,
which
means that the two negotiate
a cipher suite selecting the strongest
suite the two have in
common.
Thus,
the handshake establishes the protocols
that will be used during the
communication, selects
cryptographic
algorithms and authenticates the parties
using digital
certificates.
To
start the SSL handshake
process, a client sends a
message to the server, the server
responds and sends
its
digital
certificate that authenticates its
public key. The client
(customer's browser) generates a
secret
symmetric
key for the session. The
client encrypts the secret
key using the public key
that it has just
received
and transmits it to the server.
The server decrypts the
message using its private
key and now
has
the
secret or symmetric key.
Further communication between the
customer's browser and the
merchant's
server
can now be encrypted and
decrypted using the secret
session key.
SSL is
commonly applied in online shopping as the customer
puts in his/her credit/debit
card information
on the
web form for payment
purposes. If the web client
and the server are SSL
enabled, the SSL
handshake
would begin when the client enters the
URL starting with "https". This
handshake can be
accomplished
in seconds. The web form
opens before the client. The
client enters information in the
text
boxes
of the form and on pressing
`submit' all such
information is automatically encrypted
with the agreed
secret
or session key. This secured/encrypted
information travels across the
internet and is retrieved by the
server
side where it is automatically decrypted
with the help of same secret
or session key. Even if
someone
intercepts
the information, he cannot make any
sense out of it because of
encryption.
The
greatest advantage of SSL is
its simplicity. Since SSL is
built into many browsers, no
special encryption
software
is required either on the client or the server
side. However, a drawback of
SSL is that the
merchant
can
store credit/debit card
information after decryption that
can be accessed by unauthorized parties
from
the
merchant's database.
121
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
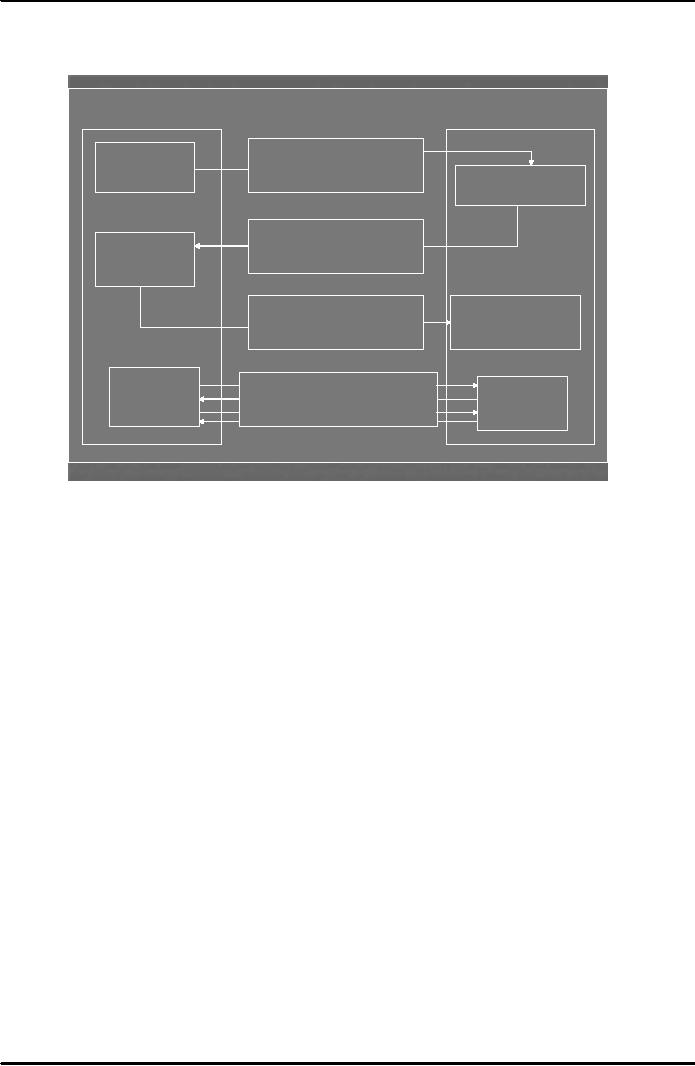
The
process of SSL handshake is
also explained in Fig. 1
below:
SSL
Client (browser)
SSL
Server
Send
encryption algorithms
Client
sends
and
key length
"hello"
message
Server
responds
With
"hello" message
Send
server certificate
Client
sends
containing
server's public key
response
Server
receives client
Send
client certificate
and
response
and
encrypted
private session key
initiates
session
Send
data between client
and
Session
Session
server
using private shared
key
Fig.
1
Secure
Electronic Transaction (SET)
The
drawback in SSL that the credit
card/debit card information
remains with the merchant led to
the
development of a
more sophisticated protocol
called SET. It was developed in
1997 jointly by Visa,
MasterCard,
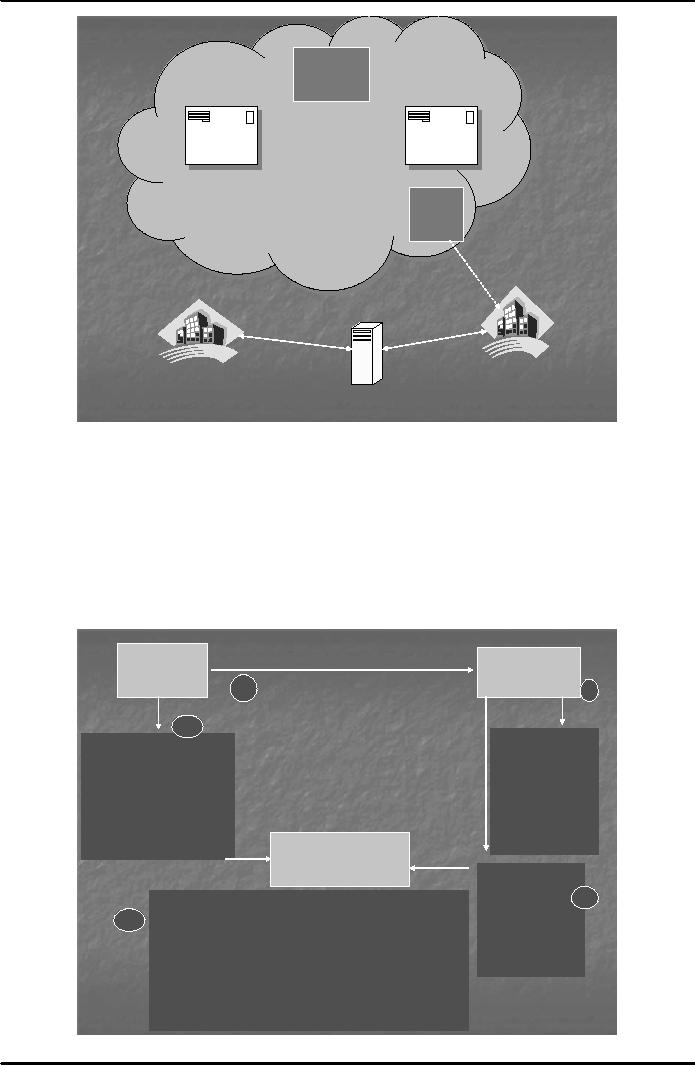
Netscape and Microsoft. There
are four entities involved in a SET
transaction cardholder,
merchant,
and certification authority
and payment gateway. The
role of payment gateway is to
connect
entities on the
internet with those which
are not on the internet such
as the electronic network of banks
(see
fig. 2
below). Payment gateway provides the
security of data transmission
to/from the acquirer bank.
Merchants
must have special SET
software to process transactions.
Customers must have digital
wallet
software
that stores certificates and
card information.
122
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Certification
Authority
Payer
Payee
Internet
Debit
Card
Debit
Card
Debit
Card
Debit
Card
Payment
Gateway
Payer's
Acquirer
Bank
Automated
Clearing
Bank
House
Fig.
2
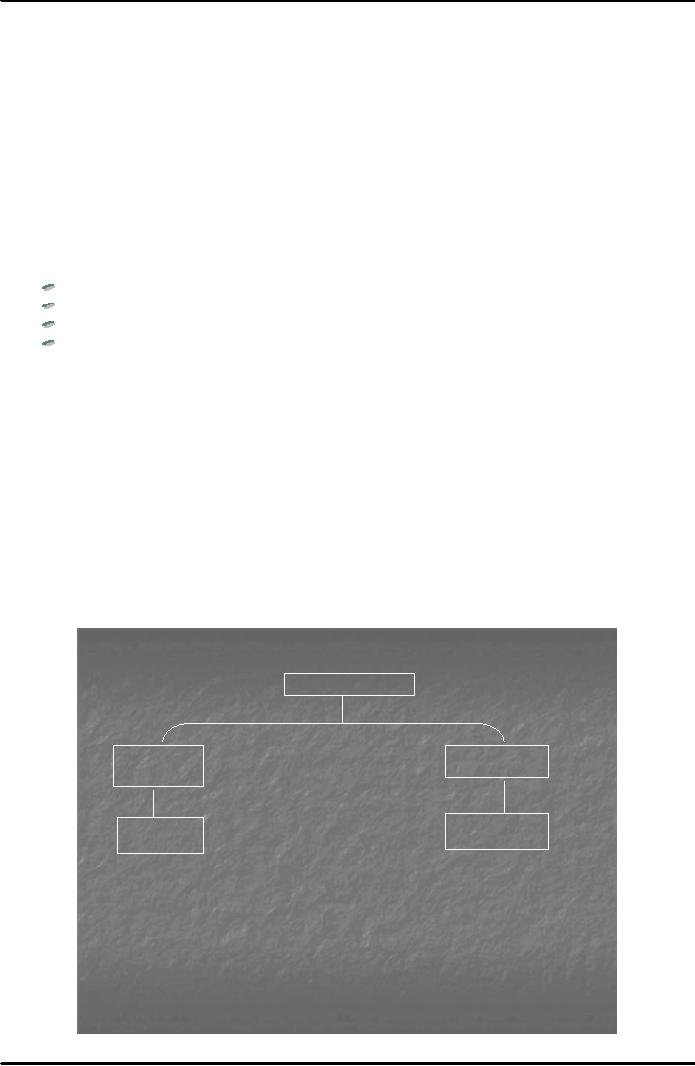
Dual
Signature in SET
SET
hides customer's credit card
information from merchants
and hides order information
from banks to
protect
privacy. This scheme is called
Dual Signature.
A dual
signature is created by combining
two message digests and
creating a new digest called
Dual
Signature
Message Digest (DSMD). Fig. 3 below
explains how the scheme of dual
signatures is
implemented in
SET.
Offer
for Items
Merchant
Buyer/Bidder
or Auction
house
�Encrypted
message includes
1b
2
amount
offered on the item,
but no
account information
1a
�MD1
encrypted with
Bidder's
�Decrypt
message
private
key
�Encrypted
message authorizing
with
auction house
payment to
the auction
private
key
house if
offer is
�Decrypt
MD1 with
accepted,
but no details
bidder's
public key
about
what item is bought
�Determine
�MD2
and DSMD
whether
to
encrypted
with
accept
bid
Bidder's
private key
Acquirer
Bank
�Encrypted
message
that
offer is
accepted 3
�Decrypt
account information with
acquirer private key
from
bidder
�Decrypt
offer acceptance message
with acquirer private
4
�MD1
encrypted
key
4
with
auction
�Decrypt
MD2 and DSMD with
bidder's public key
house's
private
�Decrypt
MD1 from step no. 3
with auction house's
public
key
key
�Concatenate
MD1 and MD2
�Recompute
dual signature and verify
against DSMD sent
by bidder
Fig.
3
123
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
SET
software on the customer side
splits the order information
from the account information. MDI is
the
message
digest obtained by applying hash
function on the order information. MD2 is
the message digest
obtained by
applying hash function on the
account information. Both,
MD1 and MD2 are concatenated
and
a
third message digest, DSMD,
is obtained by again applying the hash
function on the concatenated
message
digests. The order
information or the offer for
items is forwarded to the
merchant/auction house
in an
encrypted form along with
its message digest (MD1)
signed with the private key
of the buyer/bidder
(step
1b). The
merchant/auction house decrypts the
order information/offer and verifies the
signatures of
the
buyer/bidder through his/her
digital certificate (step
2). If the
order/offer is acceptable to the
merchant
then the merchant signs the
received MD1 with merchant's
private key and sends it to
the
acquirer
bank along with an encrypted letter of
acceptance to the offer (step3). On the
other hand, the
buyer
sends the text based account
information (credit card details) to the
acquirer in an encrypted
form.
The
buyer also sends MD2
(message digest related to
account information) and
DSMD to the acquirer bank
signed
with his/her private key
(step
1a). The
acquirer bank decrypts this information.
Mainly, the acquirer
bank
receives four pieces of
information as follows (step
4):
MD1
from merchant/auction house
related to order
information
Account
information in encrypted form
from the buyer
MD2
related to account information
from the buyer
DSMD
from the buyer
Acquirer
bank concatenates MD1 and
MD2 and applies the hash
function to compute a message
digest.
Note
that if this message digest is the
same as the DSMD received by the
acquirer, it ensures that
a
particular
order information or offer is
related to particular account
information. At the same time, we
have
achieved
our purpose that the order
information should not reach the bank
and the account
information
(credit
card no. etc.) should not
reach the merchant/auction
house.
SETCo.
SETCo.
is a company formed to lead the
implementation and promotion of
SET specifications It
ensures
that
the vendors of SET software comply with
the requirements laid down by
its originators. A merchant
holds certificate
from card brand indicating
that the merchant is authorized to accept
credit card payment.
The
customer holds certificate from the card
issuing bank. SETCo acts as a root
certification authority in
the
certification hierarchy (see Fig. 4
below)
SETCo
Card
Issuer Bank
Card
Brand
Customer
Merchant
Fig.
4
124
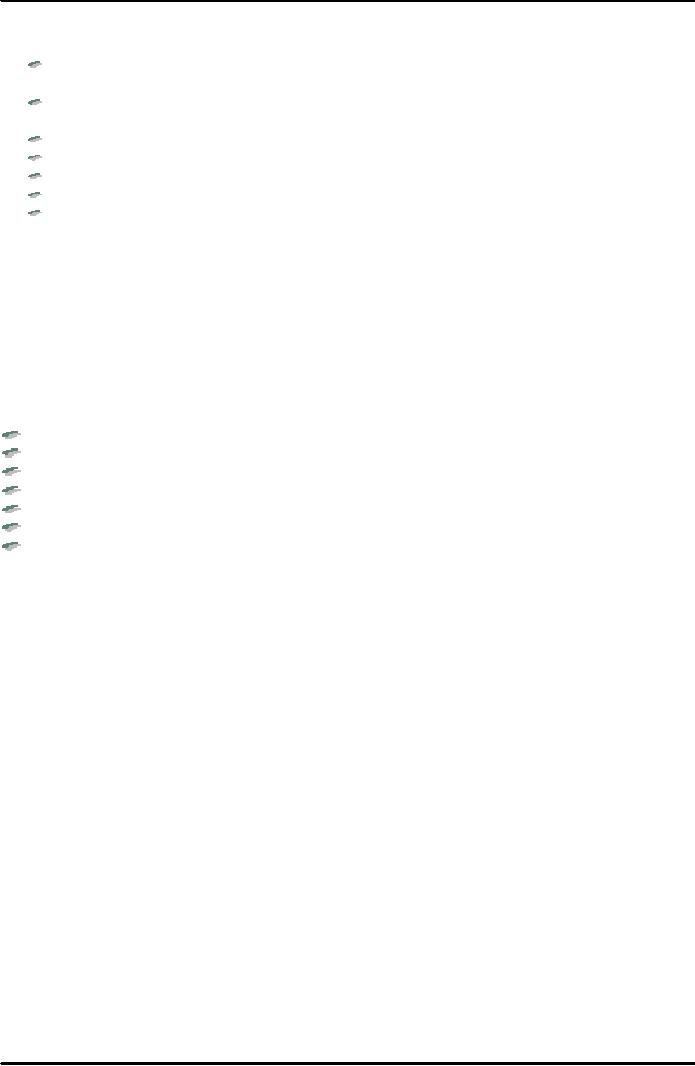
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
SSL
vs. SET
SSL
only handles secured
transmission of credit card no.
but SET is designed to handle the
whole
transaction
in a secured manner using dual
signatures.
SSL is
a general purpose protocol
built into the browser,
whereas SET requires software
on, both,
the client
and the merchant
side.
SET
uses a hierarchy of certificates
for authentication.
SET is complex
and distribution of certificates is
sometimes not stable.
SET
increases transaction
cost.
SET
transactions are slower than
SSL.
SET
uses a payment gateway for
secured transmission of
information.
E-Business
An
e-business is defined as a company/entity
that has an online presence.
E-businesses that have the
ability
to
sell, trade, barter or transact
over the web can be
considered as e-commerce businesses. An
e-business
model is
defined by a company's policy,
operations, technology and
ideology.
Advantages
of E-business
Some
of the major advantages of an e-business as
compared to a traditional business
are as under:
Personalized
service
High-quality
customer service
No
inventory cost
Worldwide
reach of the business
Electronic
catalogues (convenient and quick
transaction)
Bulk
transactions
Improved
supply chain
management
125
Table of Contents:
- E-COMMERCE
- WHAT IS A NETWORK
- HOW MANY CLASS A, B, C NETWORKS AND HOSTS ARE POSSIBLE
- NETWORKING DEVICES
- BASICS OF HTML 1
- BASICS OF HTML 2
- TEXT BOXES, CHECK BOXES, RADIO BUTTONS
- FRAMES AND IMAGES IN HTML
- TAG ATTRIBUTES, SOUNDS FILES, ANIMATIONS
- STYLE SHEETS 1
- STYLE SHEETS 2
- SOME USEFUL STYLE SHEETS PROPERTIES
- JAVA SCRIPTING 1
- JAVA SCRIPTING 2
- JAVA SCRIPTING 3
- JAVA SCRIPTING AND XML
- CLIENT AND SERVER SIDE PROCESSING OF DATA
- APPLETS, CGI SCRIPTS
- MAINTAINING STATE IN A STATELESS SYSTEM
- INTEGRATION WITH ERP SYSTEMS
- FIREWALLS
- CRYPTOGRAPHY
- HASH FUNCTION AND MESSAGE DIGEST
- SYMMETRIC KEY ALGORITHMS
- VIRTUAL PIN PAYMENT SYSTEM
- E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 1
- E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 2
- SECURE SOCKET LAYER (SSL)
- E-BUSINESS: DISADVANTAGES OF E-BUSINESS
- E-BUSINESS REVENUE MODELS
- E-MAIL MARKETING
- CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM)
- META INFORMATION
- DATA MINING
- CONFIDENCE AND SUPPORT
- ELECTRONIC DATA INTERCHANGE (EDI)
- PERSONAL FINANCE ONLINE
- SUPPLY CHAIN
- PORTER’S MODEL OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY
- BARRIERS TO INTERNATIONAL E-COMMERCE
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 1
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 2
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 3
- GLOBAL LEGAL ISSUES OF E-COMMERCE - 1
- GLOBAL LEGAL ISSUES OF E-COMMERCE - 2