5 mg and 10 mg rectal solution
diazepam
1. WHAT DIAZEPAM DESITIN IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
Diazepam belongs to a group of medicines called benzodiazepines. These are used as sedatives and anticonvulsants (to control cramps), or to relax tense muscles.
Diazepam is used
- to control epileptic seizures or febrile seizures
- as sedatives for minor surgical procedures or dental treatments
- for muscle spasms in case of tetanus
- for severe, paralyzing,g or extremely painful anxiety or upset
Diazepam solution can be used as above when an injection is impractical or undesirable.
Diazepam solution may be useful for immediate treatment of seizures in children.
Diazepam contained in Diazepam Desitin may also be approved for the treatment of other conditions not mentioned in this leaflet. Ask your doctor, pharmacist, or another healthcare professional if you have any further questions, and always follow their instructions.
2. WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW BEFORE USING DIAZEPAM SOLUTION
Do not use Diazepam solution
- if you are allergic to diazepam or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6). Allergic reactions may include rash, itching, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the face, lips, throat,t, or tongue.
- if you have myasthenia gravis (very weak muscles).
- if you suffer from sleep apnea(temporary pauses in breathing during sleep).
- if you have severe liver disease.
- if you have severe breathing problems.
Diazepam should be used in tea for premature babies.
Warnings and cautions
Talk to your doctor before using Diazepam solution
- if you have kidney or liver disease.
- if you suffer from breathing problems.
- if you have an insufficient blood supply to the brain or other brain damage.
- if you have a history of alcohol or drug abuse.
- if you suffer from a mental illness (such as depression, phobia, or obsession).
Patients in shock should only be treated with Diazepam when measures have been taken at the same time to compensate for the lack of volume.
Diazepam should not be used concomitantly with alcohol and/or drugs that have a depressant effect on the central nervous system. While use can enhance the effect of diazepam and eventually lead to coma and impaired cardiac vascular function and/or respiration, requiring urgent treatment.
Once you have received Diazepam e.g. minor surgery or during treatment at the dentist, you should always be accompanied home.
Development of tolerance
After repeated use of Diazepam solution for a few weeks, the effect of the drug may decrease (due to the development of tolerance to the hypnotic effect of benzodiazepines ).
Development of addiction
Diazepam solution is an addictive drug. Diazepam solution may cause dependence even at therapeutic doses. The risk of addiction increases with higher doses and long-term use and is greater in patients who have previously been addicted to alcohol or drugs. You should therefore use Diazepam solution for as short a time as possible.
Postponement of treatment/withdrawal symptoms
When the body has developed an addiction, you get withdrawal symptoms if the treatment is suddenly stopped. The symptoms can manifest themselves in the form of many dreams, sweating, tremors, headaches, muscle aches, extreme anxiety, mood swings, tension, restlessness, confusion, and irritability.
In severe cases, the following symptoms may also occur disturbed perception of the individual or the environment (derealization, depersonalization), confusion, hypersensitivity to light, sound (hyperacusis) and body contact, numbness, and tingling in the arms and legs, hallucinations, or epileptic seizures.
The symptoms that led to treatment with Diazepam solution may return in aggravated form when treatment is stopped. It is therefore recommended to end the treatment by gradually decreasing dose one.
Memory disorder
Diazepam may cause time-limited memory gaps (anterograde amnesia ) when using therapeutic doses. This means that you will not later remember e.g. actions you have taken after using Diazepam solution. This risk increases with the size of the dose and decreases through a sufficiently long, uninterrupted sleep period (7 – 8 hours).
Psychological and “paradoxical” reactions
Reverse effects such as restlessness, agitation, irritability, aggressive behavior, nightmares, hallucinations, delusions, tantrums, inappropriate behavior, and other behavioral disorders or abnormal states of mind ( psychosis ) may occur with benzodiazepines, especially in elderly patients or children (see section 4). In such cases, treatment with Diazepam solution should be discontinued.
Psychosis is
Diazepam is not recommended as the first treatment for mental disorders (psychotic disorders).
Depression
Diazepam should not be used as the sole drug in the treatment of depression or anxiety disorders that occur in association with depression. The disease picture of depression can be strengthened in certain circumstances (risk of suicide).
When used without a doctor’s prescription, the chance that this medicine will help you decreases. At the latest after four weeks of use, your doctor should decide whether to continue treatment. Under no circumstances increase the dose prescribed by your doctor, even if the effect decreases. By increasing the dose on its own, targeted treatment is made more difficult.
Never use a medicine that contains benzodiazepines as it has helped others so well.
Children and young people
Diazepam should only be given to children and adolescents if a doctor deems it necessary and all treatments should be kept to a minimum.
Elderly patients
The elderly should be given a reduced dose (see section 3). Caution should be exercised in elderly patients due to the risk of falls and consequently fractures, especially when getting up at night (see section 4). The increased risk of falling is due to the muscle relaxing effect of Diazepam.
Special patient groups
A lower dose is recommended for patients with chronic respiratory failure due to the risk of respiratory depression. It is also recommended that debilitated patients and patients with hepatic and renal impairment receive a reduced dose and special caution is advised in these patients (see section 3). Benzodiazepines are not indicated for the treatment of patients with severe hepatic impairment as they may cause encephalopathy.
High-risk patients
Benzodiazepines should be used with extreme caution in patients with a history of alcohol or drug abuse.
Other medicines and Diazepam solution
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken or might take any other medicines. It is especially important for the following medicines as they may affect the effect of Diazepam solution:
- antipsychotics (medicines for mental illness)
- anxiolytics (drugs for the treatment of anxiety)
- sedatives or hypnotics (eg sleeping pills)
- antidepressants (antidepressants, such as fluvoxamine, fluoxetine )
- narcotic analgesics (strong painkillers)
- anesthetics
- antiepileptics (medicines used to treat epilepsy, eg phenytoin, phenobarbital)
- sedative antihistamines (allergy medications that make you sleepy)
- analgesics, e.g. buprenorphine
- azole antifungals used to treat fungal infections (itraconazole, ketoconazole, fluconazole voriconazole)
- HIV – protease inhibitors used to treat HIV – infection
- isoniazid (against tuberculosis – TB)
- disulfiram (a drug for the treatment of alcoholism)
- cimetidine, omeprazole (medicines for heartburn and stomach ulcers )
- oral contraceptives (eg birth control pills )
- muscle relaxants
- rifampicin (an antibiotic )
- theophylline (tablets for asthma )
- levodopa (for Parkinson’s disease )
- sodium oxybate (used to treat narcolepsy )
- St. John’s wort (traditional herbal medicine for mild depression and mild anxiety).
Concomitant use of Diazepam solution and opioid drugs (strong painkillers, opioid treatment drugs, and certain cough medicines) increases the risk of drowsiness, difficulty breathing ( respiratory depression ), coma and may be life-threatening. Due to this, concomitant use should only be considered when other treatment options are not possible.
If your doctor prescribes Diazepam solution at the same time as opioid medicines, your dose and treatment time should be limited by your doctor.
Tell your doctor if you are taking any opioid medicine and carefully follow your doctor’s dose recommendations. It may be helpful to inform friends or relatives about paying attention to the signs and symptoms described above. Contact a doctor if you experience any of these symptoms.
Nicotine (eg smoking) may reduce the effect of Diazepam solution.
It is possible that you can use Diazepam Desitin anyway and your doctor may decide what is right for you.
Diazepam solution with alcohol
Do not drink alcohol while using diazepam. Alcohol can increase the sedative effects of Diazepam and make you very sleepy.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor for advice before using this medicine.
Pregnancy
You should not use this medicine if you are pregnant unless your doctor tells you to. Talk to your doctor immediately if you think you may be pregnant. In infants whose mothers have received benzodiazepines during pregnancy, a slight increase in malformations may occur, especially cleft lip, jaw, and palate. Infants who are exposed to an overdose of benzodiazepines during pregnancy may develop more slowly and may develop eye disorders ( nystagmus ) or congenital malformations. Prolonged use of Diazepam during pregnancy may lead to withdrawal symptoms in the newborn. If you have been treated with Diazepamduring the end of pregnancy or at birth, this can affect the newborn baby’s condition in the form of decreased body temperature, lethargy, difficulty breathing, and weakness (so-called “floppy infant syndrome” ).
Breast-feeding
Do not use Diazepam during breast-feeding as it enters the breast milk. If treatment is unavoidable, breast-feeding should be discontinued to avoid adverse reactions in the breast-fed infant.
Driving and using machines
You must not drive or use machines for at least 24 hours after receiving the last dose. If after 24 hours you still feel sleepy or have difficulty concentrating, notice muscle weakness or periods of memory loss, do not drive or use machines. You should also talk to a doctor.
You are responsible for assessing whether you are fit to drive a motor vehicle or perform work that requires increased attention. One of the factors that can affect your ability in these respects is the use of drugs due to their effects and/or side effects. Description of these effects and side effects are found in other sections. Read all the information in this leaflet for guidance. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
Diazepam solution contains propylene glycol, benzyl alcohol, benzoic acid, and sodium benzoate
This medicine contains 37.5 mg of benzyl alcohol in each rectal tube, which is equivalent to 15 mg/ml. Benzyl alcohol can cause allergic reactions.
This medicine contains 2.5 mg benzoic acid (E210) and 122.5 mg sodium benzoate (E211) in each rectal tube, which corresponds to 1 mg benzoic acid per ml and 49 mg sodium benzoate per ml. Benzoic acid and sodium benzoate can cause local irritation.
This medicine contains 1 mg of propylene glycol in each rectal tube equivalent to 400 mg/ml. Propylene glycol may cause skin irritation.
3. HOW TO USE DIAZEPAM DESITIN
Always use this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you are unsure.
Dosage The
usual dose is 0.25–0.5 mg / kg (body weight). The size of the dose also depends on the patient’s age and state of health. Diazepam is intended for use in adults and children (weighing more than 10 kg).
The recommended dose is:
- for children 1–3 years (10–15 kg): a tube of 5 mg
- for children over 3 years (more than 15 kg): a tube of 10 mg
- for adults: two tubes of 10 mg
Your doctor will decide on the appropriate dose and for how long you need to take this medicine. The usual treatment period should not exceed 4 weeks, including tapering. If necessary, the doctor can extend the treatment time.
Method and duration of administration one
Diazepam solution is intended for emergency use. It is not intended for long-term use. If necessary, the dose can be repeated every 12 hours. If the seizures still cannot be controlled, consult a doctor.
These tubes with Diazepam solution are for single use only and should be taken in the rectum. Treatment should be as short as possible, and the lowest dose that controls the symptoms should be used. If it is used continuously for too long, there is a risk that diazepam will become addictive or cause problems when treatment is stopped.
If no effect is seen after 10 minutes, a repeated dose in children or an additional 10 mg tube may be given to adults.
Elderly patients and patients with generalized impairment or those with impaired liver or kidney function or chronic respiratory distress may need a reduced dose.
Dosage instructions
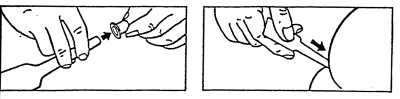
| If possible, turn the patient sideways or on his stomach (applies to children).2. Tear up the foil package.3. Remove the tube cap. | 4. Insert the tip completely into the rectal opening, pointing downwards. Note! In children under 15 kg, the tip is inserted only halfway. |
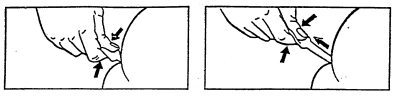
| 5. Empty the tube by pressing it firmly between your thumb and forefinger. | 6. Keep the tube fully compressed until you have pulled it out of the rectum. Note: A small amount of solution should remain in the tube after dose one has been given. 7. Maintain the patient’s position and keep the buttocks compressed for a few minutes to avoid leakage. |
If you use more Diazepam than you should
If you have ingested too much medicine or if e.g. If a child has inadvertently ingested the medicine, contact a doctor, hospital, or the Poison Information Center for risk assessment and advice.
Symptoms of overdose include drowsiness, drowsiness, confusion, lethargy(drowsiness), speech disorders, and involuntary eye movements ( nystagmus ).
When such signs occur, a doctor should be contacted immediately. The doctor assesses the severity of the overdose and decides what necessary measures should be taken. In severe cases, symptoms include low blood pressure, loss of reflexes, shallow breathing (respiratory and circulatory insufficiency, bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes [cyanosis], loss of consciousness that develops into respiratory and cardiac arrest, coordination problems ( ataxia ), lethargy, coma (rare) and death (very rare) During the phase of intoxication one can experience severe anxiety, insomnia, and possibly severe seizures.
The symptoms of overdose are stronger under the influence of alcohol and other central depressants.
If you stop using Diazepam solution
When the body has developed an addiction, you get withdrawal symptoms if the treatment is suddenly stopped. As the risk of withdrawal reactions or rebound phenomena is greater with abrupt cessation of treatment, it is recommended that a dose be gradually reduced.
Withdrawal symptoms can include headaches, muscle aches, extreme anxiety, tension, restlessness, confusion, and irritation. In severe cases, the following symptoms may occur: feelings of unreality, depersonalization (a feeling of being separated from the body), hyperacusis (sensitivity to sound), numbness and tingling, sensitivity to light, voices or physical contact, hallucinations, epileptic seizures, mood swings, anxiety, sleep disorders or restlessness.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
4. POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
All medicines can cause allergic reactions, although severe allergic reactions are very rare. Contact a doctor immediately if you suddenly have difficulty breathing, swollen eyelids, face or lips, rash, or itching (especially if it occurs all over the body).
The following side effects have been reported:
Common: may affect up to 1 in 10 people
- drowsiness, drowsiness, headache, dizziness (with the risk of falls in the elderly), instability, speech disorders such as slurred speech, trembling hands
- fatigue, day-after-effect (hangover)
- double vision
- muscle weakness
- muscle cramps
- decreased alertness, numbness, confusion, and short-term memory disorders (anterograde amnesia ) that may be associated with inappropriate behavior (see section 2)
- paradoxical reactions – instead of feeling sleepy, some patients (especially children or the elderly) may feel upset and experience a personality change. Other symptoms include restlessness, anxiety, mood swings, suicidal tendencies, aggression, anger, irritability, tension, irrational thoughts (delusions), nightmares, insomnia, hallucinations (a feeling that things are not real), hostility, or inappropriate behavior. If you experience any of these effects, talk to your doctor.
Uncommon: may affect up to 1 in 100 people
- decreased concentration
Rare: may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people
- low blood pressure
- slow heart rate, heart failure including cardiac arrest
- chest pain
- blood cell changes including decreased platelet count
- eye changes including blurred vision and involuntary eye movements ( nystagmus)
- dry mouth
- nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain (heartburn / indigestion), constipation (severe constipation), diarrhea
- jaundice (yellowed skin)
- difficulty urinating or involuntary urination
- increase or loss of sex drive, menstrual disorders
- bronchospasm, difficulty breathing, temporary pauses in sleep ( apnea ), cessation of breathing (respiratory arrest). The respiratory depressant effect may be more pronounced in existing shortness of breath caused by narrow airways (respiratory obstruction) and in patients with brain damage. This should be taken into account in particular with the concomitant use of other centrally active drugs (see section 2).
- increased appetite
- day-after-effect in the morning after evening administration, which may lead to disturbance of concentration and fatigue and may impair the reaction capacity
- changes in liver blood tests (increased transaminases and alkaline phosphatase)
Very rare: may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people
- skin rash including itching and hives
- swelling of the face, mouth, tongue, or other parts of the body that may cause difficulty breathing ( angioedema )
No known frequency (cannot be calculated from the available data):
- dizziness with disturbance of balance ( vertigo )
- increased saliva production
- risk of falls (see section 2, “Elderly patients”)
Treatment with Diazepam solution can, even at therapeutic doses, lead to the development of physical addiction. Abrupt discontinuation of treatment may result in withdrawal symptoms. In some patients, depression may occur.
5. HOW TO STORE DIAZEPAM SOLUTION
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton after EXP. or EXP. The expiration date is the last day of the specified month.
Store below 25 ° C. Short-term exposure to higher temperatures (eg in the car or emergency bag) is possible and does not affect the quality of the medicine.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
6. CONTENTS OF THE PACKAGING AND OTHER INFORMATION
Content declaration
- The active substance is diazepam.
- The other ingredients are benzyl alcohol, 96% ethanol, propylene glycol, benzoic acid, sodium benzoate, and purified water.
What the medicine looks like and the contents of the pack
Diazepam Desitin Rectal Solution is a clear, colorless, or slightly yellowish solution in a white plastic tube.
Pack of 5 rectal tubes. Each tube contains 2.5 ml of Diazepam 5 mg or 10 mg solution.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Desitin Arzneimittel GmbH
Weg beim Jäger 214
D-22335 Hamburg
Germany
Information providers
Desitin Pharma AB
Niels Leuchs Vei 99
1359 Eiksmarka
Norway
This medicinal product is authorized under the European Economic Area under the names:
| UK: | Diazepam Desitin 5 mg Rectal SolutionDiazepam Desitin 10 mg Rectal Solution |
| Netherlands: | Diazepam Allgen Rectiole 5 mgDiazepam Allgen Rectiole 10 mg |