 |
JAVA SCRIPTING AND XML |
| << JAVA SCRIPTING 3 |
| CLIENT AND SERVER SIDE PROCESSING OF DATA >> |
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Lesson
16
JAVA
SCRIPTING AND XML
For
loop can be used in the code
of Registration form to check
that users do not type
invalid characters in
the
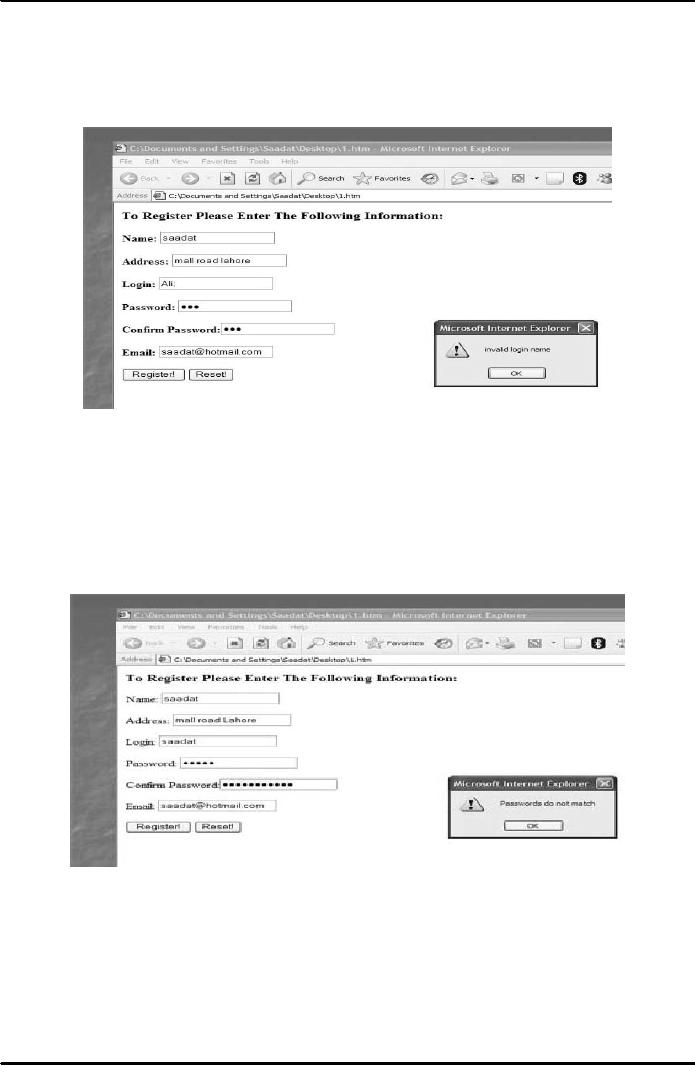
text box. For example, in
case a user types a "," in the
text box for user
login, an alert box can be
made
to
display informing him that
it is an invalid user
login.
See Fig. 1 below.
Fig.
1
Look
at the code to understand For
statement/ loop. The
initialization statement is executed
only at the
beginning
of the For loop's execution. The
condition is then tested,
and if it is true the statements
enclosed
within
the curly brackets are executed. If the
condition is false, the loop is
terminated and the statement
following
the For statement is
executed.
Another
check can also be applied to see
that the passwords entered in
two different text boxes by
the user
are
the same. In case the two
passwords do not match an alert
box can inform the user
about it (see Fig. 2
below). In
case no condition applied in the code is
violated then the function
checkValues returns true
at
`onsubmit'.
Consequently, the information provided by
the user in the form is forwarded to the
server side.
Fig.
2
Extensible
markup language
World
Wide Web Consortium (W3C), a
non-profit organization that maintains
standards for the web
presented
the draft of XML in late 1990's. It is
also used for web
page creation and includes
data
management
capabilities that HTML cannot provide.
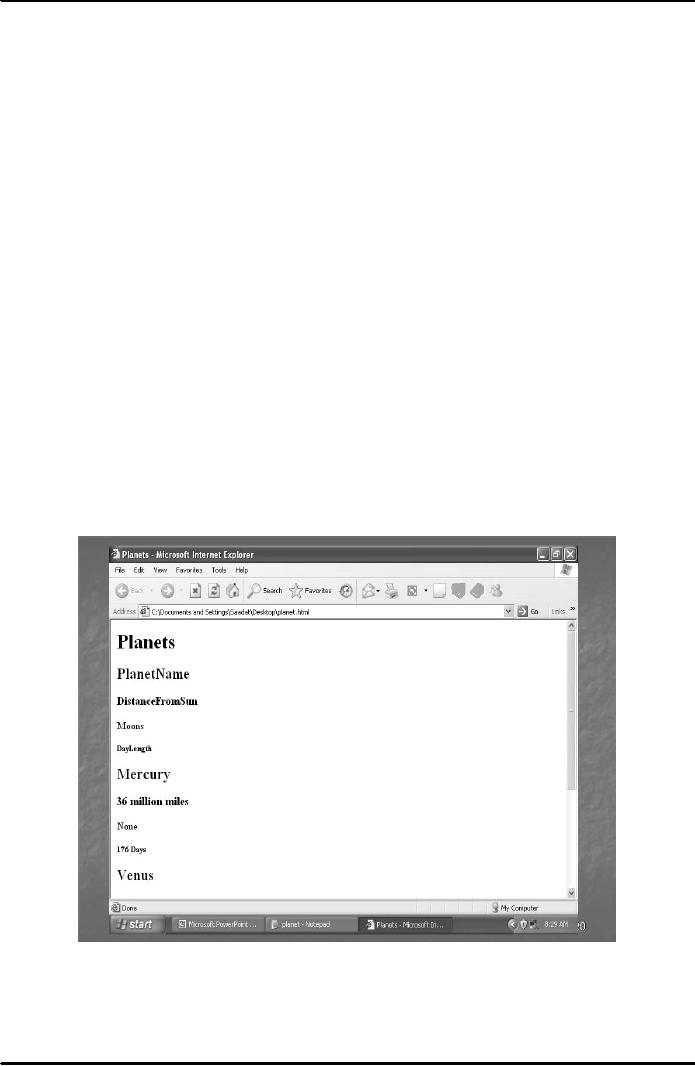
Consider the example of a list of
planets. Suppose that
same
HTML heading tags are
decided to be used each planet.
Also, suppose that it is
decided to display
different
pieces of information about a planet in
different heading sizes.
Then, there is a shortcoming in
respect
of HTML that it can only supply
upto 6 different levels of
headings. In case there are
more than six
74
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
different
pieces of information to display,
then HTML loses its
efficacy. That is why web
professionals have
found
XML as a list formatting alternative of
HTML. Following is a simple HTML
code for preparing the
list
of planets:
<HTML>
<HEAD><TITLE>Planets</TITLE> </HEAD>
<BODY>
<h1>Planets</h1>
<h2>PlanetName</h2>
<h3>DistanceFromSun</h3>
<h4>Moons</h4>
<h5>DayLength</h5>
<h2>Mercury</h2>
<h3>36
million miles</h3>
<h4>None</h4>
<h5>176
Days</h5>
<h2>Venus</h2>
<h3>67
million miles</h3>
<h4>None</h4>
<h5>117
days</h5>
<h2>Earth</h2>
<h3>93
million miles</h3>
<h4>One</h4>
<h5>24
Hours</h5>
</BODY>
</HTML>
Result
is shown in Fig. 3 below.
Fig.
3
XML
differs from HTML in two
important respects. Firstly, XML is not a
markup language with
defined
tags;
rather, one can create
one's own set of tags in
XML. Secondly, XML tags do
not provide
information
how
text would appear on a web
page. Instead of that XML tags
convey meaning of information
included
75
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
within
them. To understand these distinctions
consider the example of planets'
list again. Following is
the
XML
code for that:
<?xml
version="1.0"?>
<PlanetsList>
<Planet
Name="Mercury"> <Distance>36
million miles</Distance>
<Moons>None</Moons>
<DayLength>176
days</DayLength>
</Planet>
<Planet
Name="Venus"> <Distance>67
million miles</Distance>
<Moons>None</Moons>
<DayLength>117
days</DayLength>
</Planet>
<Planet
Name="Earth"> <Distance>93
million miles</Distance>
<Moons>One</Moons>
<DayLength>24
Hours</DayLength>
</Planet>
</PlanetsList>
First
line of the code is a declaration that it
is an XML document (version 1). Second
and last lines of the
code
are called root element
tags. We enclose other
elements within the root
element tags. We assign
a
name
to the root element that
best describes the purpose of
our file. Other elements
are called child
elements.
Thus, planet is a child element of
planetlist. Further, each property of a
planet is the child element
of the planet
element. So, distance, moons
and daylength are the child
elements of planet element. Name
is
the
attribute of the planet element. Names of
child elements can be
different between two
organizations,
which
can make the sharing of
information difficult. For
instance, some may describe
the property of a
planet as
Day and others may
use the word Daylength for
that purpose. This has led to the
necessity of
having
uniform standards for
writing different types of XML
documents. Many companies
have agreed to
follow
common standards for XML tags. A
file that uses XML tags is
called data type definition
(DTD) or
XML
schema. Different DTDs are
available for different
industries. We now have
accounting information,
legal
information standards
etc.
Rules
for writing an XML
code
-All
elements must be properly
nested
<outer><inner>content</inner></outer>
-All
attribute values must be quoted
<FRIES SIZE="LARGE">
-All
elements with empty content
must be identified by ending in
/>
<BR/>,
<img src="image2.gif" />
- All
elements must be cased
consistently <PART> must
not be closed as
</part>
- Certain
characters having reserved meanings
cannot be used e.g, & , < etc.
Embedding XML into
HTML
documents
<XML>
element can be used anywhere
within HTML document to enclose XML
content.
See the
following example in this
regard:
<html>
<head>
<title>XML-example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>HTML
text here</h1>
<xml>
<meal>
<burger>
<name>spicy</name>
</burger>
</meal>
</xml>
</body>
</html>
76
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Also,
<script> element can be
used for such purpose
e.g, <script
language="xml"
type="text/xml">......</script>
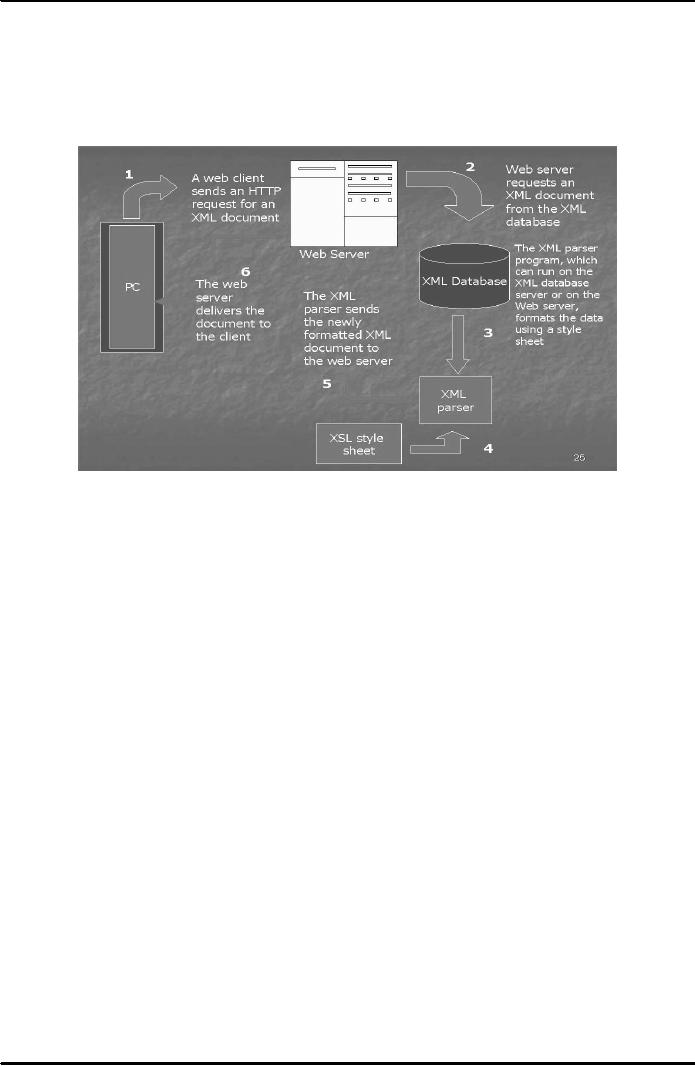
Extensible
Style sheet Language (XSL)
XML files are translated using another
file which contains
formatting
instructions. Formatting instructions are
often written in Extensible Style
sheet Language (XSL).
These
formatting instructions are read
over by special programs
usually these programs are
written in Java
programming
language- called XML Parsers.
Following diagram (Fig. 4) explains
how web server
might
process
http request for an XML
page.
Fig.
4
We
write XSL rules that
match various xml elements.
For that consider the
following example:
XML
code <?xml version="1.0"?>
<?xml-stylesheet href="catalog.xsl"
type="text/xsl" ?>
<CATALOG>
<PART>
<NAME>Switch</NAME> <DESCRIPTION>A
very efficient
device</DESCRIPTION>
<PRICE>Rs.
1000</PRICE>
</PART>
<PART>......</PART>
....
</CATALOG> </xml>
XSL
code
We can
provide the formatting instructions for
the above XML code by writing an
XSL
code
as given below:
<?xml
version="1.0"?>
<xsl>
<rule>
<root
/> <html> <body
bgcolor=yellow> <children
/>
</body>
</html>
</rule> <rule>
<target-element
type="PART" /> <DIV
style="margin-bottom:20px"> <children />
</DIV>
</rule>
<rule>
<element type="PART"> <target-element
type="NAME" /> </element>
<B>
<children />
<B>
<BR /> </rule> .........
</xsl>
Note
that we use <rule>
elements and <target-element> in
our XSL code to provide
formatting
instructions
for the corresponding XML
elements.
77

E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
HTML and XML
editors
General
purpose text-editors for HTML are
Notepad, Wordpad etc. However,
there are certain
HTML
editors
that help create web
pages more easily, e.g,
Macromedia Dreamweaver and Microsoft
FrontPage.
XML
code can also be written in
any general purpose text
editor. However, there are
special programs such
as
Epic Editor, TurboXML which
can facilitate the editing job
considerably.
78
Table of Contents:
- E-COMMERCE
- WHAT IS A NETWORK
- HOW MANY CLASS A, B, C NETWORKS AND HOSTS ARE POSSIBLE
- NETWORKING DEVICES
- BASICS OF HTML 1
- BASICS OF HTML 2
- TEXT BOXES, CHECK BOXES, RADIO BUTTONS
- FRAMES AND IMAGES IN HTML
- TAG ATTRIBUTES, SOUNDS FILES, ANIMATIONS
- STYLE SHEETS 1
- STYLE SHEETS 2
- SOME USEFUL STYLE SHEETS PROPERTIES
- JAVA SCRIPTING 1
- JAVA SCRIPTING 2
- JAVA SCRIPTING 3
- JAVA SCRIPTING AND XML
- CLIENT AND SERVER SIDE PROCESSING OF DATA
- APPLETS, CGI SCRIPTS
- MAINTAINING STATE IN A STATELESS SYSTEM
- INTEGRATION WITH ERP SYSTEMS
- FIREWALLS
- CRYPTOGRAPHY
- HASH FUNCTION AND MESSAGE DIGEST
- SYMMETRIC KEY ALGORITHMS
- VIRTUAL PIN PAYMENT SYSTEM
- E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 1
- E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 2
- SECURE SOCKET LAYER (SSL)
- E-BUSINESS: DISADVANTAGES OF E-BUSINESS
- E-BUSINESS REVENUE MODELS
- E-MAIL MARKETING
- CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM)
- META INFORMATION
- DATA MINING
- CONFIDENCE AND SUPPORT
- ELECTRONIC DATA INTERCHANGE (EDI)
- PERSONAL FINANCE ONLINE
- SUPPLY CHAIN
- PORTER’S MODEL OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY
- BARRIERS TO INTERNATIONAL E-COMMERCE
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 1
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 2
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 3
- GLOBAL LEGAL ISSUES OF E-COMMERCE - 1
- GLOBAL LEGAL ISSUES OF E-COMMERCE - 2