 |
E-COMMERCE |
| << Table of Contents |
| WHAT IS A NETWORK >> |

E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Lesson
01
E-COMMERCE
Course
outline
E-Commerce
and its types, Internet
and WWW Basics, Internet
standards and protocols, IP
addressing,
Data communication
on internet, Domain name
system
Networking
devices Bridges, Switches,
Routers etc., Role of ISP's
on Internet, Getting Domain
name
and IP
addresses, Understanding electronic mail
Markup
languages and the Web, Web
designing using HTML, CSS
and Java Scripting
Client
side & server side
processing, Cookies, Maintaining
state in a stateless environment,
two tier/n-
tier
architecture
Security
issues on the internet, Firewalls,
Proxy Server, Virtual Private
Network
Cryptography
and Public key infrastructure (PKI),
Certification Authorities and
Digital Certificates,
Digital
signatures Technology
Electronic
Payment Systems Virtual
Pin payment system,
Centralized account system,
Electronic
Check,
E-Cash, SSL and SET based
payment systems
E-business
advantages/disadvantages, Paper and
electronic catalogues
Electronic
Data Interchange (EDI)
E-business
models
Internet
marketing
Data
mining and knowledge discovery
Process, OLAP, Types and
business application of data
mining
E-business
strategy, supply chain/value chain
analysis and Porter's model,
role of e-commerce in
competitive
strategy
E-banking,
ERP
Legal/policy
issues in e-commerce salient
features of Electronic Transactions
Ordinance, 2002 in
Pakistan
Territorial
jurisdiction and conflict of
laws, online contracts,
online defamation, in
Cyberspace
Issue
of ISP's liability, domain-name
and trade mark conflicts, privacy
issue on the internet,
Cyber
crimes
Suggested
books
Electronic
Commerce (4th edition) by
Gary P. Schneider
Electronic
Commerce : Security, Risk
Management and Control by Greenstein
& Feinman
Electronic
commerce A Managerial Perspective by
Turban et al.
Absolute
Beginner's Guide to Networking (3rd
edition) by Joe
Habraken
Creating
a Web Page (5th edition) by
Paul Mcfedries
Web
Security, Privacy & Commerce by
Garfinkel & Spafford
Data
Mining Concepts & Techniques by
Han Kamber
E-commerce
Strategy, Technologies and
Applications by David Whiteley
Internet
Law in Canada (6th edition) by
Michael Geist
1
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
E-Commerce
definition
Electronic
commerce is an emerging concept
that describes the process of
buying and selling or
exchanging
of
products, services and
information via computer networks including the
internet
E-commerce
classification
A common
classification of EC is by the nature of
transaction:
Business-to-Business
(B2B): electronic
market transactions that
take place between
organizations
Business-to-Consumer
(B2C):
retailing transactions with
individual shoppers typical shopper
at
Amazon.com
is a consumer
Consumer-to-Consumer
(C2C):
consumer sells directly to consumers,
examples -individuals
selling
in
classified ads, auction sites
allowing individuals to put up
items for auction e.g,
e-bay
Consumer-to-Business
(C2B):
individuals who sell products or
services to organizations and
those
who
seek sellers and conclude a
transaction
Intra
Business (organizational) EC: all
internal organizational activities
involving exchange of
goods,
services or information, selling
corporate products to employees, online
training and cost
reduction
activities
Non-Business
EC:
academic institutions, not-for-profit
organizations, religious/social
organizations
and
government agencies using EC to improve
their operations, customer service
and reduce expense
Basic
Definitions
Web
client- machine that initiates
internet request
Web
server machine that
services internet
request
Browser
- software at the client side to interact
with web data
Intranet
an internal network of computers
confined to a single
place
Extranet
when two or more intranets are
connected with each other,
they form an Extranet e.g,
Virtual
Private
Network
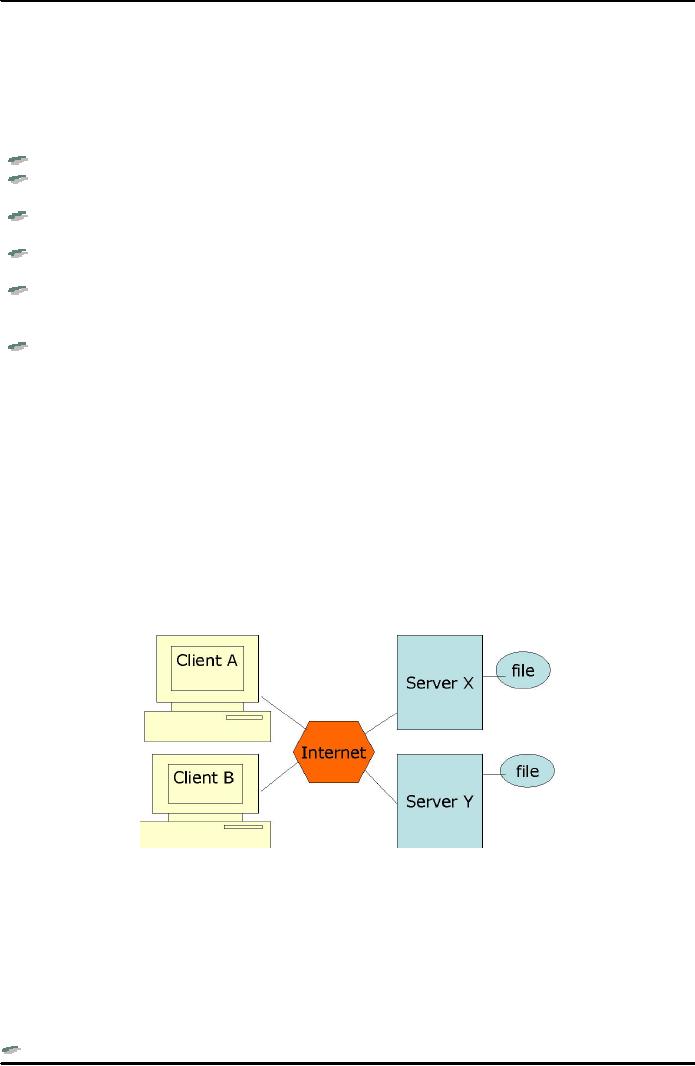
Internet
a global network of networks is defined as
internet
Internet
presents a two-way client server communication model
as
shown in Fig. 1 below:
Client-Server
Model
Fig.
1
What
is the WEB?
The
Web is a protocol that uses
the internet as the communication structure. It
links documents stored
in
computers
that communicate on the internet. It is
based on Hypertext Transfer Protocol
(HTTP) - native
protocol
of WWW designed for making
web page requests.
HTTP
is a four step process per
transaction
1.
Client
Makes
an HTTP request for a web
page
2
E-COMMERCE
IT430
VU
Makes
a TCP/IP connection
2.
Sever accepts request
Sends
page as HTTP
1
Client downloads the
page
2
Server breaks the connection
HTTP
is stateless because in the fourth
step the server breaks the connection. We
can say, therefore:
Each
operation or transaction makes a
new connection
Each
operation is unaware of any
other connection
Each
click is a new connection
Side
Effect of HTTP Transfers
A
record is left of all web
transaction in a file that
resides at the server called common
log file. Good
news
is
that some user data
(record of his visits to the
web sites) is recorded in a particular
format in the log
files.
Bad
news is that user privacy is
not maintained.
What
can you do with this
data?
Rearrange
your site by knowing which
portions of your web site
are popularly accessed and
which are
ignored
by the users
Change
your marketing strategy e.g.,
you can introduce some
promotional scheme for
boosting the
sale
of ignored items
Make a
mailing list you can
trace the location from
where customers are visiting
and prepare a mailing
list
for marketing purposes
3
Table of Contents:
- E-COMMERCE
- WHAT IS A NETWORK
- HOW MANY CLASS A, B, C NETWORKS AND HOSTS ARE POSSIBLE
- NETWORKING DEVICES
- BASICS OF HTML 1
- BASICS OF HTML 2
- TEXT BOXES, CHECK BOXES, RADIO BUTTONS
- FRAMES AND IMAGES IN HTML
- TAG ATTRIBUTES, SOUNDS FILES, ANIMATIONS
- STYLE SHEETS 1
- STYLE SHEETS 2
- SOME USEFUL STYLE SHEETS PROPERTIES
- JAVA SCRIPTING 1
- JAVA SCRIPTING 2
- JAVA SCRIPTING 3
- JAVA SCRIPTING AND XML
- CLIENT AND SERVER SIDE PROCESSING OF DATA
- APPLETS, CGI SCRIPTS
- MAINTAINING STATE IN A STATELESS SYSTEM
- INTEGRATION WITH ERP SYSTEMS
- FIREWALLS
- CRYPTOGRAPHY
- HASH FUNCTION AND MESSAGE DIGEST
- SYMMETRIC KEY ALGORITHMS
- VIRTUAL PIN PAYMENT SYSTEM
- E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 1
- E-CASH PAYMENT SYSTEM 2
- SECURE SOCKET LAYER (SSL)
- E-BUSINESS: DISADVANTAGES OF E-BUSINESS
- E-BUSINESS REVENUE MODELS
- E-MAIL MARKETING
- CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT (CRM)
- META INFORMATION
- DATA MINING
- CONFIDENCE AND SUPPORT
- ELECTRONIC DATA INTERCHANGE (EDI)
- PERSONAL FINANCE ONLINE
- SUPPLY CHAIN
- PORTER’S MODEL OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY
- BARRIERS TO INTERNATIONAL E-COMMERCE
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 1
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 2
- ELECTRONIC TRANSACTIONS ORDINANCE, 2002 - 3
- GLOBAL LEGAL ISSUES OF E-COMMERCE - 1
- GLOBAL LEGAL ISSUES OF E-COMMERCE - 2