 |
MAINTAINING STATE IN A STATELESS SYSTEM |
| << APPLETS, CGI SCRIPTS |
| INTEGRATION WITH ERP SYSTEMS >> |

E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Lesson
19
MAINTAINING
STATE IN A STATELESS
SYSTEM
You
know that http is stateless.
Another reason why we need
to write scripts or develop our
back end is
that
we want to maintain state. In other
words, we want to link different
clicks/steps involved in an e-
commerce
transaction. When we go to an ecommerce
site, we are generally asked
to take three
different
steps,
that is, provide
Registration information, and
make selection of items (Add
to Cart) and Confirm
Order.
The question is how do we create
link or maintain state among
these different steps. There
are
following
options available for
programmers in this regard:
A temporary
file may be created on the
server side and we code
our scripts behind the
steps/clicks -
Register,
Add to Cart and Confirm
Order - in a way that the
information of each step/click is
stored in that
temporary
file using the same common
ID. At the end our confirm
order script puts this
information in
some
database using insert
query.
Another
method is to use the client
side or cookies for maintaining
state. Information
regarding
Registration
and Add to Cart can be
stored in cookies and at
Confirm Order cookies
against these URLs
would
revert to the serve side and be
stored in databases against a common
ID.
We can
also use hidden forms'
fields. We keep data back
and forth within forms to maintain
state.
Following
is a piece of HTML code for a
form (Add to cart) in which
hidden fields are used. I
have used
pairs
of input tags with type
hidden and type checkboxes. (I
can also use them in a For
loop using
Recordset
object of ASP then it would be
possible that these pairs of
input tags are generated in
a loop and
information
of records available in databases is
directly picked up and printed
for me). Because of
type
hidden
the item name and item code/value
for each item would be there
in the form against each item
but
would
remain hidden. When the user
selects items (through check
boxes) and presses Add to
Cart his
selected
information would go to some
script which would be coded
such that it would open a
new page
with
button Confirm Order. In this
new form the item code or
value of selected items
would be present but
would
remain hidden. When a user
presses the button Confirm
Order the information of selected
items is
stored
in the databases (through a script)
against the item code present in the
form, though hidden. We
can
say
that state is maintained here
between steps Add to Cart
and Confirm Order in the
sense that selections
made
in step Add to Cart were
passed over or provided to the
next step Confirm
Order.
Example
- Hidden Fields
<FORM
NAME="Form1"> <INPUT TYPE= "HIDDEN"
NAME= "Shirt1" VALUE="25">
<INPUT
TYPE=
"CHECKBOX" NAME= "Check1">Blue Cotton
Shirt <br> <INPUT TYPE=
"HIDDEN"
NAME=
"Shirt2" VALUE="26"> <INPUT
TYPE= "CHECKBOX" NAME= "Check2"
>Green Cotton
Shirt
<br>
<INPUT
TYPE= "HIDDEN" NAME= "Shirt3"
VALUE="27"> <INPUT TYPE=
"CHECKBOX"
NAME=
"Check3">White Silk Shirt ....
<P>
<INPUT
TYPE="submit" NAME="Go"
VALUE="Register!"> <INPUT
TYPE="RESET"
VALUE="Reset!"></FORM>
Another
option is to keep everything in
databases. Here, information of
each step is recorded in
appropriate
tables
of a database itself and
linked up with the help of a
commonID. It is relatively more costly
and time
consuming
option.
We can
use Servlets to write our
scripts to speed up processing. It
gets tricky, as one must
have a solid
knowledge of
programming to implement these methods. Here, the
idea is just to give you a broad
concept/picture
as to how the state is maintained.
Client
server architecture
Note
that we may have different
tiers in client server architecture
depending on where the processing
of
data
takes place. In 1-tier
architecture, the entire processing takes
place at a single place/zone. For
example,
88
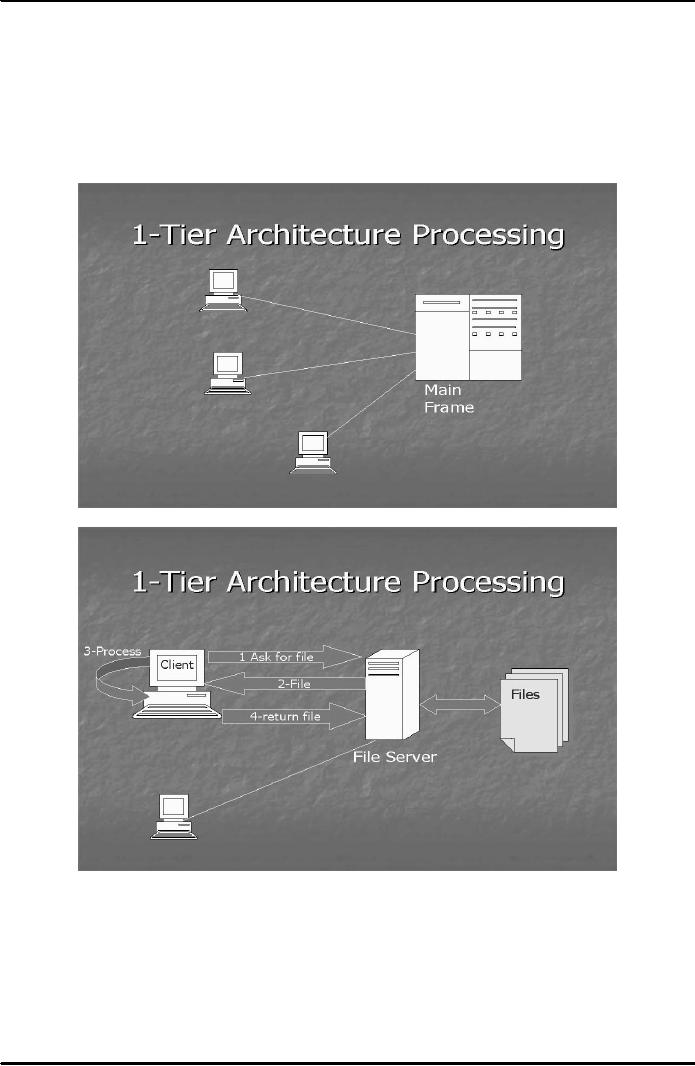
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
in Fig. 1 below,
the processing of data only
takes place in the main
frame and different machines
are
attached
to it just as display terminals.
Conversely, the entire processing may
take place at
individual
terminals
and a centralized machine
called file server just
stores the files having no role in the
processing of
data.
Again, that would be an
example of 1-tier architecture (Fig.
2). Example of 2-tier architecture is
where
processing
of HTML code takes place on the
client side and the web
page request is processed on the
server
side
(Fig. 3). In a 3-tier architecture, we
can place our database
management system or application
software
on a
different processing zone or
tier than the web server
(Fig. 4). Similarly in a 4-tier
architecture ,for
example,
we can place the payment
processing system at the 4th tier. Thus, we can
divide the client
server
architecture
into n tiers.
Fig.
1
Fig.
2
89
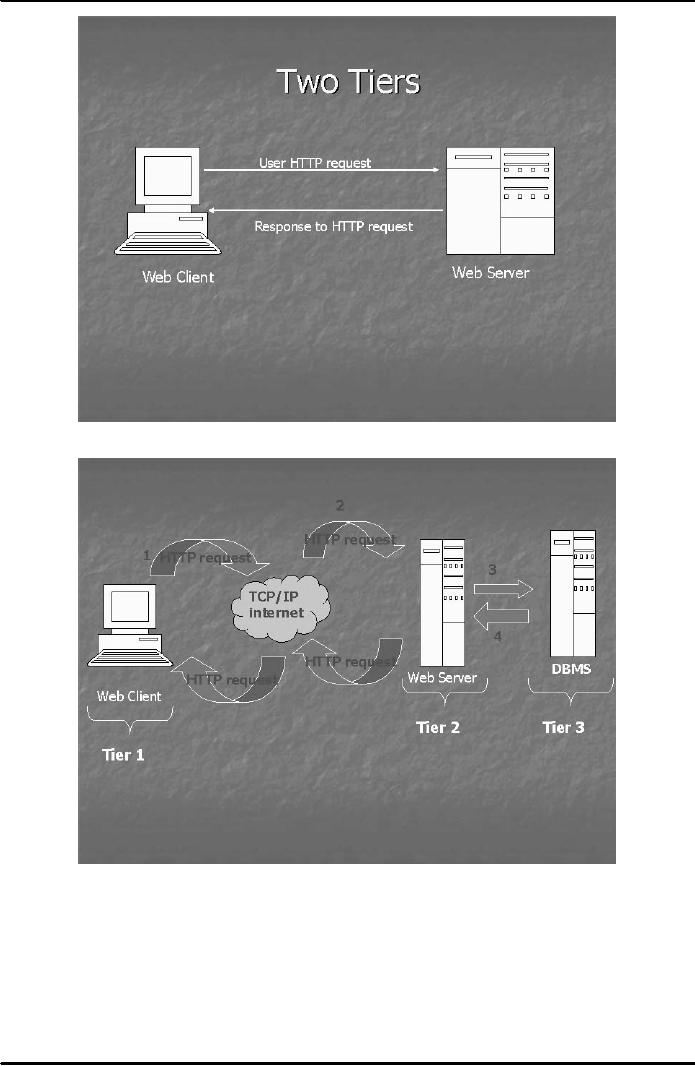
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Fig.
3
Fig.
4
Web
server
You
know that web server is a
machine that serves up the
web page requests of a
client on the internet. It is
a
combination of hardware and
software. Decision as regards the type of a
web server is largely
dependent
on the
volume and type of web
activities. So, transaction
processing sites generating
dynamic pages with
high
traffic volumes would need
web server software that is
more efficient and can
easily be upgraded.
90

E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Operating
systems for web
servers
A computer
must have an operating system to
run programs. It also provides
input and output services
to
devices
connected to a computer such as monitor,
printer etc. Commonly used
web server operating
systems
are Microsoft Windows NT
Server, Microsoft Windows 2000 Advanced
Server, Microsoft.NET
Server,
Linux or Unix based operating
systems such as Solaris. Unix-based
web servers are more
popular
and
are considered to be more
secured. Linux is open source operating
system which is fast, efficient
and
easy
to install. Open source software is
developed by a community of programmers who
make it available
for
download at no cost. Web
Server Software Common examples of
web server software are
Apache
HTTP
server, MS Internet Information
Server (IIS) and Sun ONE
web server. Apache is open
source code
developed in
1994. Today, it dominates the web,
because it is free and performs very
efficiently. IIS
comes
with
MS windows 2000 and NT operating systems.
IIS's inclusion of ASP provides an
environment in
which
HTML pages and scripts can
be combined to produce dynamic web
pages. Sun one (iPlanet
or
Netscape)
web server is a joint
product of AOL and Sun
Microsystems. It can run on
many operating
systems
including Solaris and
Windows. Web Server Hardware
Web Server computers have
generally more
memory.
They have larger and faster
hard disk drives and faster
processors than the typical desktop
PCs.
Companies
that sell web server
hardware such as Dell,
Hewlett Packard etc. all
have configuration tools
on
their
web sites that allow
visitors to design their own
web servers.
Performance
of web sever
Performance
of web servers can be
evaluated mainly on the basis of two
factors:
Throughput,
which is the number of http requests
that a particular server hardware
and
software
can handle in the unit time;
and
Response
time, which is the amount of time a web
server requires to process
one request.
Web
server hardware
architectures
We can
divide e-commerce sites up to
n-tier architectures. Some
web sites are so large
that we need more
than
one computer within each
tier. For sites which
have to deliver millions of
individual pages and
process
thousand
of customer and vendor
transactions each day, site
administrators must plan carefully
how to
configure
their web server computers.
They may adopt two different
approaches in this regard. They
can
use
centralized architecture approach
where they can use few but
very fast and large
computers within each
tier;
or they may adopt decentralized
approach using many less
powerful computers and
dividing workload
among
them. Web hosting choices
ISPs also offer web hosting
arrangements.
Shared
hosting means that a client's
web site is hosted on a
server that simultaneously
hosts other web
sites
and is
operated by an ISP through its
location.
In
Dedicated hosting a web server is
arranged by the ISP for a client
but that client does
not share it with
other
clients of the ISP. In both
cases ISP owns the hardware
but leases it to the client and is
responsible
for
its maintenance. In Co-location hosting,
the ISP offers on rent a physical space
to client to install its
own
server hardware and software
and maintain it by itself. Companies may
opt to run a server in
house
which
is called self hosting.
E-commerce
software
Size
and objectives of e-commerce
sites vary thus variety of software
and hardware products are
developed
which
can be used to build those
sites. Type of e-commerce
software that an organization needs
depends
on
several factors. Typically
all e-commerce software must
at least provide:
A
catalog display
Shopping
cart capabilities
Transaction
processing
Large
or complex e-commerce sites also
use software that adds
other features and
capabilities as follows:
Middleware
Application
integration
Web
services
91

E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Integration
with ERP Software
Supply
chain management
software
Customer
Relationship Management (CRM)
Software
Content
Management Software
Knowledge
Management Software
Catalog
display
A
Static catalog is a simple
list written in HTML. One
has to edit the HTML code to
change it. A dynamic
catalog
stores information about items in a
database usually on a different computer
accessible by the web
server.
It can provide photos, detailed
description and search facility about the
availability of items.
Shopping
cart
In
early days form based
shopping cart was used wherein the
user had to remember and
type certain
information.
It is now replaced by electronic shopping cart/basket
that keeps record of the
items the
customer
has selected and allows
customers to view the details of the
items selected. The customer
can add
new
items or remove items. To
order an item, a customer simply clicks
at that item option. All
details of an
item,
including its price, product
no. and order identifying
information are stored automatically in
the cart.
Transaction
processing
It
occurs when a customer clicks at
checkout or confirm order
button and is subjected to
some payment
processing
mechanism. It represents the most complex
part of online sale. Calculation of
taxes, shipping
costs
etc. is important parts of this
process. Some software
enables a web server to
obtain updated shipping
rates
by directly connecting to shipping companies'
web sites.
Advanced
functions of e-commerce
software
Middleware
Large
companies establish connections
between their e-commerce
software and their existing
accounting
system
by using a type of software called
Middleware which is a part of
e-commerce software
package.
Application
integration
A program
that performs a specific function
such as creating invoices/bills or
processing payment
received
from
customers is called an application
program. We know that
Database Management Software
stores
information
in a structured way. Experts should
properly consider that their
e-commerce software
application
programs must be compatible and
fully integrated with the Database
Management Software.
For
example if a company has existing
inventory database then the
experts should select that
e-commerce
application
program that supports such a
system.
Web
Services
Web
services are defined as a
combination of software tools
that allow application
software in one
organization
communicate with other
programs/applications over a network by
using a specific set
of
standard
protocols. For example a company
that wants to gather all
its financial management information
in
one
spreadsheet can use web
services to automatically get bank
account details, information about
loans,
stock
value etc. from different
independent sources. Similarly, web
services can be used to
obtain price and
delivery
information about goods from
different vendors/suppliers, review this information,
place the order
to the
right vendor/supplier and
track the order till shipment is
received.
92
Table of Contents:
- E-COMMERCE
- WHAT IS A NETWORK
- HOW MANY CLASS A, B, C NETWORKS AND HOSTS ARE POSSIBLE
- NETWORKING DEVICES
- BASICS OF HTML 1
- BASICS OF HTML 2
- TEXT BOXES, CHECK BOXES, RADIO BUTTONS
- FRAMES AND IMAGES IN HTML
- TAG ATTRIBUTES, SOUNDS FILES, ANIMATIONS
- STYLE SHEETS 1
- STYLE SHEETS 2
- SOME USEFUL STYLE SHEETS PROPERTIES
- JAVA SCRIPTING 1
- JAVA SCRIPTING 2
- JAVA SCRIPTING 3
- JAVA SCRIPTING AND XML
- CLIENT AND SERVER SIDE PROCESSING OF DATA
- APPLETS, CGI SCRIPTS
- MAINTAINING STATE IN A STATELESS SYSTEM
- INTEGRATION WITH ERP SYSTEMS
- FIREWALLS
- CRYPTOGRAPHY
- HASH FUNCTION AND MESSAGE DIGEST
- SYMMETRIC KEY ALGORITHMS
- VIRTUAL PIN PAYMENT SYSTEM
- E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 1
- E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 2
- SECURE SOCKET LAYER (SSL)
- E-BUSINESS: DISADVANTAGES OF E-BUSINESS
- E-BUSINESS REVENUE MODELS
- E-MAIL MARKETING
- CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM)
- META INFORMATION
- DATA MINING
- CONFIDENCE AND SUPPORT
- ELECTRONIC DATA INTERCHANGE (EDI)
- PERSONAL FINANCE ONLINE
- SUPPLY CHAIN
- PORTER’S MODEL OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY
- BARRIERS TO INTERNATIONAL E-COMMERCE
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 1
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 2
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 3
- GLOBAL LEGAL ISSUES OF E-COMMERCE - 1
- GLOBAL LEGAL ISSUES OF E-COMMERCE - 2